92 KiB
Sensor Fusion - Test Bench
- Introduction
- Experimental Setup
- First identification of the system
- Optimal IFF Development
- Generate the excitation signal
- Identification of the Inertial Sensors Dynamics
- Inertial Sensor Noise and the $\mathcal{H}_2$ Synthesis of complementary filters
- Inertial Sensor Dynamics Uncertainty and the $\mathcal{H}_\infty$ Synthesis of complementary filters
- Optimal and Robust sensor fusion using the $\mathcal{H}_2/\mathcal{H}_\infty$ synthesis
- Matlab Functions
- Bibliography
This report is also available as a pdf.
Introduction ignore
In this document, we wish the experimentally validate sensor fusion of inertial sensors.
This document is divided into the following sections:
- Section sec:experimental_setup: the experimental setup is described
- Section sec:first_identification: a first identification of the system dynamics is performed
- Section sec:integral_force_feedback: the integral force feedback active damping technique is applied on the system
- Section sec:optimal_excitation: the optimal excitation signal is determine in order to have the best possible system dynamics estimation
- Section sec:inertial_sensor_dynamics: the inertial sensor dynamics are experimentally estimated
- Section sec:inertial_sensor_noise: the inertial sensor noises are estimated and the $\mathcal{H}_2$ synthesis of complementary filters is performed in order to yield a super sensor with minimal noise
- Section sec:inertial_sensor_uncertainty: the dynamical uncertainty of the inertial sensors is estimated. Then the $\mathcal{H}_\infty$ synthesis of complementary filters is performed in order to minimize the super sensor dynamical uncertainty
- Section sec:optimal_sensor_fusion: Optimal sensor fusion is performed using the $\mathcal{H}_2/\mathcal{H}_\infty$ synthesis
Experimental Setup
<<sec:experimental_setup>>
The goal of this experimental setup is to experimentally merge inertial sensors. To merge the sensors, optimal and robust complementary filters are designed.
A schematic of the test-bench used is shown in Figure fig:exp_setup_sensor_fusion and a picture of it is shown in Figure fig:test-bench-sensor-fusion-picture.
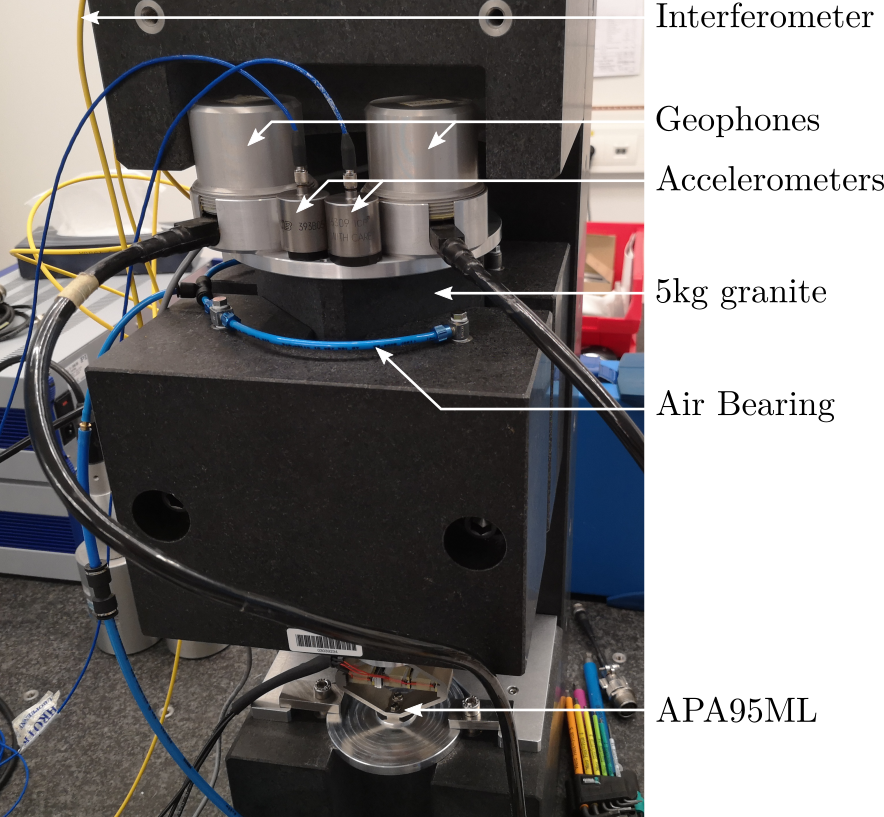
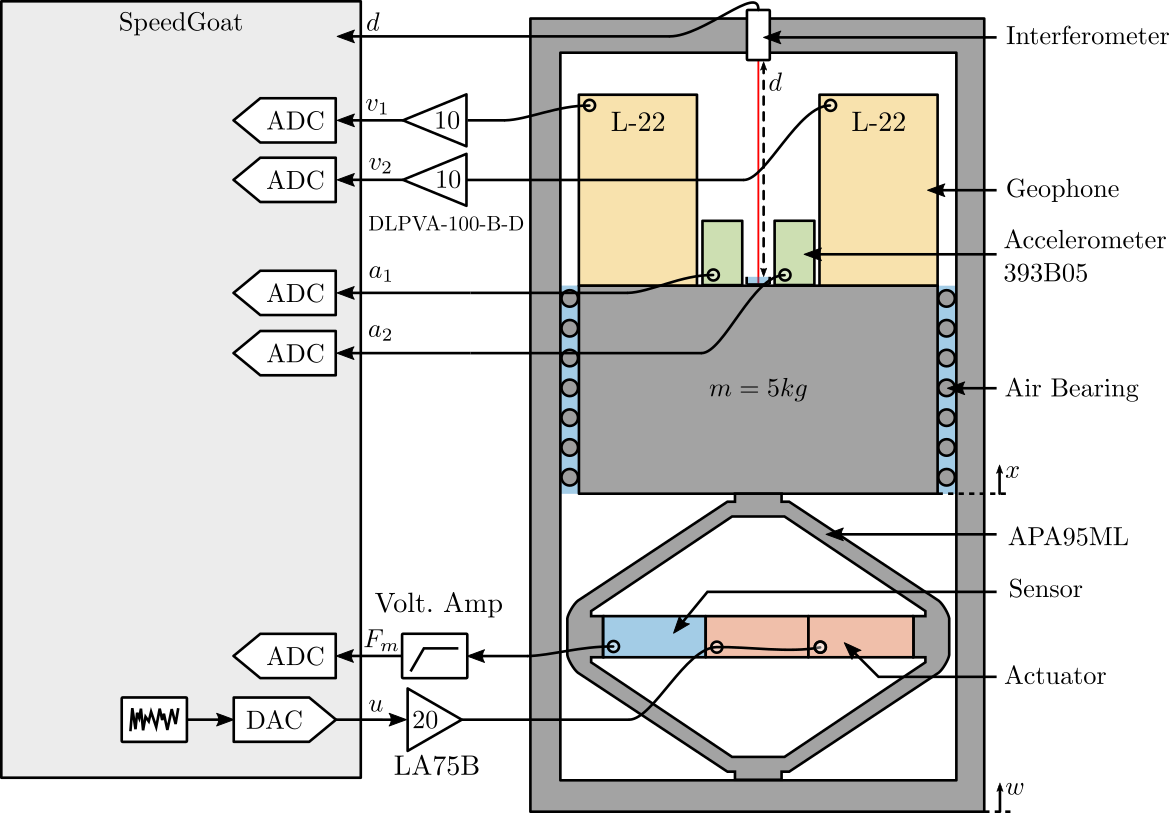

Two inertial sensors are used:
- An vertical accelerometer PCB 393B05 (doc)
- A vertical geophone Mark Product L-22
Basic characteristics of both sensors are shown in Tables tab:393B05_spec and tab:L22_spec.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 1.02 [V/(m/s2)] |
| Resonant Frequency | > 2.5 [kHz] |
| Resolution (1 to 10kHz) | 0.00004 [m/s2 rms] |
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | To be measured [V/(m/s)] |
| Resonant Frequency | 2 [Hz] |
The ADC used are the IO131 Speedgoat module (link) with a 16bit resolution over +/- 10V.
