42 KiB
- Effect of all the control systems on the Sample vibrations
- Effect of all the control systems on the Sample vibrations - One stage at a time
- Effect of the Symetrie Driver
- Transfer function from one stage to the other
#+TITLE:Measurements
For all the measurements shown here:
- geophones used are L22 with a resonance frequency of 1Hz
- the signals are amplified with voltage amplifiers with a gain of 60dB
- the voltage amplifiers include a low pass filter with a cut-off frequency at 1kHz
Effect of all the control systems on the Sample vibrations
<<sec:effect_control_all>>
ZIP file containing the data and matlab files ignore
All the files (data and Matlab scripts) are accessible here.
Experimental Setup
We here measure the signals of two geophones:
- One is located on top of the Sample platform
- One is located on the marble
The signal from the top geophone does not go trought the slip-ring.
First, all the control systems are turned ON, then, they are turned one by one. Each measurement are done during 50s.
| Ty | Ry | Slip Ring | Spindle | Hexapod | Meas. file |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ON | ON | ON | ON | ON | meas_003.mat |
| OFF | ON | ON | ON | ON | meas_004.mat |
| OFF | OFF | ON | ON | ON | meas_005.mat |
| OFF | OFF | OFF | ON | ON | meas_006.mat |
| OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF | ON | meas_007.mat |
| OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF | meas_008.mat |
Each of the mat file contains one array data with 3 columns:
| Column number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Geophone - Marble |
| 2 | Geophone - Sample |
| 3 | Time |
Load data
We load the data of the z axis of two geophones.
d3 = load('mat/data_003.mat', 'data'); d3 = d3.data;
d4 = load('mat/data_004.mat', 'data'); d4 = d4.data;
d5 = load('mat/data_005.mat', 'data'); d5 = d5.data;
d6 = load('mat/data_006.mat', 'data'); d6 = d6.data;
d7 = load('mat/data_007.mat', 'data'); d7 = d7.data;
d8 = load('mat/data_008.mat', 'data'); d8 = d8.data;Analysis - Time Domain
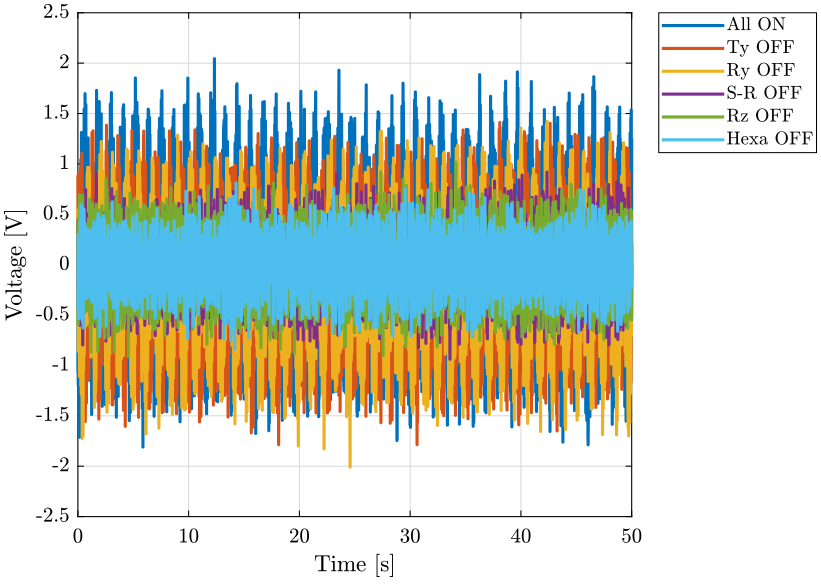
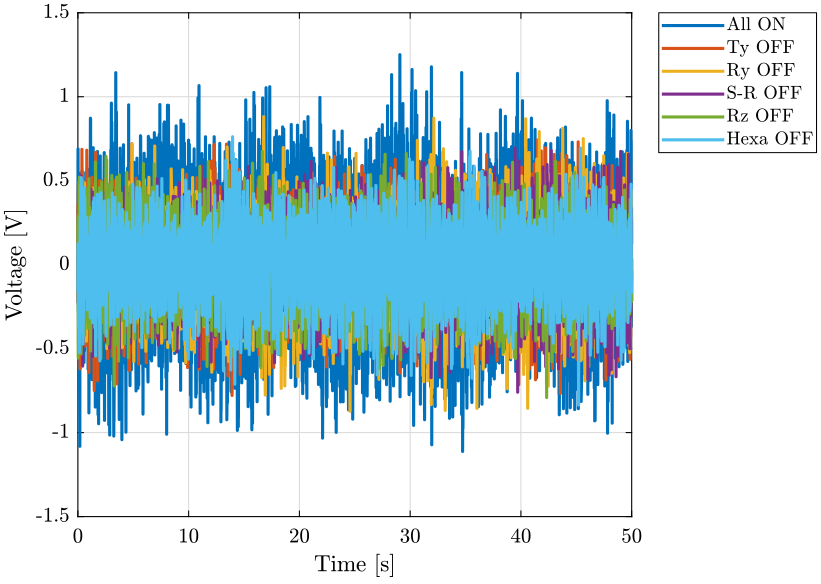
First, we can look at the time domain data and compare all the measurements:
- comparison for the geophone at the sample location (figure fig:time_domain_sample)
- comparison for the geophone on the granite (figure fig:time_domain_marble)
figure;
hold on;
plot(d3(:, 3), d3(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'All ON');
plot(d4(:, 3), d4(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Ty OFF');
plot(d5(:, 3), d5(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Ry OFF');
plot(d6(:, 3), d6(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'S-R OFF');
plot(d7(:, 3), d7(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Rz OFF');
plot(d8(:, 3), d8(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Hexa OFF');
hold off;
xlabel('Time [s]'); ylabel('Voltage [V]');
xlim([0, 50]);
legend('Location', 'bestoutside'); <<plt-matlab>> figure;
hold on;
plot(d3(:, 3), d3(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'All ON');
plot(d4(:, 3), d4(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Ty OFF');
plot(d5(:, 3), d5(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Ry OFF');
plot(d6(:, 3), d6(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'S-R OFF');
plot(d7(:, 3), d7(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Rz OFF');
plot(d8(:, 3), d8(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Hexa OFF');
hold off;
xlabel('Time [s]'); ylabel('Voltage [V]');
xlim([0, 50]);
legend('Location', 'bestoutside'); <<plt-matlab>>Analysis - Frequency Domain
dt = d3(2, 3) - d3(1, 3);
Fs = 1/dt;
win = hanning(ceil(10*Fs));Vibrations at the sample location
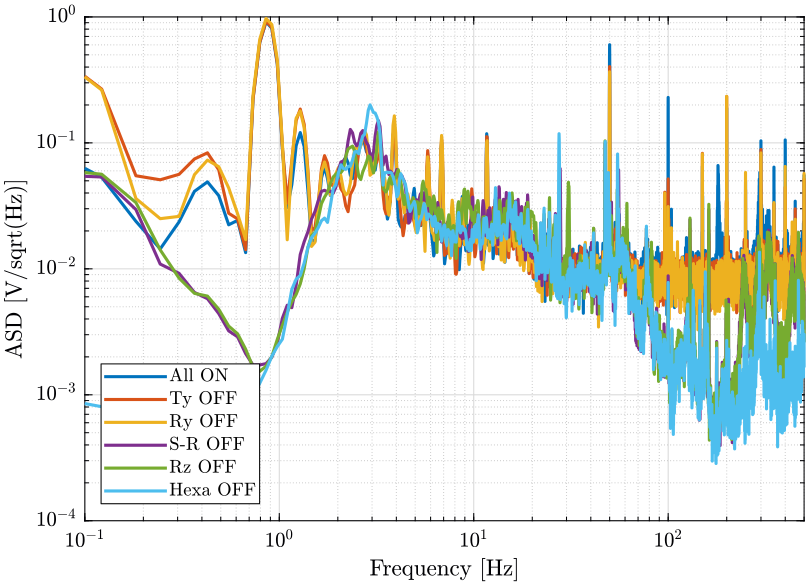
First, we compute the Power Spectral Density of the signals coming from the Geophone located at the sample location.