The geophone signals are amplified using a DLPVA-100-B-D voltage amplified from Femto (doc). The force sensor signal is amplified using a Low Noise Voltage Preamplifier from Ametek (doc).
The excitation signal is amplified by a linear amplified from Cedrat (LA75B) with a gain equals to 20 (doc).
Geophone electronics:
- gain: 10 (20dB)
- low pass filter: 1.5Hz
- hifh pass filter: 100kHz (2nd order)
Force Sensor electronics:
- gain: 10 (20dB)
- low pass filter: 1st order at 3Hz
- high pass filter: 1st order at 30kHz
First identification of the system
<<sec:first_identification>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, a first identification of each elements of the system is performed. This include the dynamics from the actuator to the force sensor, interferometer and inertial sensors.
Each of the dynamics is compared with the dynamics identified form a Simscape model.
Load Data
The data is loaded in the Matlab workspace.
id_ol = load('identification_noise_bis.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't');Then, any offset is removed.
id_ol.d = detrend(id_ol.d, 0);
id_ol.acc_1 = detrend(id_ol.acc_1, 0);
id_ol.acc_2 = detrend(id_ol.acc_2, 0);
id_ol.geo_1 = detrend(id_ol.geo_1, 0);
id_ol.geo_2 = detrend(id_ol.geo_2, 0);
id_ol.f_meas = detrend(id_ol.f_meas, 0);
id_ol.u = detrend(id_ol.u, 0);Excitation Signal
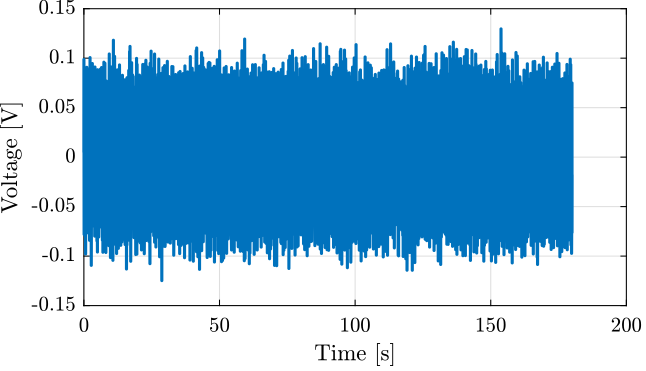
The generated voltage used to excite the system is a white noise and can be seen in Figure fig:excitation_signal_first_identification.
Identified Plant
The transfer function from the excitation voltage to the mass displacement and to the force sensor stack voltage are identified using the tfestimate command.
Ts = id_ol.t(2) - id_ol.t(1);
win = hann(ceil(10/Ts)); [tf_fmeas_est, f] = tfestimate(id_ol.u, id_ol.f_meas, win, [], [], 1/Ts); % [V/V]
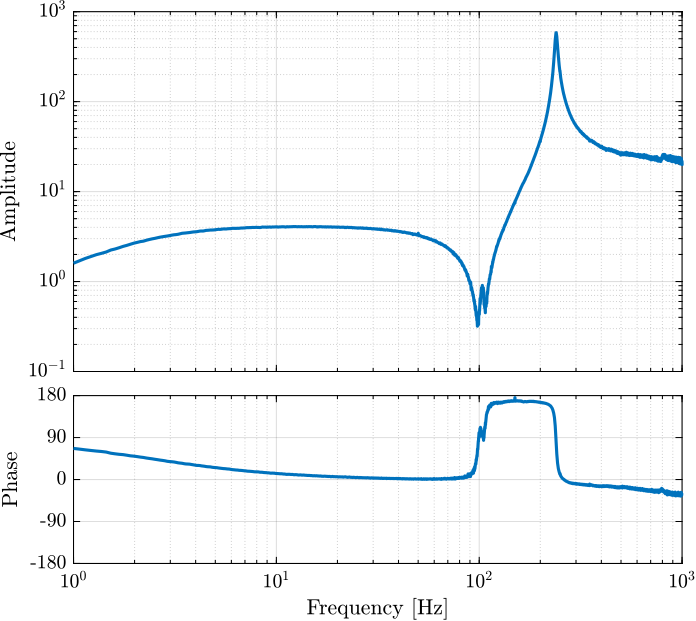
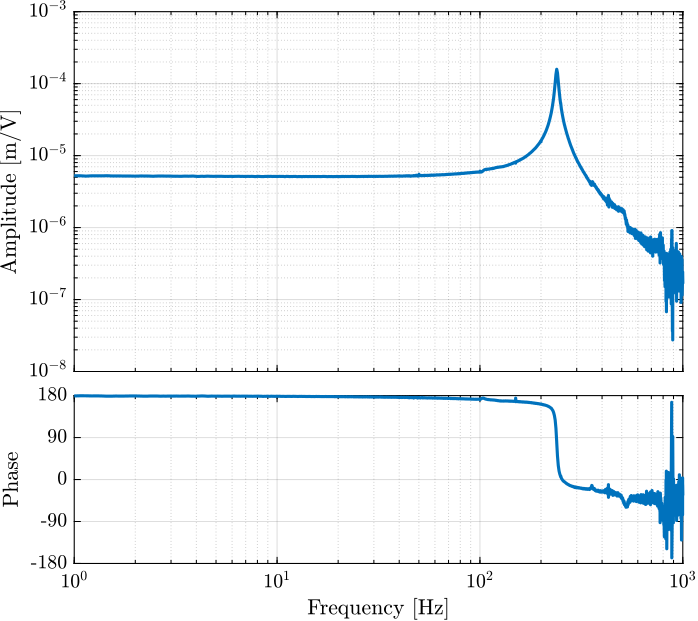
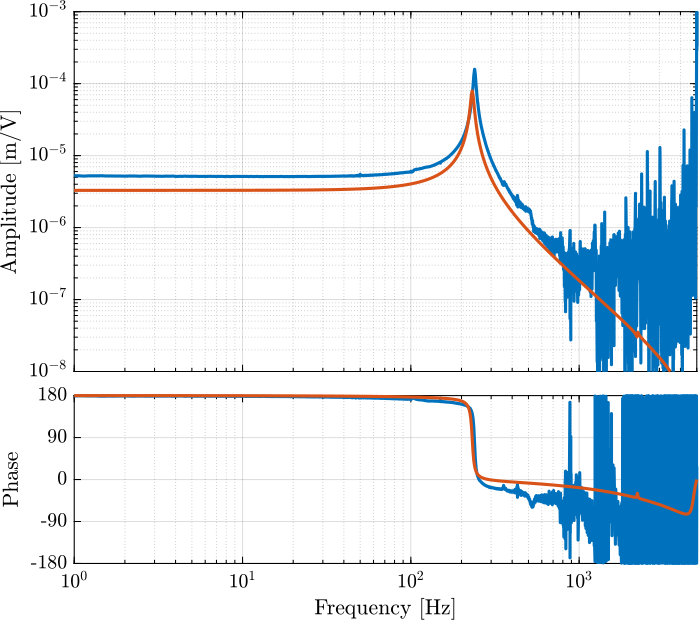
[tf_G_ol_est, ~] = tfestimate(id_ol.u, id_ol.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts); % [m/V]The bode plots of the obtained dynamics are shown in Figures fig:force_sensor_bode_plot and fig:displacement_sensor_bode_plot.