[px3, f] = pwelch(d3(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[px4, ~] = pwelch(d4(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[px5, ~] = pwelch(d5(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[px6, ~] = pwelch(d6(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[px7, ~] = pwelch(d7(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
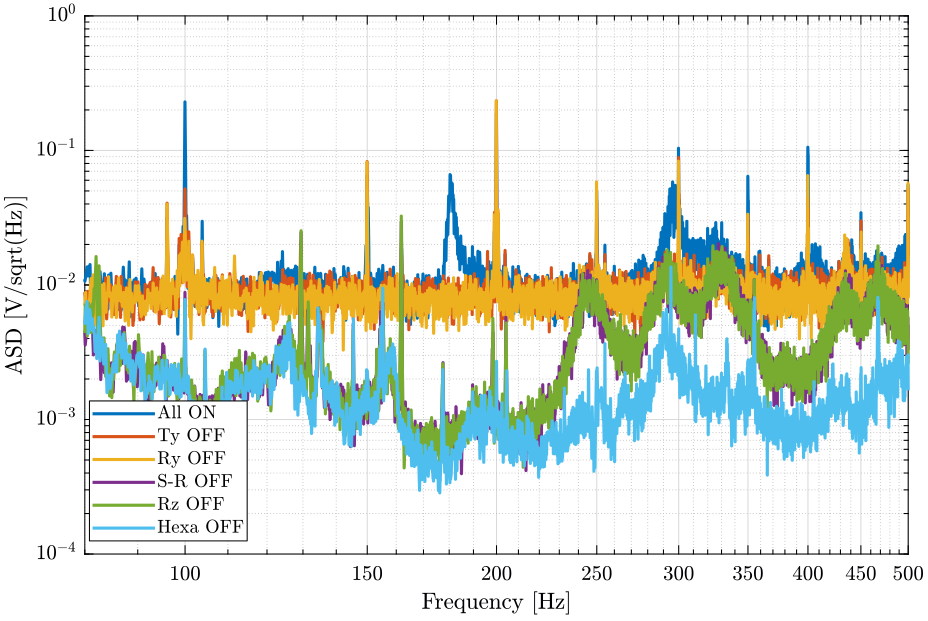
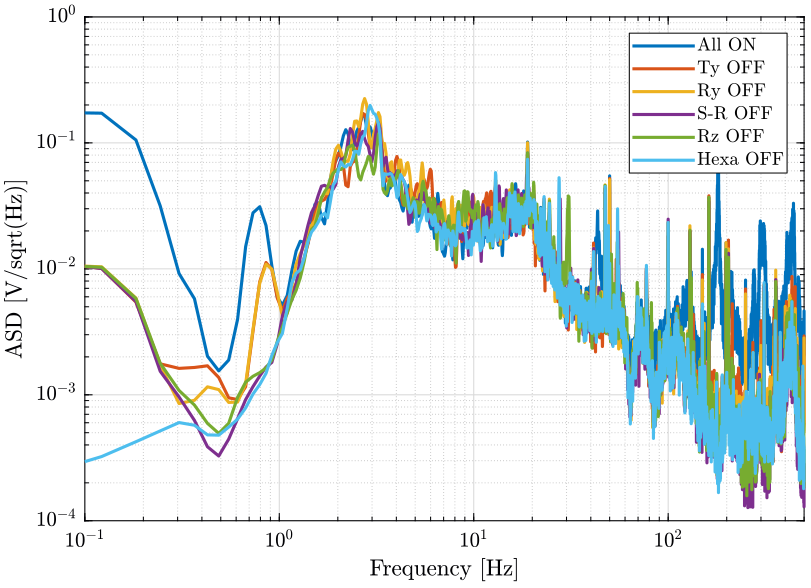
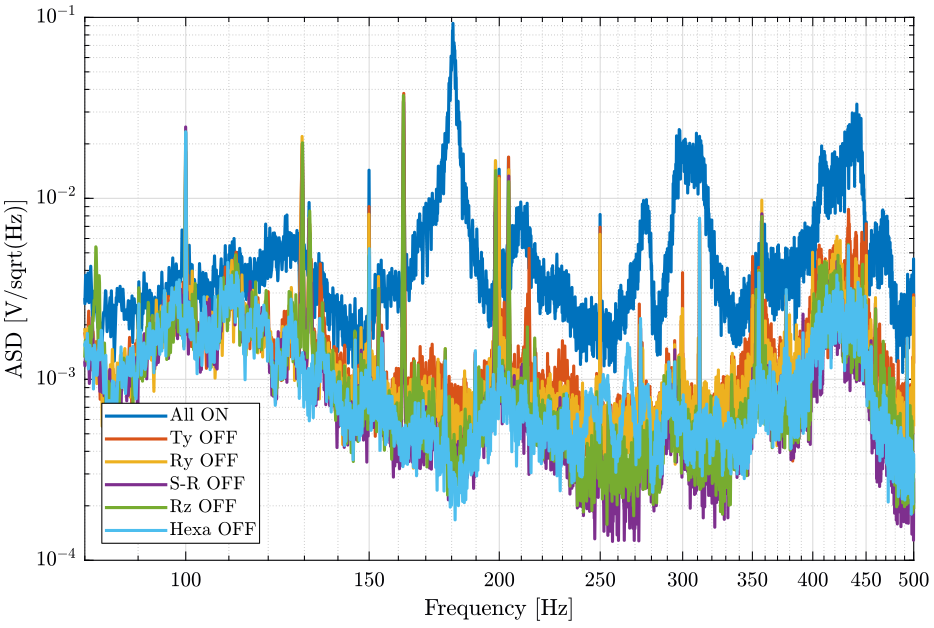
[px8, ~] = pwelch(d8(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);And we compare all the signals (figures fig:psd_sample_comp and fig:psd_sample_comp_high_freq).
figure;
hold on;
plot(f, sqrt(px3), 'DisplayName', 'All ON');
plot(f, sqrt(px4), 'DisplayName', 'Ty OFF');
plot(f, sqrt(px5), 'DisplayName', 'Ry OFF');
plot(f, sqrt(px6), 'DisplayName', 'S-R OFF');
plot(f, sqrt(px7), 'DisplayName', 'Rz OFF');
plot(f, sqrt(px8), 'DisplayName', 'Hexa OFF');
hold off;
set(gca, 'xscale', 'log');
set(gca, 'yscale', 'log');
xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'); ylabel('Amplitude Spectral Density $\left[\frac{V}{\sqrt{Hz}}\right]$')
xlim([0.1, 500]);
legend('Location', 'southwest'); <<plt-matlab>> <<plt-matlab>>Vibrations on the marble
Now we plot the same curves for the geophone located on the marble.
[px3, f] = pwelch(d3(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px4, ~] = pwelch(d4(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px5, ~] = pwelch(d5(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px6, ~] = pwelch(d6(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px7, ~] = pwelch(d7(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px8, ~] = pwelch(d8(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);And we compare the Amplitude Spectral Densities (figures fig:psd_marble_comp and fig:psd_marble_comp_high_freq)
figure;
hold on;
plot(f, sqrt(px3), 'DisplayName', 'All ON');
plot(f, sqrt(px4), 'DisplayName', 'Ty OFF');
plot(f, sqrt(px5), 'DisplayName', 'Ry OFF');
plot(f, sqrt(px6), 'DisplayName', 'S-R OFF');
plot(f, sqrt(px7), 'DisplayName', 'Rz OFF');
plot(f, sqrt(px8), 'DisplayName', 'Hexa OFF');
hold off;
set(gca, 'xscale', 'log');
set(gca, 'yscale', 'log');
xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'); ylabel('Amplitude Spectral Density $\left[\frac{V}{\sqrt{Hz}}\right]$')
xlim([0.1, 500]);
legend('Location', 'northeast'); <<plt-matlab>> <<plt-matlab>>Effect of the control system on the transmissibility from ground to sample
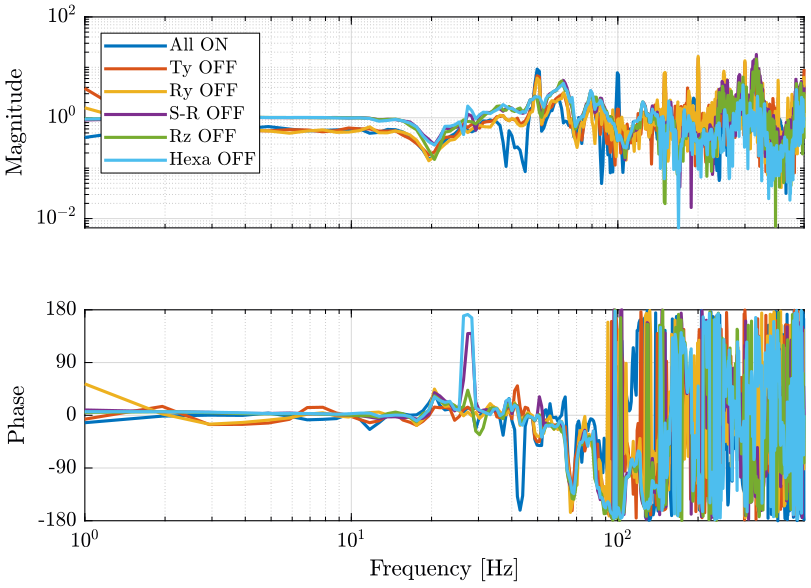
As the feedback loops change the dynamics of the system, we should see differences on the transfer function from marble velocity to sample velocity when turning off the control systems (figure fig:trans_comp).
dt = d3(2, 3) - d3(1, 3);
Fs = 1/dt;
win = hanning(ceil(1*Fs));First, we compute the Power Spectral Density of the signals coming from the Geophone located at the sample location.
[T3, f] = tfestimate(d3(:, 1), d3(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[T4, ~] = tfestimate(d4(:, 1), d4(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[T5, ~] = tfestimate(d5(:, 1), d5(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[T6, ~] = tfestimate(d6(:, 1), d6(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[T7, ~] = tfestimate(d7(:, 1), d7(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[T8, ~] = tfestimate(d8(:, 1), d8(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs); figure;
ax1 = subplot(2, 1, 1);
hold on;
plot(f, abs(T3), 'DisplayName', 'All ON');
plot(f, abs(T4), 'DisplayName', 'Ty OFF');
plot(f, abs(T5), 'DisplayName', 'Ry OFF');
plot(f, abs(T6), 'DisplayName', 'S-R OFF');
plot(f, abs(T7), 'DisplayName', 'Rz OFF');
plot(f, abs(T8), 'DisplayName', 'Hexa OFF');
hold off;
set(gca, 'xscale', 'log'); set(gca, 'yscale', 'log');
set(gca, 'XTickLabel',[]);
ylabel('Magnitude');
legend('Location', 'northwest');
ax2 = subplot(2, 1, 2);
hold on;
plot(f, mod(180+180/pi*phase(T3), 360)-180);
plot(f, mod(180+180/pi*phase(T4), 360)-180);
plot(f, mod(180+180/pi*phase(T5), 360)-180);
plot(f, mod(180+180/pi*phase(T6), 360)-180);
plot(f, mod(180+180/pi*phase(T7), 360)-180);
plot(f, mod(180+180/pi*phase(T8), 360)-180);
hold off;
set(gca, 'xscale', 'log');
ylim([-180, 180]);
yticks([-180, -90, 0, 90, 180]);
xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'); ylabel('Phase');
linkaxes([ax1,ax2],'x');
xlim([1, 500]); <<plt-matlab>>Conclusion
- The control system of the Ty stage induces a lot of vibrations of the marble
- Why it seems that the measurement noise at high frequency is the limiting factor when the slip ring is ON but not when it is OFF?
Effect of all the control systems on the Sample vibrations - One stage at a time
<<sec:effect_control_one>>
ZIP file containing the data and matlab files ignore
All the files (data and Matlab scripts) are accessible here.
Experimental Setup
We here measure the signals of two geophones:
- One is located on top of the Sample platform
- One is located on the marble
The signal from the top geophone does go trought the slip-ring.
All the control systems are turned OFF, then, they are turned on one at a time.
Each measurement are done during 100s.
The settings of the voltage amplifier are shown on figure fig:amplifier_settings. A first order low pass filter with a cut-off frequency of 1kHz is added before the voltage amplifier.
| Ty | Ry | Slip Ring | Spindle | Hexapod | Meas. file |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF | meas_013.mat |
| ON | OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF | meas_014.mat |
| OFF | ON | OFF | OFF | OFF | meas_015.mat |
| OFF | OFF | ON | OFF | OFF | meas_016.mat |
| OFF | OFF | OFF | ON | OFF | meas_017.mat |
| OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF | ON | meas_018.mat |
Each of the mat file contains one array data with 3 columns:
| Column number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Geophone - Marble |
| 2 | Geophone - Sample |
| 3 | Time |

Load data
We load the data of the z axis of two geophones.
d_of = load('mat/data_013.mat', 'data'); d_of = d_of.data;
d_ty = load('mat/data_014.mat', 'data'); d_ty = d_ty.data;
d_ry = load('mat/data_015.mat', 'data'); d_ry = d_ry.data;
d_sr = load('mat/data_016.mat', 'data'); d_sr = d_sr.data;
d_rz = load('mat/data_017.mat', 'data'); d_rz = d_rz.data;
d_he = load('mat/data_018.mat', 'data'); d_he = d_he.data;Analysis - Time Domain
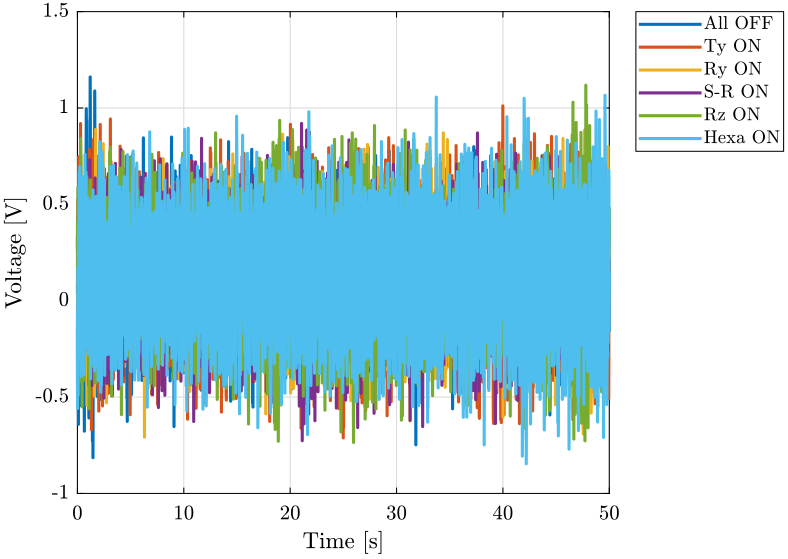
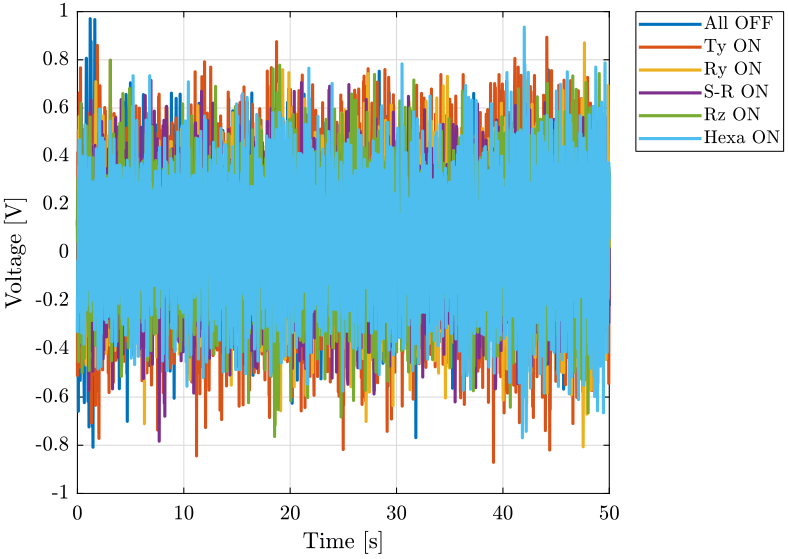
First, we can look at the time domain data and compare all the measurements:
- comparison for the geophone at the sample location (figure fig:time_domain_sample_lpf)
- comparison for the geophone on the granite (figure fig:time_domain_marble_lpf)
figure;
hold on;
plot(d_of(:, 3), d_of(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'All OFF';
plot(d_ty(:, 3), d_ty(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Ty ON');
plot(d_ry(:, 3), d_ry(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Ry ON');
plot(d_sr(:, 3), d_sr(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'S-R ON');
plot(d_rz(:, 3), d_rz(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Rz ON');
plot(d_he(:, 3), d_he(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Hexa ON');
hold off;
xlabel('Time [s]'); ylabel('Voltage [V]');
xlim([0, 50]);
legend('Location', 'bestoutside'); <<plt-matlab>> figure;
hold on;
plot(d_of(:, 3), d_of(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'All OFF');
plot(d_ty(:, 3), d_ty(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Ty ON');
plot(d_ry(:, 3), d_ry(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Ry ON');
plot(d_sr(:, 3), d_sr(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'S-R ON');
plot(d_rz(:, 3), d_rz(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Rz ON');
plot(d_he(:, 3), d_he(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Hexa ON');
hold off;
xlabel('Time [s]'); ylabel('Voltage [V]');
xlim([0, 50]);
legend('Location', 'bestoutside'); <<plt-matlab>>Analysis - Frequency Domain
dt = d_of(2, 3) - d_of(1, 3);
Fs = 1/dt;
win = hanning(ceil(10*Fs));Vibrations at the sample location
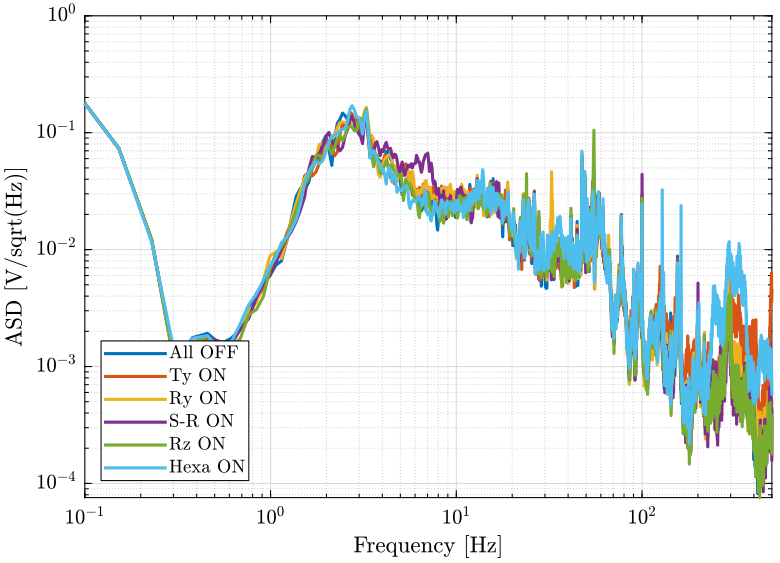
First, we compute the Power Spectral Density of the signals coming from the Geophone located at the sample location.
[px_of, f] = pwelch(d_of(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[px_ty, ~] = pwelch(d_ty(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[px_ry, ~] = pwelch(d_ry(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[px_sr, ~] = pwelch(d_sr(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[px_rz, ~] = pwelch(d_rz(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
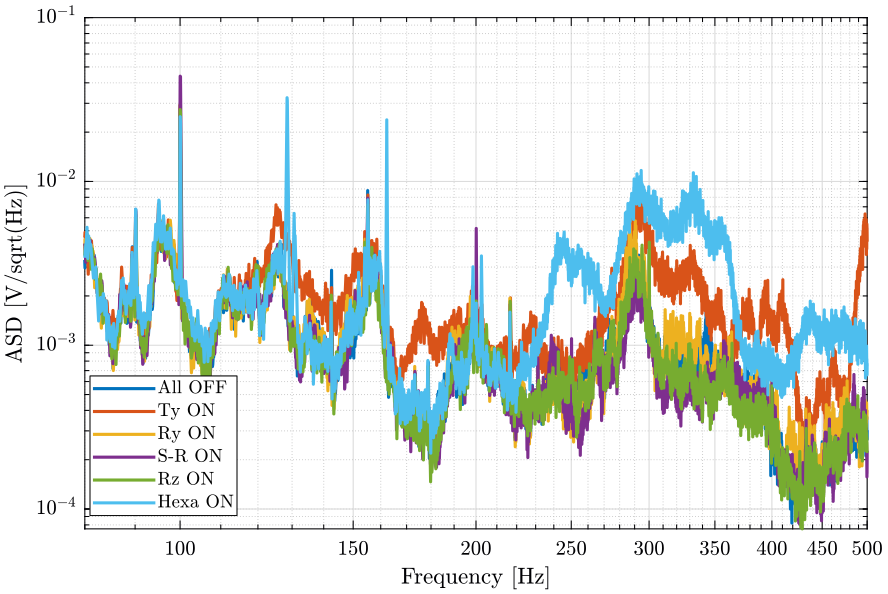
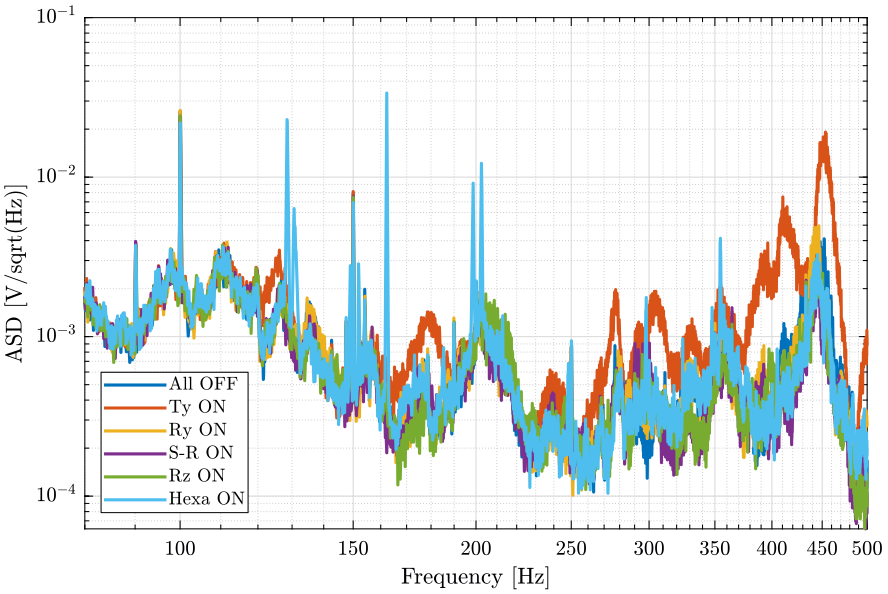
[px_he, ~] = pwelch(d_he(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);And we compare all the signals (figures fig:psd_sample_comp_lpf and fig:psd_sample_comp_high_freq_lpf).