Simscape Model - Comparison
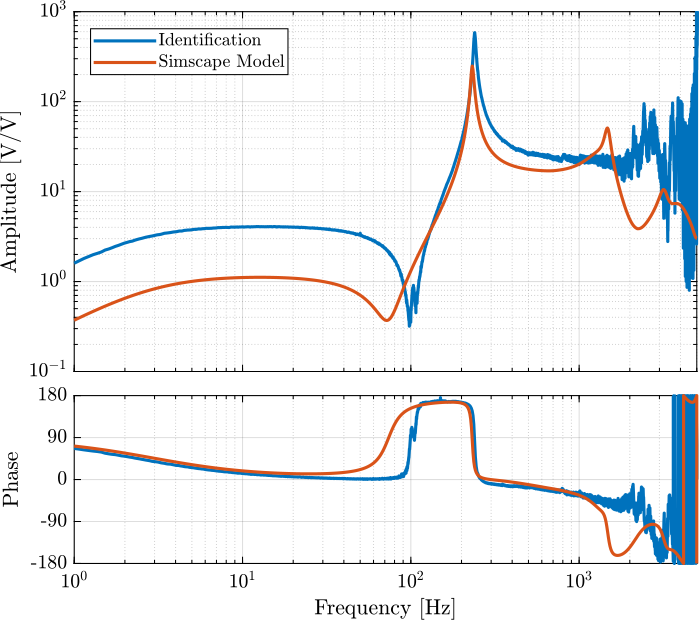
A simscape model representing the test-bench has been developed. The same transfer functions as the one identified using the test-bench can be obtained thanks to the simscape model.
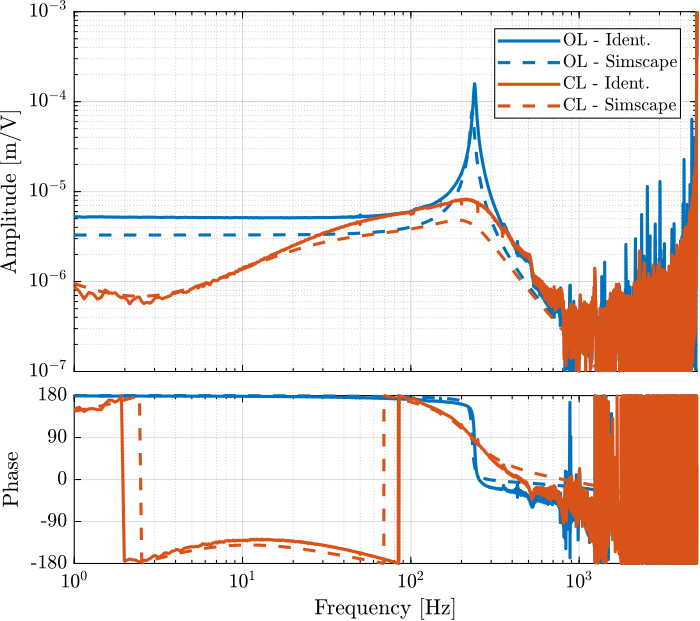
They are compared in Figure fig:simscape_comp_iff_plant and fig:simscape_comp_disp_plant. It is shown that there is a good agreement between the model and the experiment.
load('piezo_amplified_3d.mat', 'int_xyz', 'int_i', 'n_xyz', 'n_i', 'nodes', 'M', 'K');Integral Force Feedback
The force sensor stack can be used to damp the system. This makes the system easier to excite properly without too much amplification near resonances.
This is done thanks to the integral force feedback control architecture.
The force sensor stack signal is integrated (or rather low pass filtered) and fed back to the force sensor stacks.
The low pass filter used as the controller is defined below:
Kiff = 102/(s + 2*pi*2);The integral force feedback control strategy is applied to the simscape model as well as to the real test bench.
The damped system is then identified again using a noise excitation.
The data is loaded into Matlab and any offset is removed.
id_cl = load('identification_noise_iff_bis.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't');
id_cl.d = detrend(id_cl.d, 0);
id_cl.acc_1 = detrend(id_cl.acc_1, 0);
id_cl.acc_2 = detrend(id_cl.acc_2, 0);
id_cl.geo_1 = detrend(id_cl.geo_1, 0);
id_cl.geo_2 = detrend(id_cl.geo_2, 0);
id_cl.f_meas = detrend(id_cl.f_meas, 0);
id_cl.u = detrend(id_cl.u, 0);
The transfer functions are estimated using tfestimate.
[tf_G_cl_est, ~] = tfestimate(id_cl.u, id_cl.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
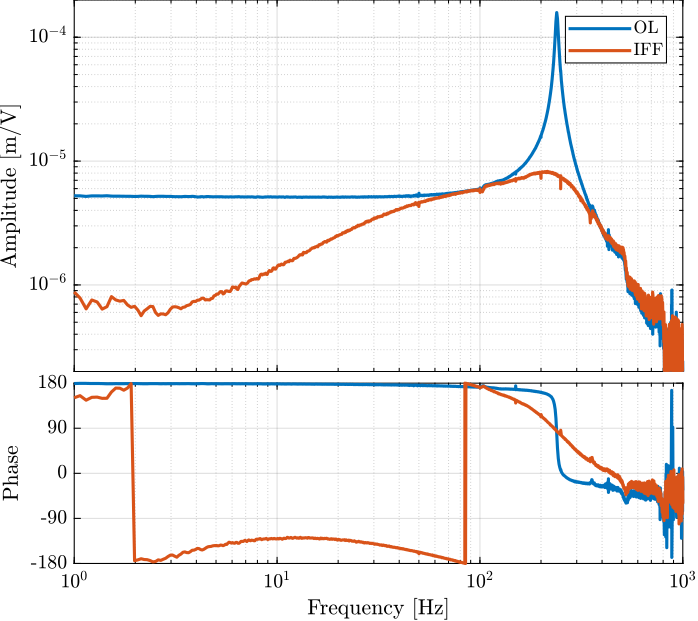
[co_G_cl_est, ~] = mscohere( id_cl.u, id_cl.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);The dynamics from driving voltage to the measured displacement are compared both in the open-loop and IFF case, and for the test-bench experimental identification and for the Simscape model in Figure fig:iff_ol_cl_identified_simscape_comp. This shows that the Integral Force Feedback architecture effectively damps the first resonance of the system.
Inertial Sensors
In order to estimate the dynamics of the inertial sensor (the transfer function from the "absolute" displacement to the measured voltage), the following experiment can be performed:
- The mass is excited such that is relative displacement as measured by the interferometer is much larger that the ground "absolute" motion.
- The transfer function from the measured displacement by the interferometer to the measured voltage generated by the inertial sensors can be estimated.
The first point is quite important in order to have a good coherence between the interferometer measurement and the inertial sensor measurement.
Here, a first identification is performed were the excitation signal is a white noise.
As usual, the data is loaded and any offset is removed.
id = load('identification_noise_opt_iff.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't');
id.d = detrend(id.d, 0);
id.acc_1 = detrend(id.acc_1, 0);
id.acc_2 = detrend(id.acc_2, 0);
id.geo_1 = detrend(id.geo_1, 0);
id.geo_2 = detrend(id.geo_2, 0);
id.f_meas = detrend(id.f_meas, 0);Then the transfer functions from the measured displacement by the interferometer to the generated voltage of the inertial sensors are computed..
Ts = id.t(2) - id.t(1);
win = hann(ceil(10/Ts)); [tf_acc1_est, f] = tfestimate(id.d, id.acc_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_acc1_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.acc_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[tf_acc2_est, ~] = tfestimate(id.d, id.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_acc2_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[tf_geo1_est, ~] = tfestimate(id.d, id.geo_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_geo1_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.geo_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[tf_geo2_est, ~] = tfestimate(id.d, id.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_geo2_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);The same transfer functions are estimated using the Simscape model.
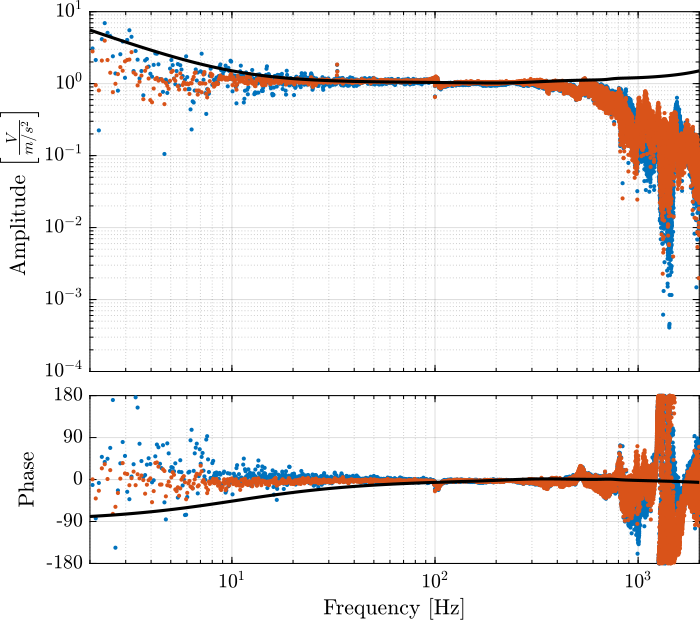
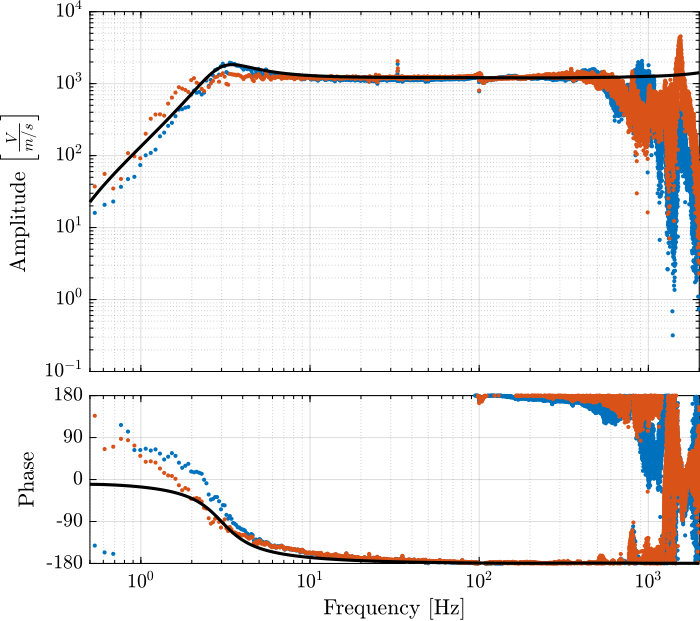
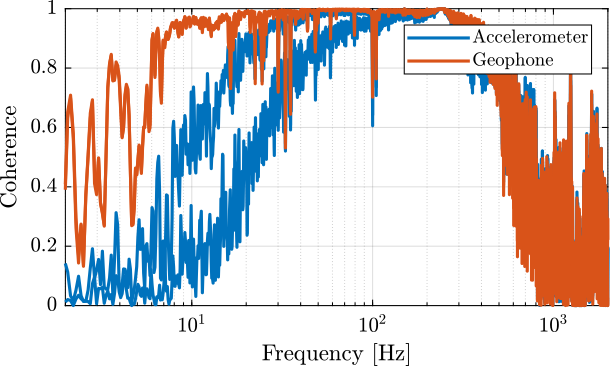
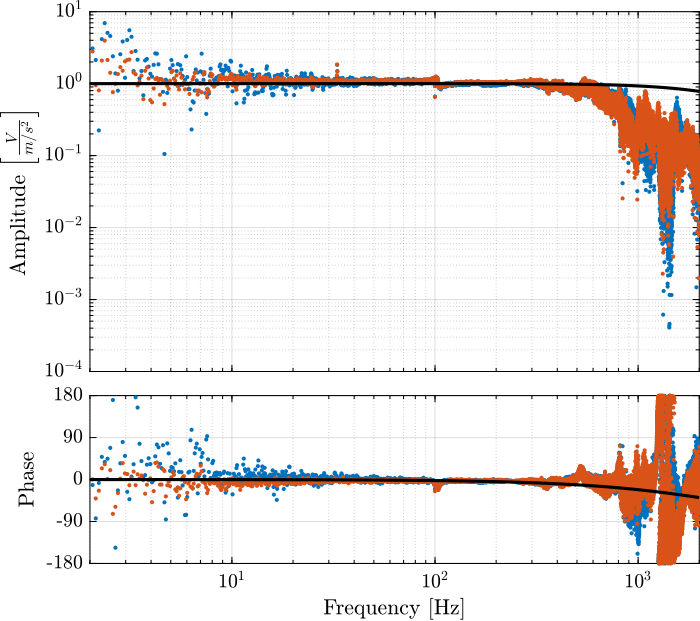
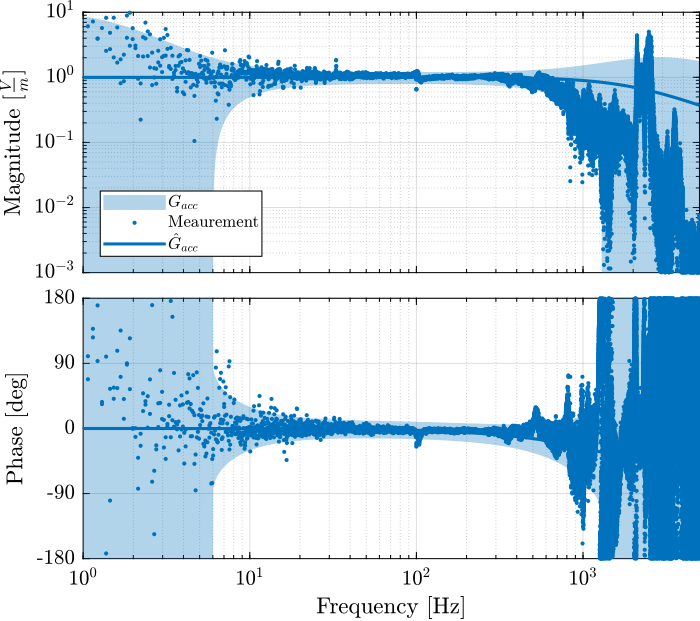
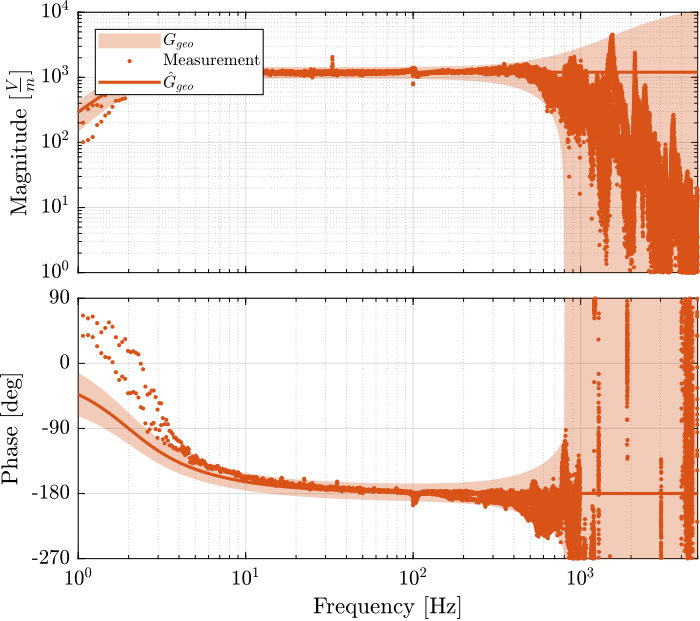
The obtained dynamics of the accelerometer are compared in Figure fig:comp_dynamics_accelerometer while the one of the geophones are compared in Figure fig:comp_dynamics_geophone.