figure;
hold on;
plot(f, sqrt(px_of), 'DisplayName', 'All OFF');
plot(f, sqrt(px_ty), 'DisplayName', 'Ty ON');
plot(f, sqrt(px_ry), 'DisplayName', 'Ry ON');
plot(f, sqrt(px_sr), 'DisplayName', 'S-R ON');
plot(f, sqrt(px_rz), 'DisplayName', 'Rz ON');
plot(f, sqrt(px_he), 'DisplayName', 'Hexa ON');
hold off;
set(gca, 'xscale', 'log');
set(gca, 'yscale', 'log');
xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'); ylabel('Amplitude Spectral Density $\left[\frac{V}{\sqrt{Hz}}\right]$')
xlim([0.1, 500]);
legend('Location', 'southwest'); <<plt-matlab>> <<plt-matlab>>Vibrations on the marble
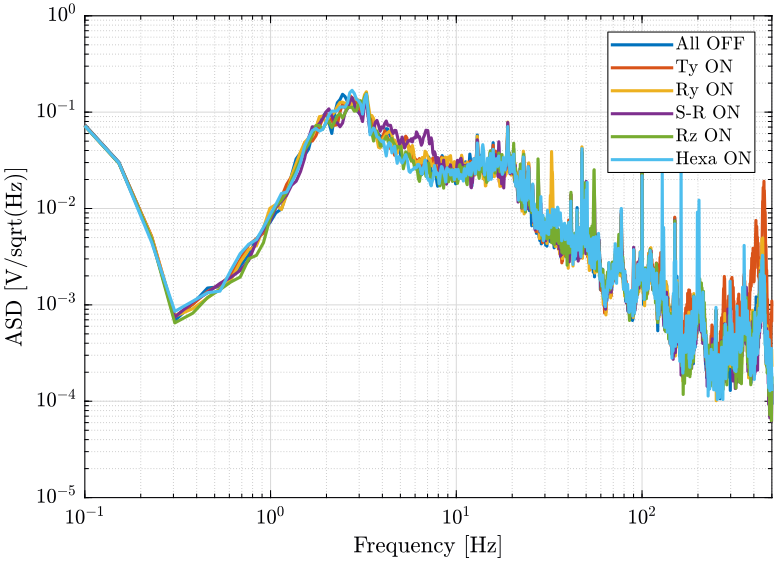
Now we plot the same curves for the geophone located on the marble.
[px_of, f] = pwelch(d_of(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px_ty, ~] = pwelch(d_ty(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px_ry, ~] = pwelch(d_ry(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px_sr, ~] = pwelch(d_sr(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px_rz, ~] = pwelch(d_rz(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px_he, ~] = pwelch(d_he(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);And we compare the Amplitude Spectral Densities (figures fig:psd_marble_comp_lpf and fig:psd_marble_comp_lpf_high_freq)
figure;
hold on;
plot(f, sqrt(px_of), 'DisplayName', 'All OFF');
plot(f, sqrt(px_ty), 'DisplayName', 'Ty ON');
plot(f, sqrt(px_ry), 'DisplayName', 'Ry ON');
plot(f, sqrt(px_sr), 'DisplayName', 'S-R ON');
plot(f, sqrt(px_rz), 'DisplayName', 'Rz ON');
plot(f, sqrt(px_he), 'DisplayName', 'Hexa ON');
hold off;
set(gca, 'xscale', 'log');
set(gca, 'yscale', 'log');
xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'); ylabel('Amplitude Spectral Density $\left[\frac{V}{\sqrt{Hz}}\right]$')
xlim([0.1, 500]);
legend('Location', 'northeast'); <<plt-matlab>> <<plt-matlab>>Conclusion
- The Ty stage induces vibrations of the marble and at the sample location above 100Hz
- The hexapod stage induces vibrations at the sample position above 220Hz
Effect of the Symetrie Driver
<<sec:effect_symetrie_driver>>
ZIP file containing the data and matlab files ignore
All the files (data and Matlab scripts) are accessible here.
Experimental Setup
We here measure the signals of two geophones:
- One is located on top of the Sample platform
- One is located on the marble
The signal from the top geophone does go trought the slip-ring.
All the control systems are turned OFF except the Hexapod one.
Each measurement are done during 100s.
The settings of the voltage amplifier are:
- DC
- 60dB
- 1kHz
A first order low pass filter with a cut-off frequency of 1kHz is added before the voltage amplifier.
The measurements are:
meas_018.mat: Hexapod's driver on the granitemeas_019.mat: Hexapod's driver on the ground
Each of the mat file contains one array data with 3 columns:
| Column number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Geophone - Marble |
| 2 | Geophone - Sample |
| 3 | Time |
Load data
We load the data of the z axis of two geophones.
d_18 = load('mat/data_018.mat', 'data'); d_18 = d_18.data;
d_19 = load('mat/data_019.mat', 'data'); d_19 = d_19.data;Analysis - Time Domain
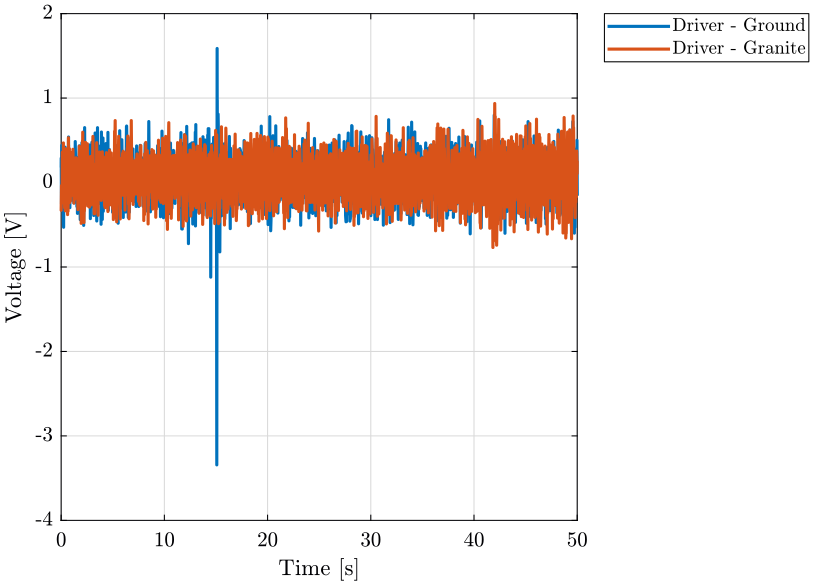
figure;
hold on;
plot(d_19(:, 3), d_19(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Driver - Ground');
plot(d_18(:, 3), d_18(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Driver - Granite');
hold off;
xlabel('Time [s]'); ylabel('Voltage [V]');
xlim([0, 50]);
legend('Location', 'bestoutside'); <<plt-matlab>>Analysis - Frequency Domain
dt = d_18(2, 3) - d_18(1, 3);
Fs = 1/dt;
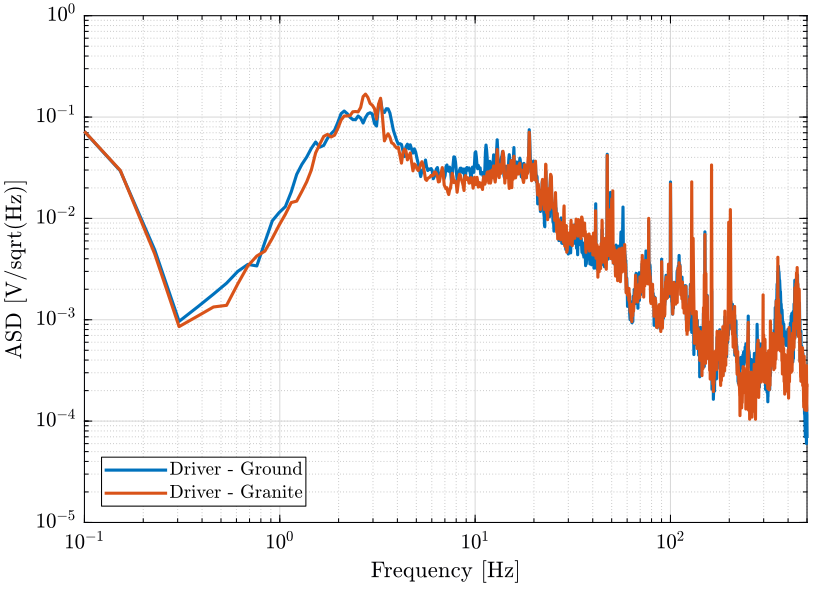
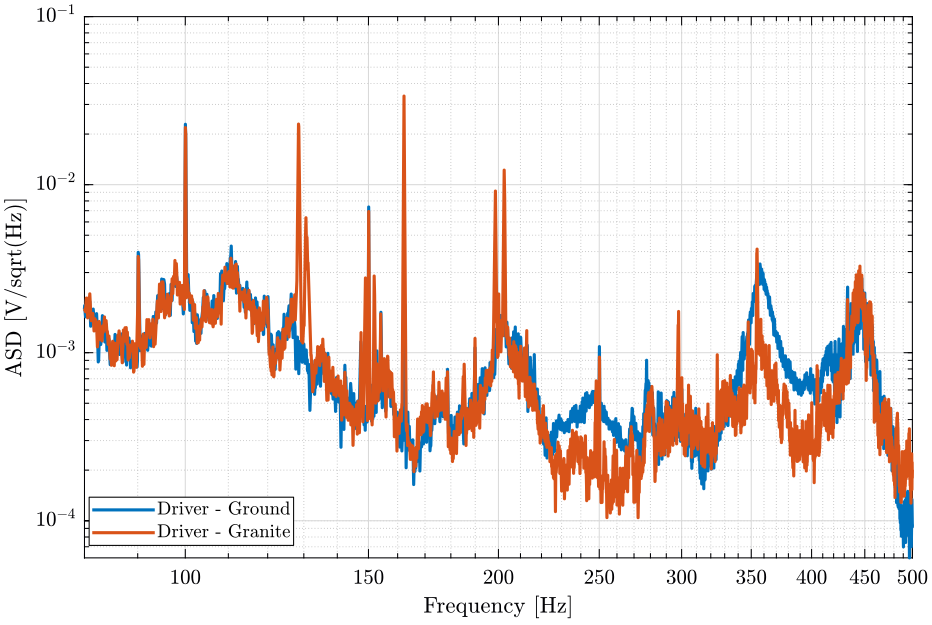
win = hanning(ceil(10*Fs));Vibrations at the sample location
First, we compute the Power Spectral Density of the signals coming from the Geophone located at the sample location.