Optimal IFF Development
<<sec:integral_force_feedback>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, a proper identification of the transfer function from the force actuator to the force sensor is performed. Then, an optimal IFF controller is developed and applied experimentally.
The damped system is identified to verified the effectiveness of the added method.
Load Data
The experimental data is loaded and any offset is removed.
id_ol = load('identification_noise_bis.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't'); id_ol.d = detrend(id_ol.d, 0);
id_ol.acc_1 = detrend(id_ol.acc_1, 0);
id_ol.acc_2 = detrend(id_ol.acc_2, 0);
id_ol.geo_1 = detrend(id_ol.geo_1, 0);
id_ol.geo_2 = detrend(id_ol.geo_2, 0);
id_ol.f_meas = detrend(id_ol.f_meas, 0);
id_ol.u = detrend(id_ol.u, 0);Experimental Data
The transfer function from force actuator to force sensors is estimated.
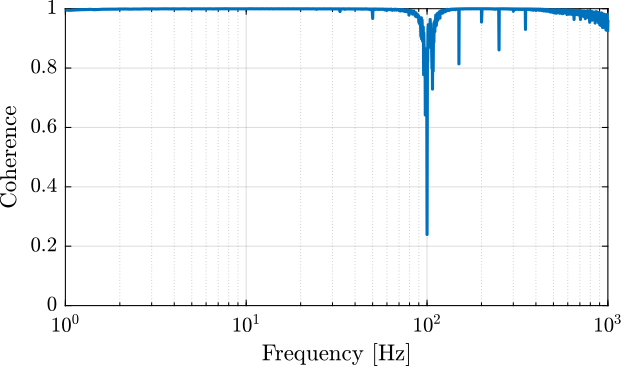
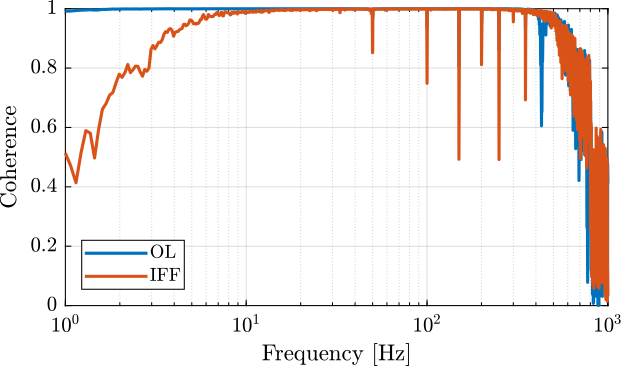
The coherence shown in Figure fig:iff_identification_coh shows that the excitation signal is good enough.
Ts = id_ol.t(2) - id_ol.t(1);
win = hann(ceil(10/Ts)); [tf_fmeas_est, f] = tfestimate(id_ol.u, id_ol.f_meas, win, [], [], 1/Ts); % [V/m]
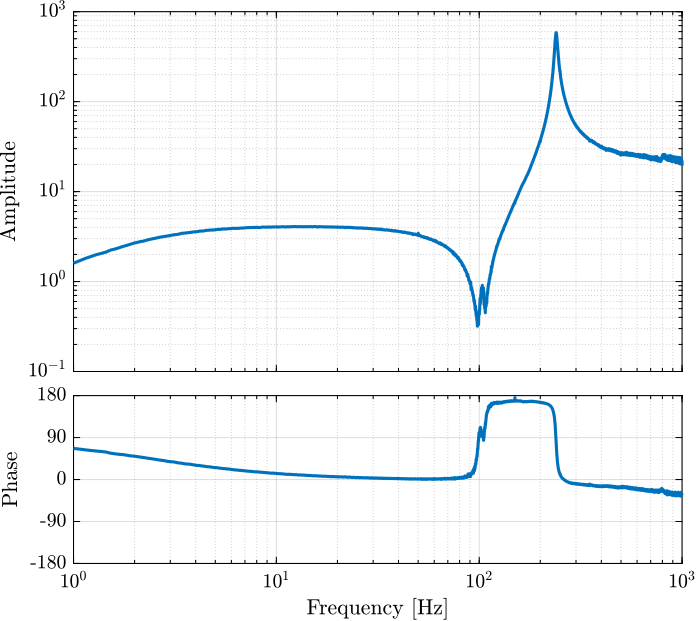
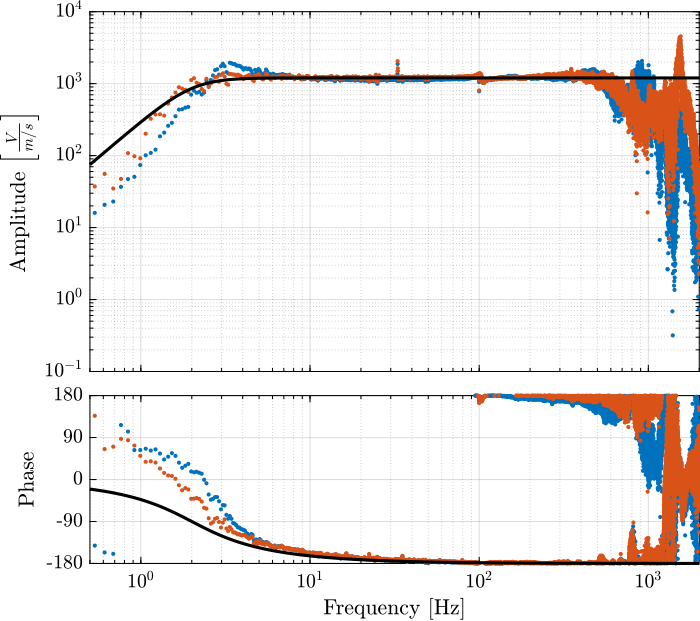
[co_fmeas_est, ~] = mscohere( id_ol.u, id_ol.f_meas, win, [], [], 1/Ts);The obtained dynamics is shown in Figure fig:iff_identification_bode_plot.
Model of the IFF Plant
In order to plot the root locus for the IFF control strategy, a model of the identified plant is developed.
It consists of several poles and zeros are shown below.
wz = 2*pi*102;
xi_z = 0.01;
wp = 2*pi*239.4;
xi_p = 0.015;
Giff = 2.2*(s^2 + 2*xi_z*s*wz + wz^2)/(s^2 + 2*xi_p*s*wp + wp^2) * ... % Dynamics
10*(s/3/pi/(1 + s/3/pi)) * ... % Low pass filter and gain of the voltage amplifier
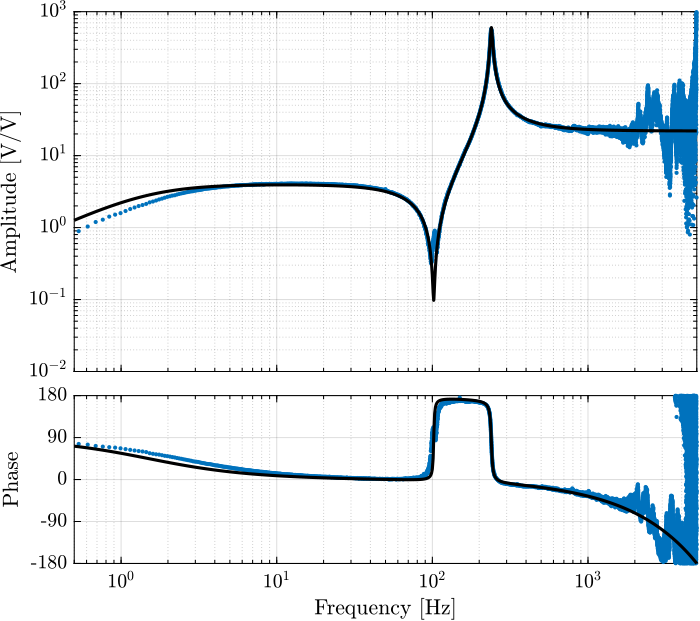
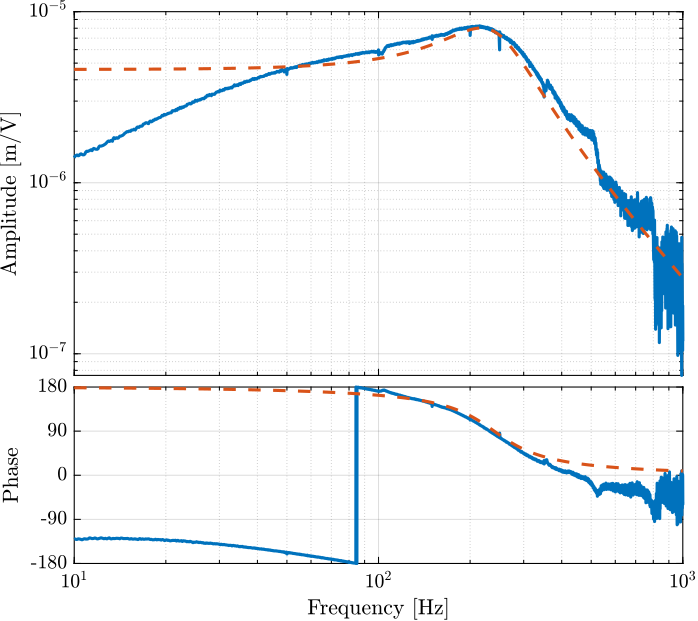
exp(-Ts*s); % Time delay induced by ADC/DACThe comparison of the identified dynamics and the developed model is done in Figure fig:iff_plant_model.
Root Locus and optimal Controller
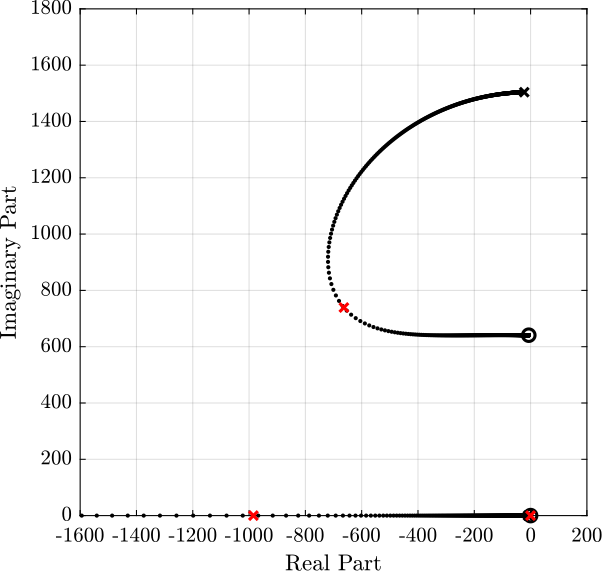
Now, the root locus for the Integral Force Feedback strategy is computed and shown in Figure fig:iff_root_locus.
Note that the controller used is not a pure integrator but rather a first order low pass filter with a cut-off frequency set at 2Hz.
The controller that yield maximum damping (shown by the red cross in Figure fig:iff_root_locus) is:
Kiff_opt = 102/(s + 2*pi*2);Verification of the achievable damping
A new identification is performed with the IFF control strategy applied to the system.
Data is loaded and offset removed.
id_cl = load('identification_noise_iff_bis.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't'); id_cl.d = detrend(id_cl.d, 0);
id_cl.acc_1 = detrend(id_cl.acc_1, 0);
id_cl.acc_2 = detrend(id_cl.acc_2, 0);
id_cl.geo_1 = detrend(id_cl.geo_1, 0);
id_cl.geo_2 = detrend(id_cl.geo_2, 0);
id_cl.f_meas = detrend(id_cl.f_meas, 0);
id_cl.u = detrend(id_cl.u, 0);The open-loop and closed-loop dynamics are estimated.
[tf_G_ol_est, f] = tfestimate(id_ol.u, id_ol.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_G_ol_est, ~] = mscohere( id_ol.u, id_ol.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[tf_G_cl_est, ~] = tfestimate(id_cl.u, id_cl.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_G_cl_est, ~] = mscohere( id_cl.u, id_cl.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);The obtained coherence is shown in Figure fig:Gd_identification_iff_coherence and the dynamics in Figure fig:Gd_identification_iff_bode_plot.
Generate the excitation signal
<<sec:optimal_excitation>>
Introduction ignore
In order to properly estimate the dynamics of the inertial sensor, the excitation signal must be properly chosen.
The requirements on the excitation signal is:
- General much larger motion that the measured motion during the huddle test
- Don't damage the actuator
To determine the perfect voltage signal to be generated, we need two things:
- the transfer function from voltage to mass displacement
- the PSD of the measured motion by the inertial sensors
- not saturate the sensor signals
- provide enough signal/noise ratio (good coherence) in the frequency band of interest (~0.5Hz to 3kHz)
Transfer function from excitation signal to displacement
Let's first estimate the transfer function from the excitation signal in [V] to the generated displacement in [m] as measured by the inteferometer.
id_cl = load('identification_noise_iff_bis.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't'); Ts = id_cl.t(2) - id_cl.t(1);
win = hann(ceil(10/Ts)); [tf_G_cl_est, f] = tfestimate(id_cl.u, id_cl.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_G_cl_est, ~] = mscohere( id_cl.u, id_cl.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);Approximate transfer function from voltage output to generated displacement when IFF is used, in [m/V].