[px_18, f] = pwelch(d_18(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs);
[px_19, ~] = pwelch(d_19(:, 1), win, [], [], Fs); figure;
hold on;
plot(f, sqrt(px_19), 'DisplayName', 'Driver - Ground');
plot(f, sqrt(px_18), 'DisplayName', 'Driver - Granite');
hold off;
set(gca, 'xscale', 'log');
set(gca, 'yscale', 'log');
xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'); ylabel('Amplitude Spectral Density $\left[\frac{V}{\sqrt{Hz}}\right]$')
xlim([0.1, 500]);
legend('Location', 'southwest'); <<plt-matlab>> <<plt-matlab>>Conclusion
Even tough the Hexapod's driver vibrates quite a lot, it does not generate significant vibrations of the granite when either placed on the granite or on the ground.
Transfer function from one stage to the other
<<sec:tf_stages_geophone>>
ZIP file containing the data and matlab files ignore
All the files (data and Matlab scripts) are accessible here.
Experimental Setup
For all the measurements in this section:
- all the control stages are OFF.
- the measurements are on the $z$ direction
From Marble to Ty - mat/meas_010.mat
One geophone is on the marble, one is on the Ty stage (see figures fig:setup_m_ty, fig:setup_m_ty_zoom and fig:setup_m_ty_top).
The data array contains the following columns:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ground |
| 2 | Ty |
| 3 | Time |
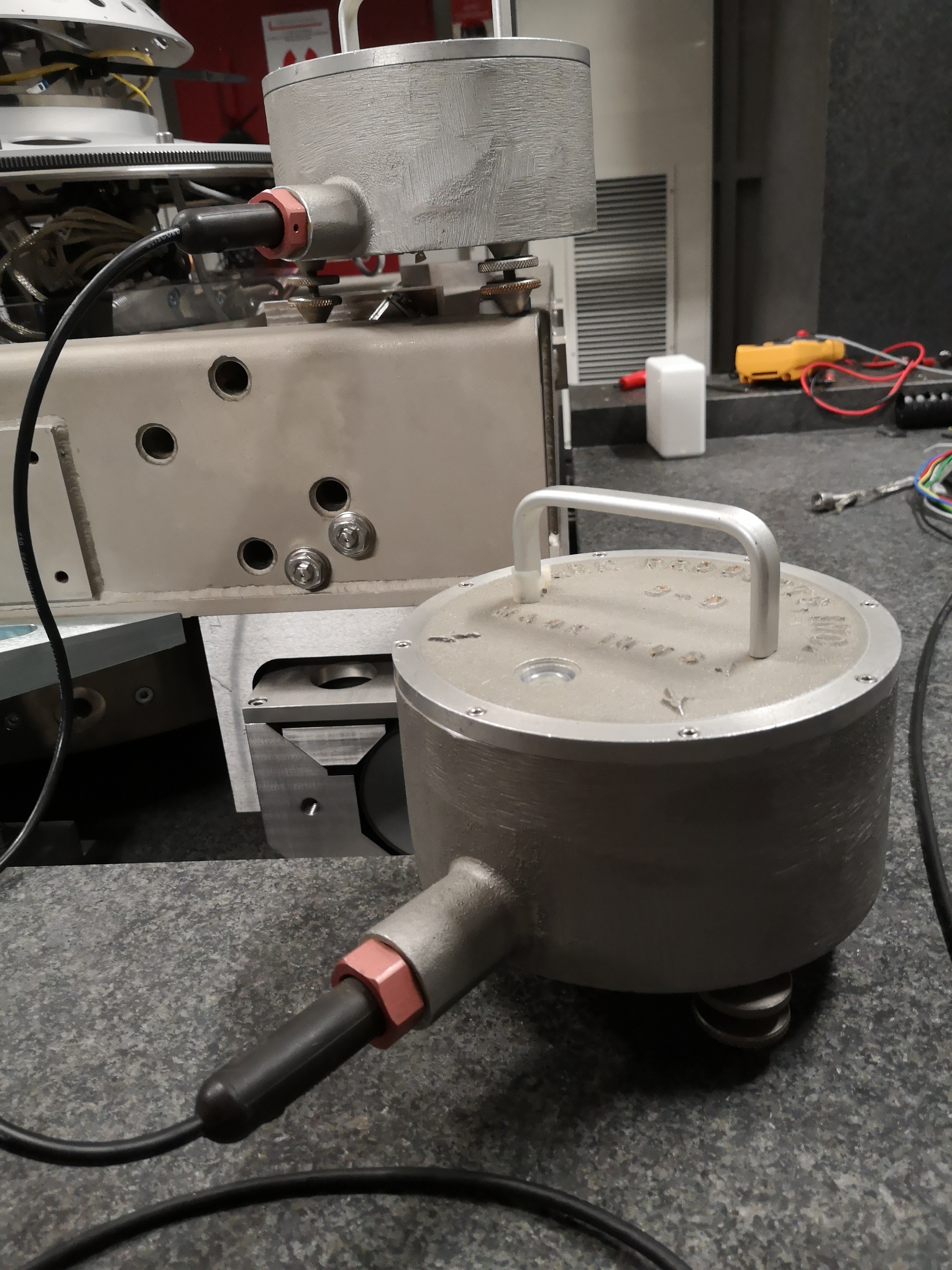
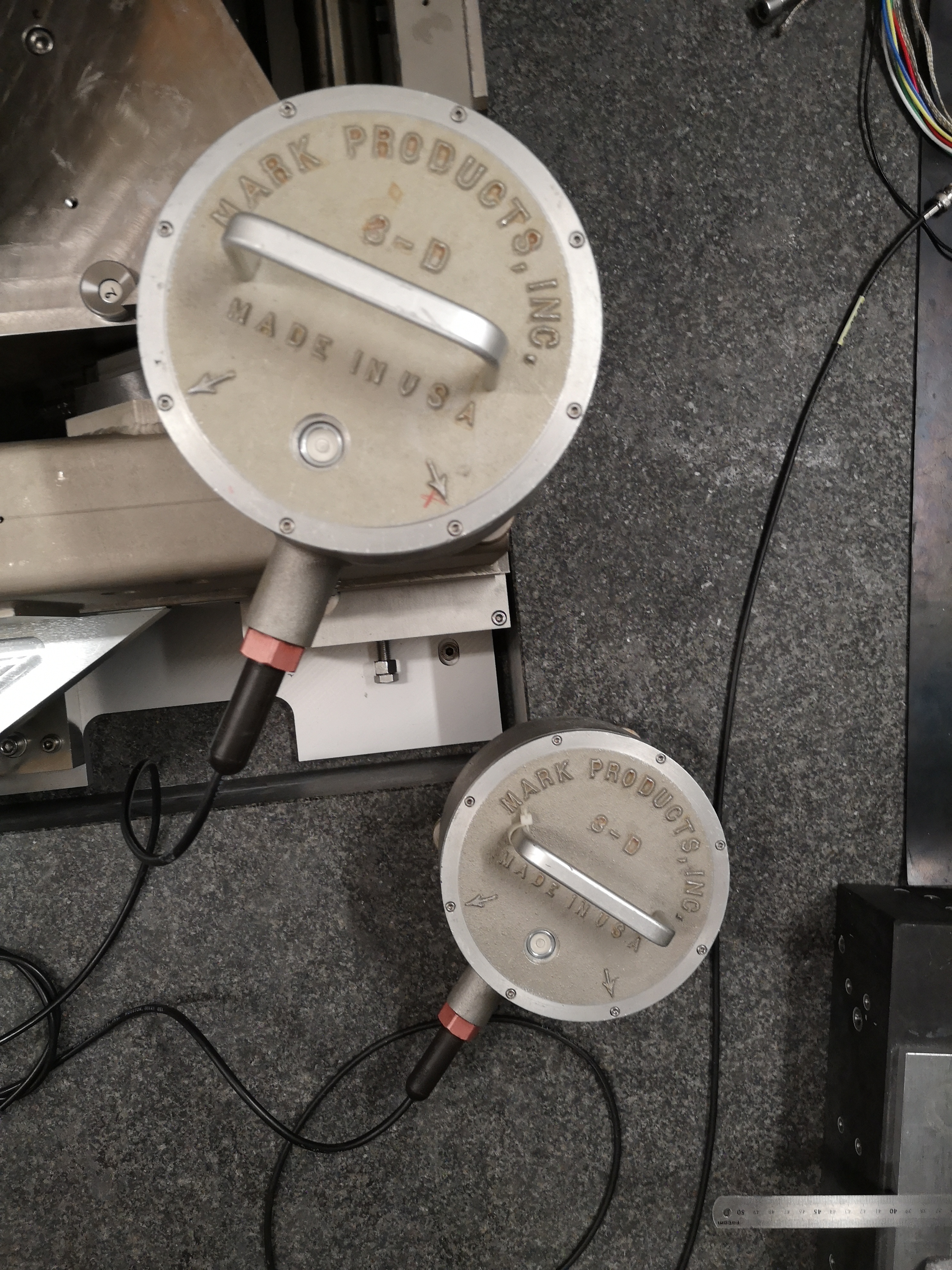
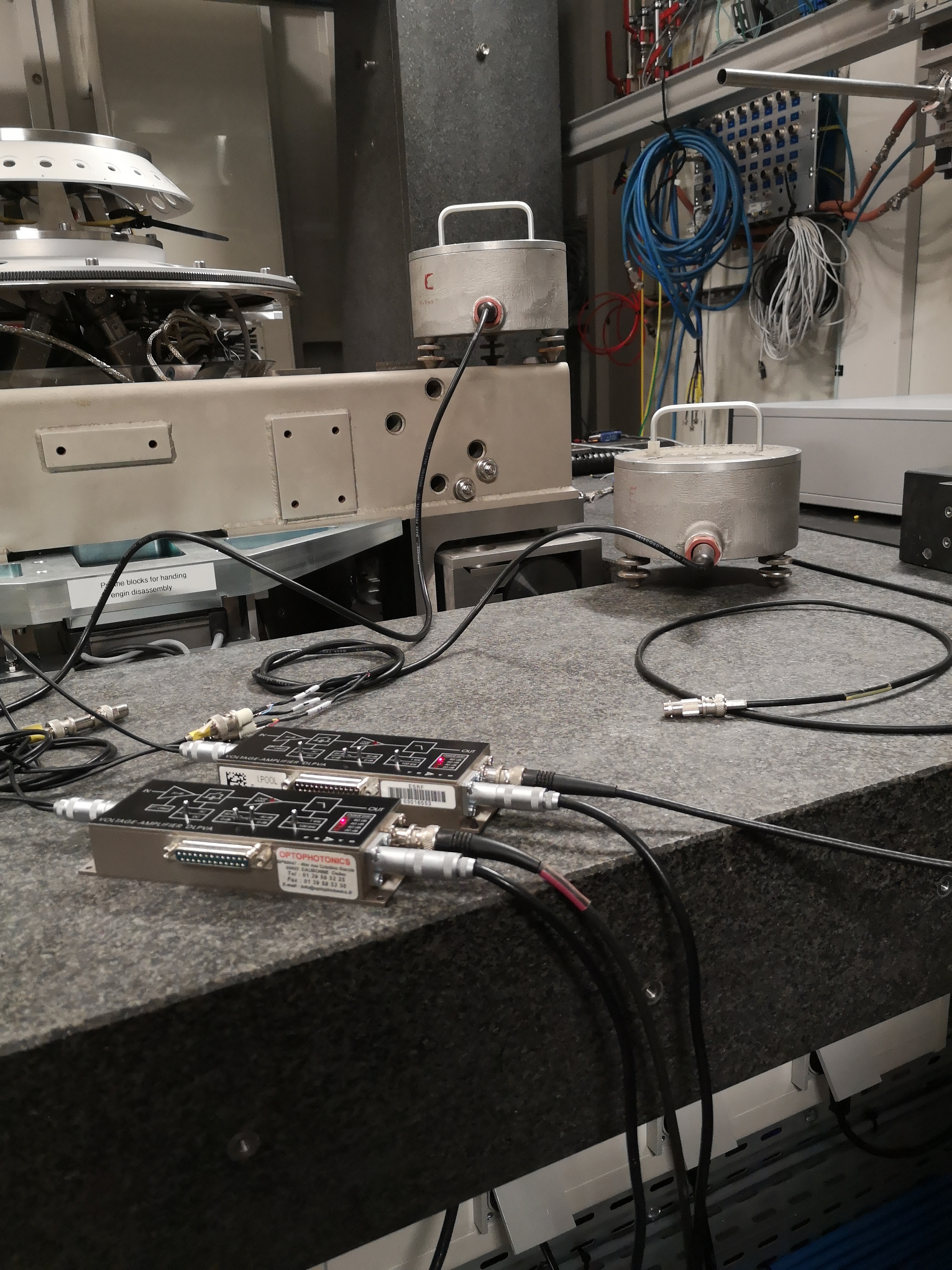


From Marble to Ry - mat/meas_011.mat
One geophone is on the marble, one is on the Ry stage (see figure fig:setup_m_ry)
The data array contains the following columns:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ground |
| 2 | Ry |
| 3 | Time |
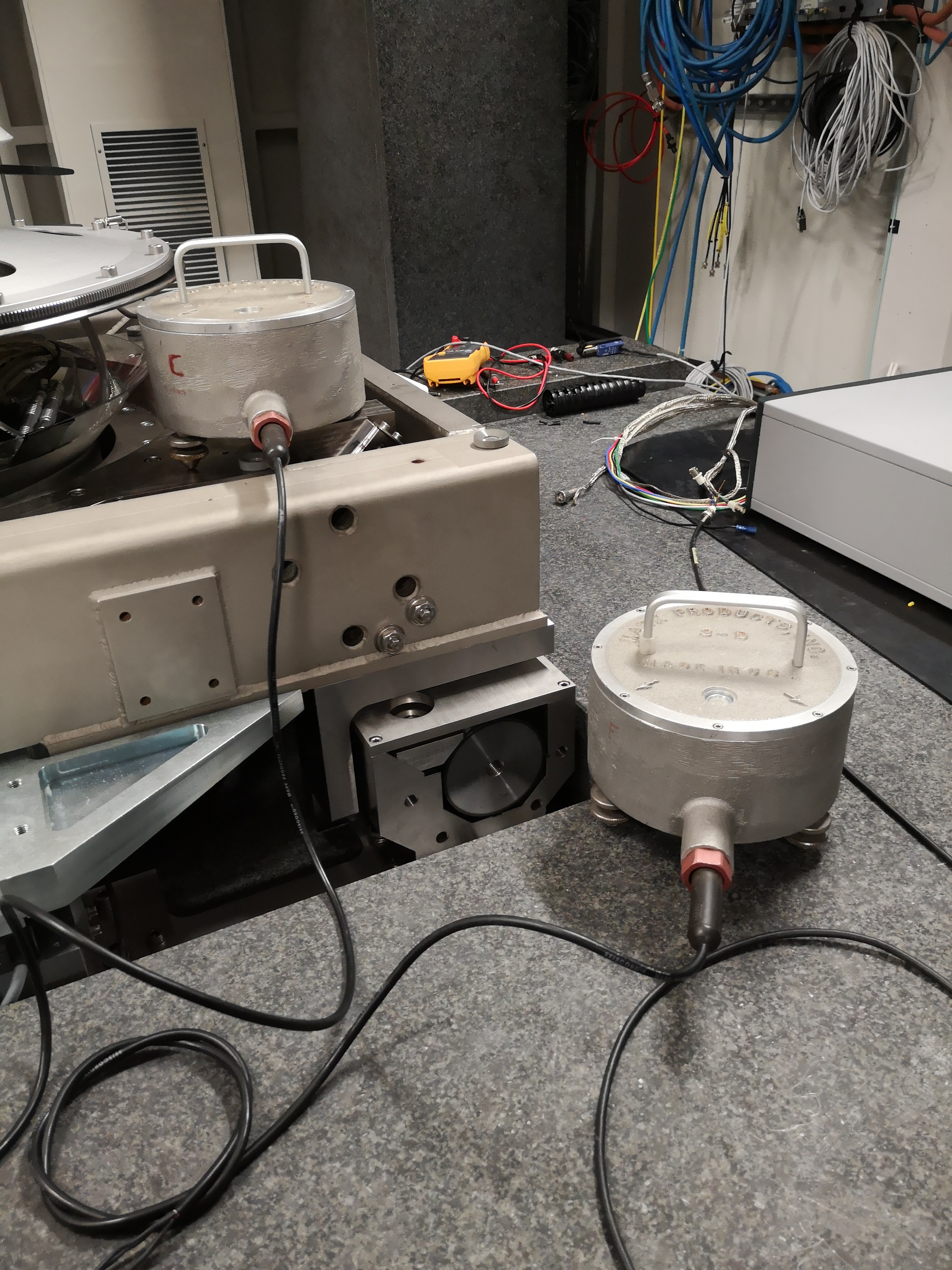

From Ty to Ry - mat/meas_012.mat
One geophone is on the Ty stage, one is on the Ry stage (see figures fig:setup_ty_ry, fig:setup_ty_ry_top and fig:setup_ty_ry_zoom) One geophone on the Ty stage, one geophone on the Ry stage.