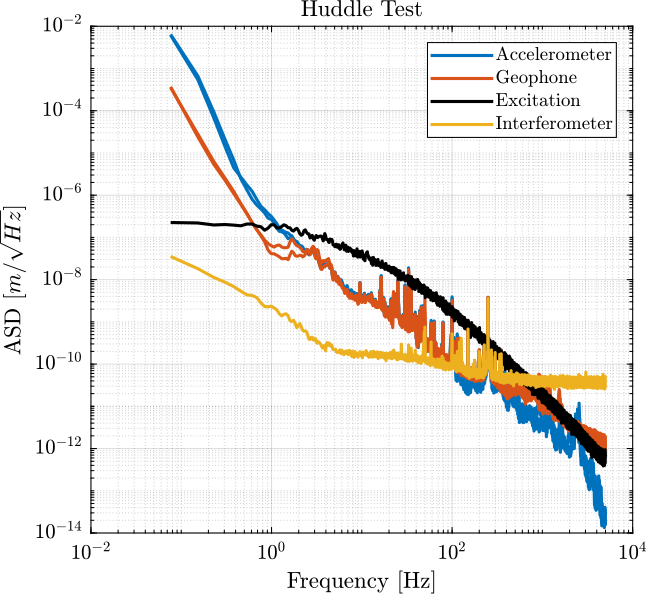
G_d_est = -5e-6*(2*pi*230)^2/(s^2 + 2*0.3*2*pi*240*s + (2*pi*240)^2);Motion measured during Huddle test
We now compute the PSD of the measured motion by the inertial sensors during the huddle test.
ht = load('huddle_test.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't');
ht.d = detrend(ht.d, 0);
ht.acc_1 = detrend(ht.acc_1, 0);
ht.acc_2 = detrend(ht.acc_2, 0);
ht.geo_1 = detrend(ht.geo_1, 0);
ht.geo_2 = detrend(ht.geo_2, 0); [p_d, f] = pwelch(ht.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_acc1, ~] = pwelch(ht.acc_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_acc2, ~] = pwelch(ht.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_geo1, ~] = pwelch(ht.geo_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_geo2, ~] = pwelch(ht.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);Using an estimated model of the sensor dynamics from the documentation of the sensors, we can compute the ASD of the motion in $m/\sqrt{Hz}$ measured by the sensors.
G_acc = 1/(1 + s/2/pi/2500); % [V/(m/s2)]
G_geo = -120*s^2/(s^2 + 2*0.7*2*pi*2*s + (2*pi*2)^2); % [V/(m/s)]From the ASD of the motion measured by the sensors, we can create an excitation signal that will generate much motion motion that the motion under no excitation.
We create G_exc that corresponds to the wanted generated motion.
G_exc = 0.2e-6/(1 + s/2/pi/2)/(1 + s/2/pi/50);
And we create a time domain signal y_d that have the spectral density described by G_exc.
Fs = 1/Ts;
t = 0:Ts:180; % Time Vector [s]
u = sqrt(Fs/2)*randn(length(t), 1); % Signal with an ASD equal to one
y_d = lsim(G_exc, u, t); [pxx, ~] = pwelch(y_d, win, 0, [], Fs);We can now generate the voltage signal that will generate the wanted motion.
y_v = lsim(G_exc * ... % from unit PSD to shaped PSD
(1 + s/2/pi/50) * ... % Inverse of pre-filter included in the Simulink file
1/G_d_est * ... % Wanted displacement => required voltage
1/(1 + s/2/pi/5e3), ... % Add some high frequency filtering
u, t);Identification of the Inertial Sensors Dynamics
<<sec:inertial_sensor_dynamics>>
Introduction ignore
Using the excitation signal generated in Section sec:optimal_excitation, the dynamics of the inertial sensors are identified.
Load Data
Both the measurement data during the identification test and during an "huddle test" are loaded.
id = load('identification_noise_opt_iff.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't');
ht = load('huddle_test.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't'); ht.d = detrend(ht.d, 0);
ht.acc_1 = detrend(ht.acc_1, 0);
ht.acc_2 = detrend(ht.acc_2, 0);
ht.geo_1 = detrend(ht.geo_1, 0);
ht.geo_2 = detrend(ht.geo_2, 0);
ht.f_meas = detrend(ht.f_meas, 0); id.d = detrend(id.d, 0);
id.acc_1 = detrend(id.acc_1, 0);
id.acc_2 = detrend(id.acc_2, 0);
id.geo_1 = detrend(id.geo_1, 0);
id.geo_2 = detrend(id.geo_2, 0);
id.f_meas = detrend(id.f_meas, 0);Compare PSD during Huddle and and during identification
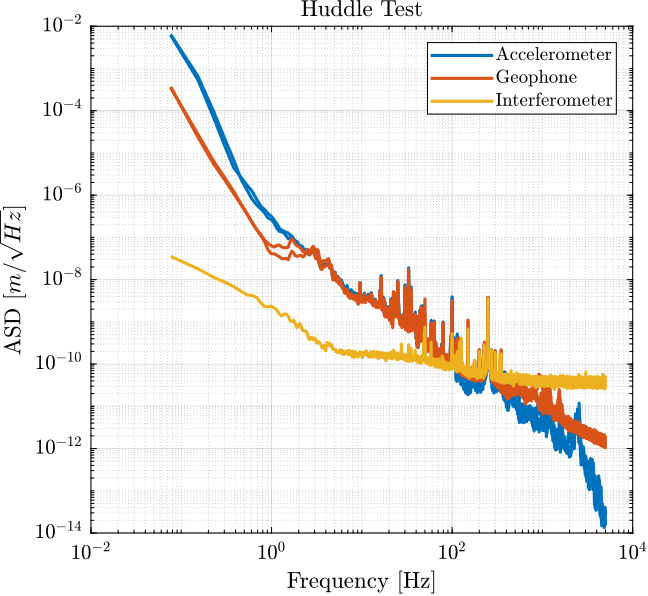
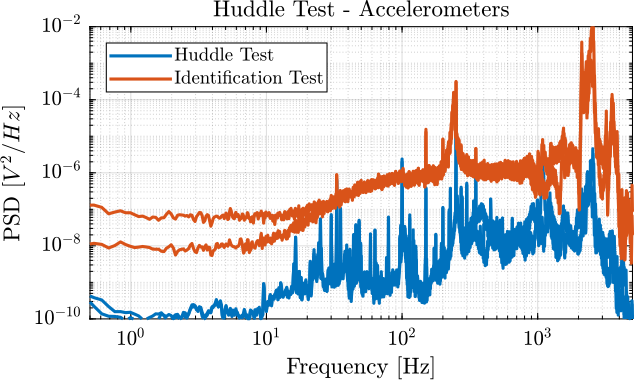
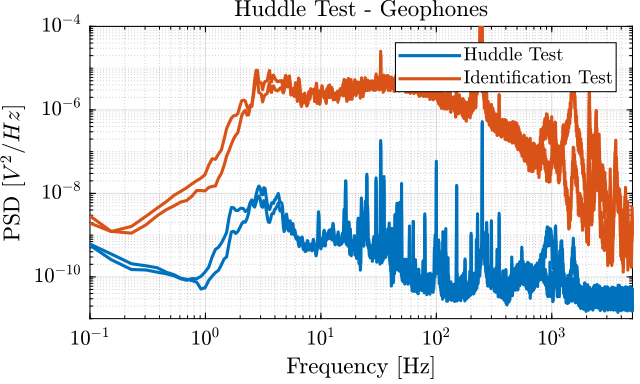
The Power Spectral Density of the measured motion during the huddle test and during the identification test are compared in Figures fig:comp_psd_huddle_test_identification_acc and fig:comp_psd_huddle_test_identification_geo.