The data array contains the following columns:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ty |
| 2 | Ry |
| 3 | Time |
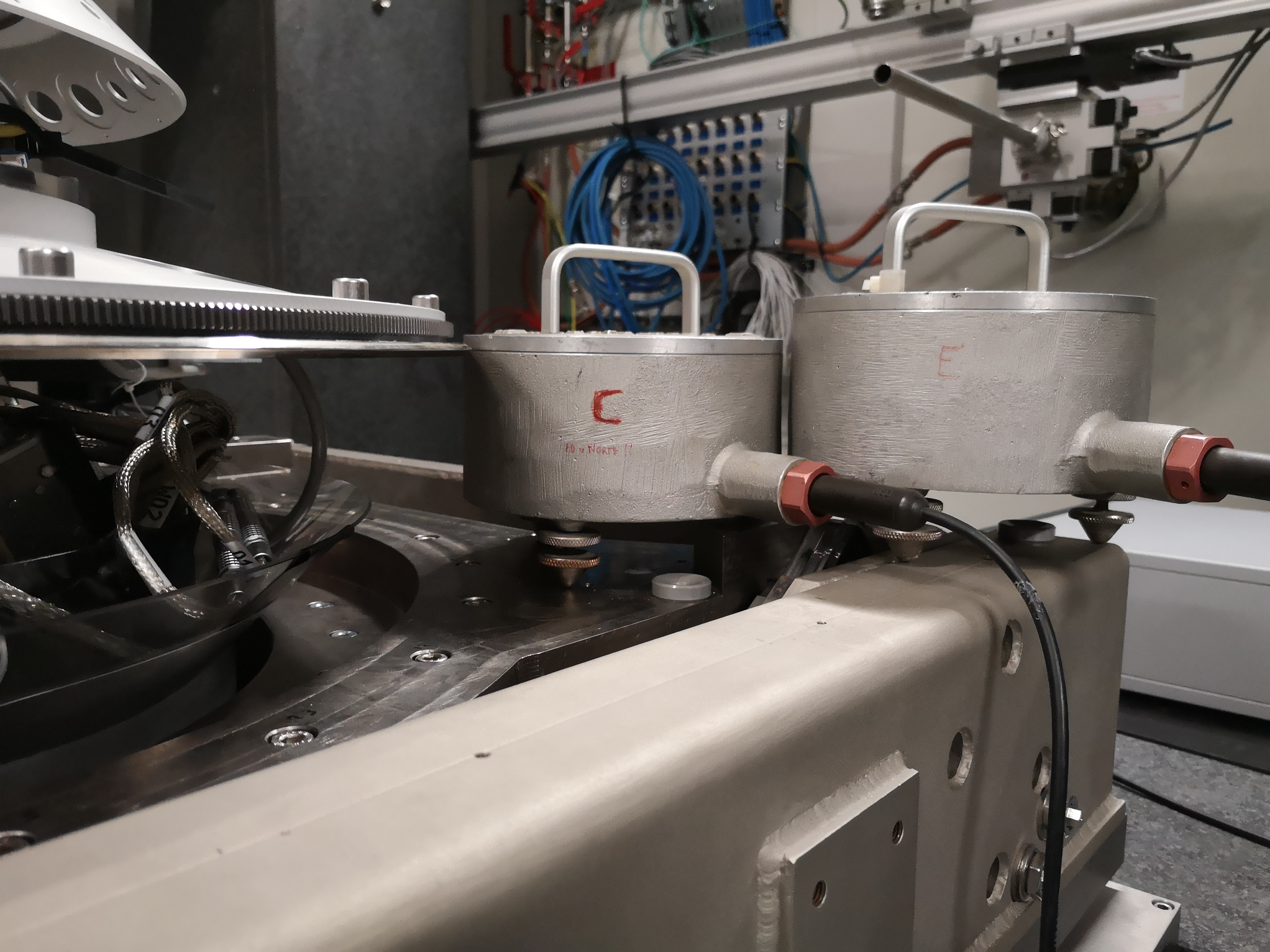
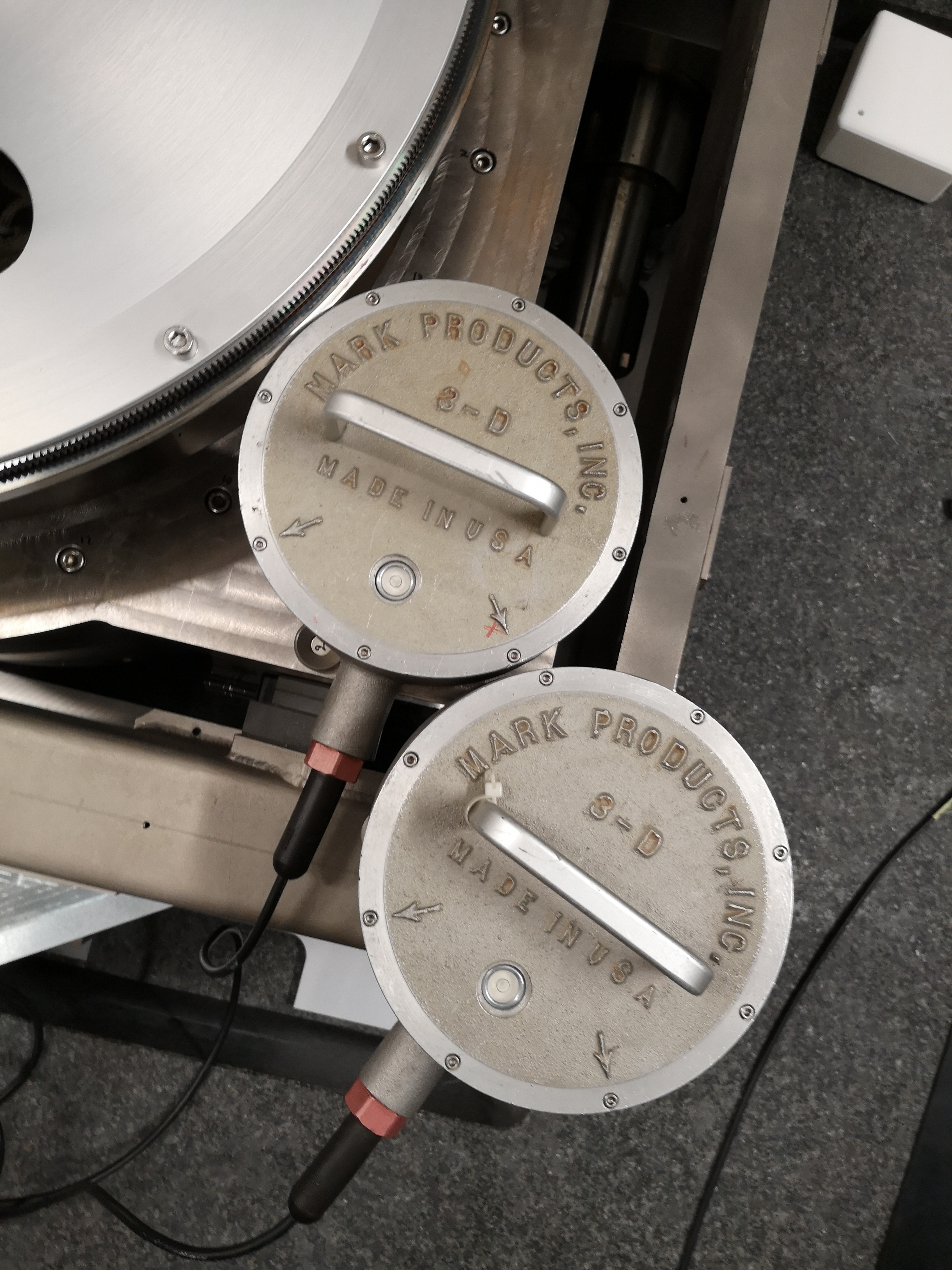
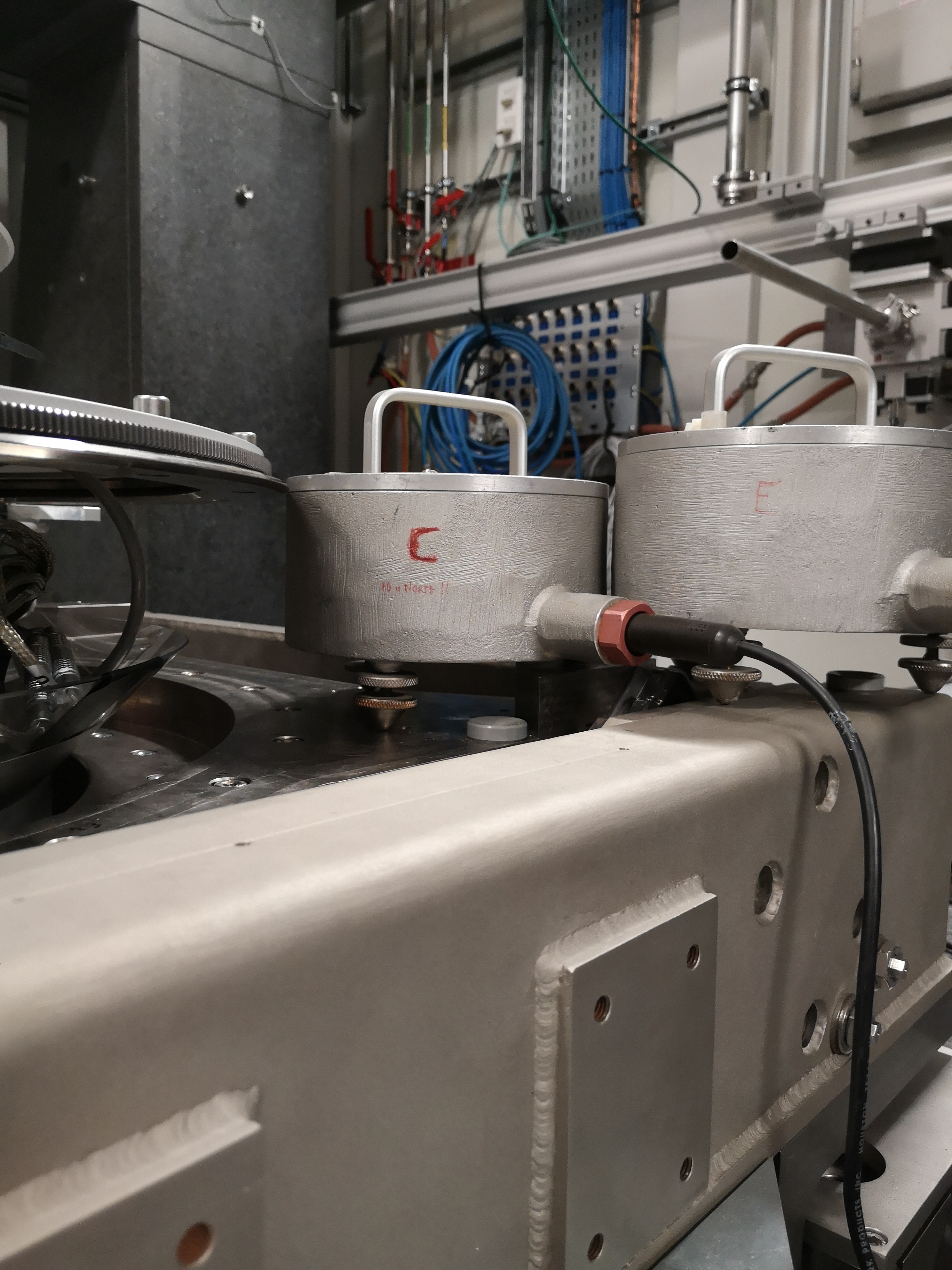



Load data
We load the data of the z axis of two geophones.
m_ty = load('mat/data_010.mat', 'data'); m_ty = m_ty.data;
m_ry = load('mat/data_011.mat', 'data'); m_ry = m_ry.data;
ty_ry = load('mat/data_012.mat', 'data'); ty_ry = ty_ry.data;Analysis - Time Domain
First, we can look at the time domain data.
figure;
hold on;
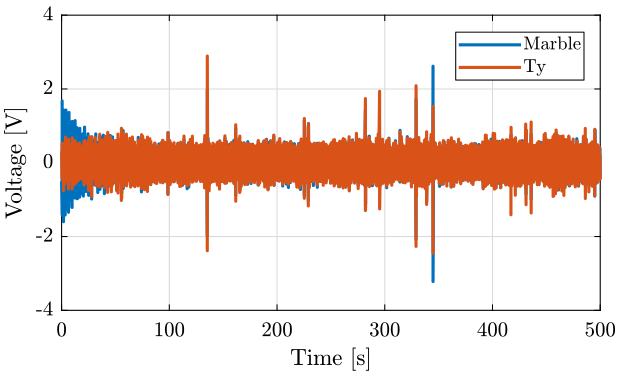
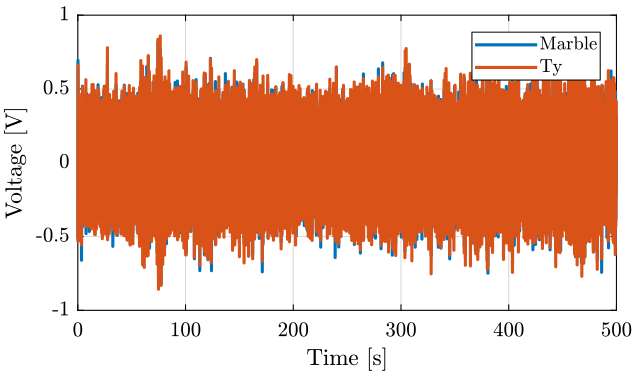
plot(m_ty(:, 3), m_ty(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Marble');
plot(m_ty(:, 3), m_ty(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Ty');
hold off;
xlabel('Time [s]'); ylabel('Voltage [V]');
legend('Location', 'northeast');
xlim([0, 500]); <<plt-matlab>> figure;
hold on;
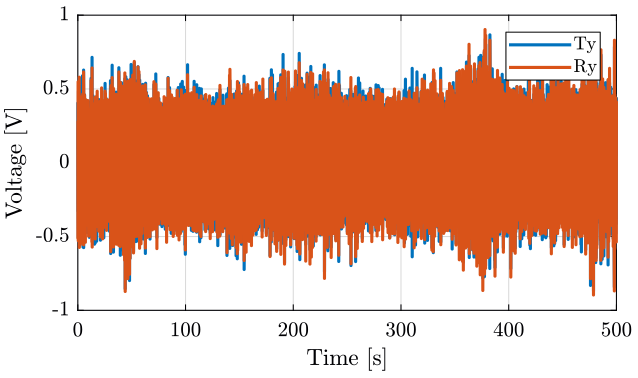
plot(m_ry(:, 3), m_ry(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Marble');
plot(m_ry(:, 3), m_ry(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Ty');
hold off;
xlabel('Time [s]'); ylabel('Voltage [V]');
legend('Location', 'northeast');
xlim([0, 500]); <<plt-matlab>> figure;
hold on;
plot(ty_ry(:, 3), ty_ry(:, 1), 'DisplayName', 'Ty');
plot(ty_ry(:, 3), ty_ry(:, 2), 'DisplayName', 'Ry');
hold off;
xlabel('Time [s]'); ylabel('Voltage [V]');
legend('Location', 'northeast');
xlim([0, 500]); <<plt-matlab>>Analysis - Frequency Domain
dt = m_ty(2, 3) - m_ty(1, 3);
Fs = 1/dt;
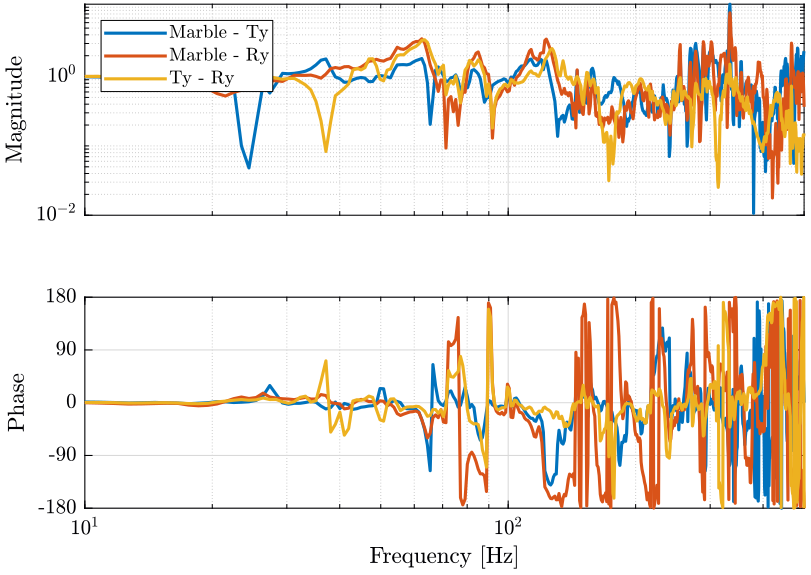
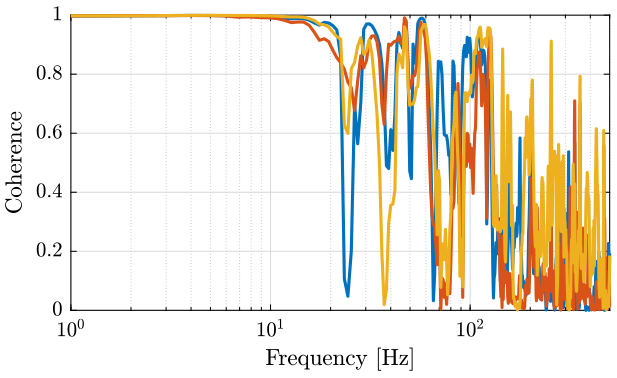
win = hanning(ceil(1*Fs));First, we compute the transfer function estimate between the two geophones for the 3 experiments (figure fig:compare_tf_geophones). We also plot their coherence (figure fig:coherence_two_geophones).
[T_m_ty, f] = tfestimate(m_ty(:, 1), m_ty(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[T_m_ry, ~] = tfestimate(m_ry(:, 1), m_ry(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[T_ty_ry, ~] = tfestimate(ty_ry(:, 1), ty_ry(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs); figure;
ax1 = subplot(2, 1, 1);
hold on;
plot(f, abs(T_m_ty), 'DisplayName', 'Marble - Ty');
plot(f, abs(T_m_ry), 'DisplayName', 'Marble - Ry');
plot(f, abs(T_ty_ry), 'DisplayName', 'Ty - Ry');
hold off;
set(gca, 'xscale', 'log'); set(gca, 'yscale', 'log');
set(gca, 'XTickLabel',[]);
ylabel('Magnitude');
legend('Location', 'northwest');
ax2 = subplot(2, 1, 2);
hold on;
plot(f, mod(180+180/pi*phase(T_m_ty), 360)-180);
plot(f, mod(180+180/pi*phase(T_m_ry), 360)-180);
plot(f, mod(180+180/pi*phase(T_ty_ry), 360)-180);
hold off;
set(gca, 'xscale', 'log');
ylim([-180, 180]);
yticks([-180, -90, 0, 90, 180]);
xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'); ylabel('Phase');
linkaxes([ax1,ax2],'x');
xlim([10, 500]); <<plt-matlab>> [coh_m_ty, f] = mscohere(m_ty(:, 1), m_ty(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[coh_m_ry, ~] = mscohere(m_ry(:, 1), m_ry(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs);
[coh_ty_ry, ~] = mscohere(ty_ry(:, 1), ty_ry(:, 2), win, [], [], Fs); <<plt-matlab>>Conclusion
These measurements are not relevant.