Ts = ht.t(2) - ht.t(1);
win = hann(ceil(10/Ts)); [p_id_d, f] = pwelch(id.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_id_acc1, ~] = pwelch(id.acc_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_id_acc2, ~] = pwelch(id.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_id_geo1, ~] = pwelch(id.geo_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_id_geo2, ~] = pwelch(id.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [p_ht_d, ~] = pwelch(ht.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_ht_acc1, ~] = pwelch(ht.acc_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_ht_acc2, ~] = pwelch(ht.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_ht_geo1, ~] = pwelch(ht.geo_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_ht_geo2, ~] = pwelch(ht.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_ht_fmeas, ~] = pwelch(ht.f_meas, win, [], [], 1/Ts);Compute transfer functions
The transfer functions from the motion as measured by the interferometer (and that should represent the absolute motion of the mass) to the inertial sensors are estimated:
[tf_acc1_est, f] = tfestimate(id.d, id.acc_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_acc1_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.acc_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[tf_acc2_est, ~] = tfestimate(id.d, id.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_acc2_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[tf_geo1_est, ~] = tfestimate(id.d, id.geo_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_geo1_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.geo_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[tf_geo2_est, ~] = tfestimate(id.d, id.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_geo2_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);The obtained coherence are shown in Figure fig:id_sensor_dynamics_coherence.
We also make a simplified model of the inertial sensors to be compared with the identified dynamics.
G_acc = 1/(1 + s/2/pi/2500); % [V/(m/s2)]
G_geo = -1200*s^2/(s^2 + 2*0.7*2*pi*2*s + (2*pi*2)^2); % [[V/(m/s)]The model and identified dynamics show good agreement (Figures fig:id_sensor_dynamics_accelerometers and fig:id_sensor_dynamics_geophones.)
Inertial Sensor Noise and the $\mathcal{H}_2$ Synthesis of complementary filters
<<sec:inertial_sensor_noise>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, the noise of the inertial sensors (geophones and accelerometers) is estimated.
Load Data
As before, the identification data is loaded and any offset if removed.
id = load('identification_noise_opt_iff.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't'); id.d = detrend(id.d, 0);
id.acc_1 = detrend(id.acc_1, 0);
id.acc_2 = detrend(id.acc_2, 0);
id.geo_1 = detrend(id.geo_1, 0);
id.geo_2 = detrend(id.geo_2, 0);
id.f_meas = detrend(id.f_meas, 0);ASD of the Measured displacement
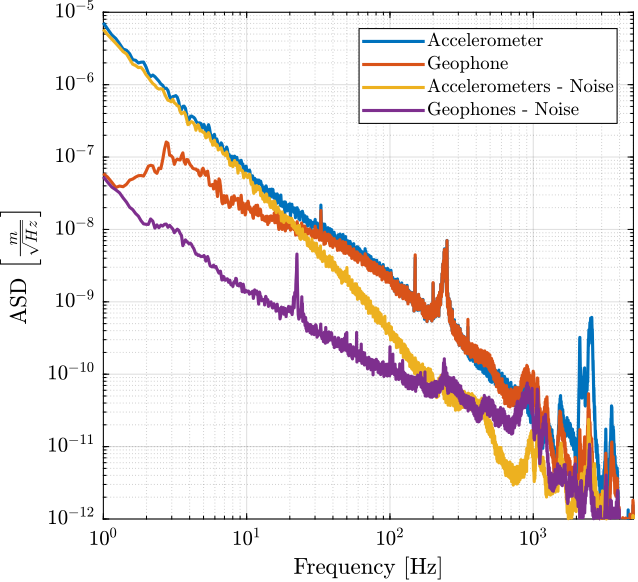
The Power Spectral Density of the displacement as measured by the interferometer and the inertial sensors is computed.
Ts = id.t(2) - id.t(1);
win = hann(ceil(10/Ts)); [p_id_d, f] = pwelch(id.d, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_id_acc1, ~] = pwelch(id.acc_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_id_acc2, ~] = pwelch(id.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_id_geo1, ~] = pwelch(id.geo_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[p_id_geo2, ~] = pwelch(id.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);Let's use a model of the accelerometer and geophone to compute the motion from the measured voltage.
G_acc = 1/(1 + s/2/pi/2500); % [V/(m/s2)]
G_geo = -1200*s^2/(s^2 + 2*0.7*2*pi*2*s + (2*pi*2)^2); % [[V/(m/s)]The obtained ASD in $m/\sqrt{Hz}$ is shown in Figure fig:measure_displacement_all_sensors.
ASD of the Sensor Noise
The noise of a sensor can be estimated using two identical sensors by computing:
- the Power Spectral Density of the measured motion by the two sensors
- the Cross Spectral Density between the two sensors (coherence)
This technique to estimate the sensor noise is described in cite:barzilai98_techn_measur_noise_sensor_presen.
The Power Spectral Density of the sensor noise can be estimated using the following equation:
\begin{equation} |S_n(\omega)| = |S_{x_1}(\omega)| \Big( 1 - \gamma_{x_1 x_2}(\omega) \Big) \end{equation}with $S_{x_1}$ the PSD of one of the sensor and $\gamma_{x_1 x_2}$ the coherence between the two sensors.
The coherence between the two accelerometers and between the two geophones is computed.
[coh_acc, ~] = mscohere(id.acc_1, id.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[coh_geo, ~] = mscohere(id.geo_1, id.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);Finally, the Power Spectral Density of the sensors is computed and converted in $[m^2/Hz]$.
pN_acc = p_id_acc1.*(1 - coh_acc) .* ... % [V^2/Hz]
1./abs(squeeze(freqresp(G_acc*s^2, f, 'Hz'))).^2; % [(m/V)^2]
pN_geo = p_id_geo1.*(1 - coh_geo) .* ... % [V^2/Hz]
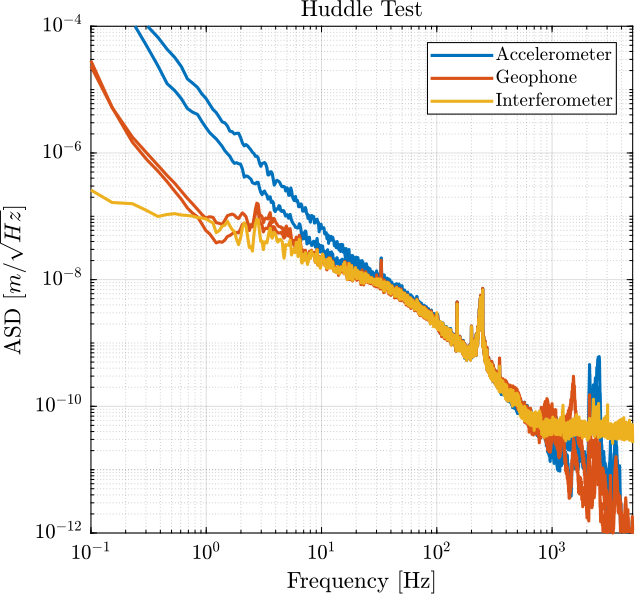
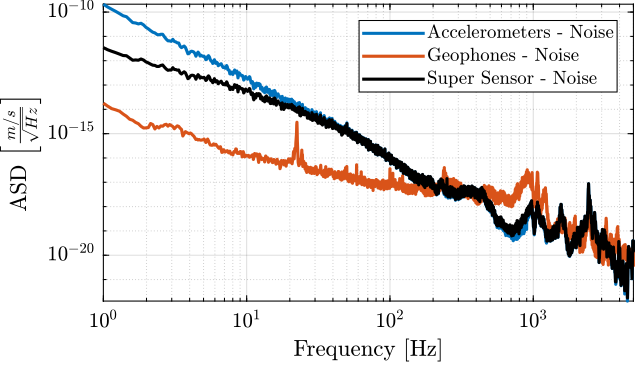
1./abs(squeeze(freqresp(G_geo*s, f, 'Hz'))).^2; % [(m/V)^2]The ASD of obtained noises are compared with the ASD of the measured signals in Figure fig:noise_inertial_sensors_comparison.
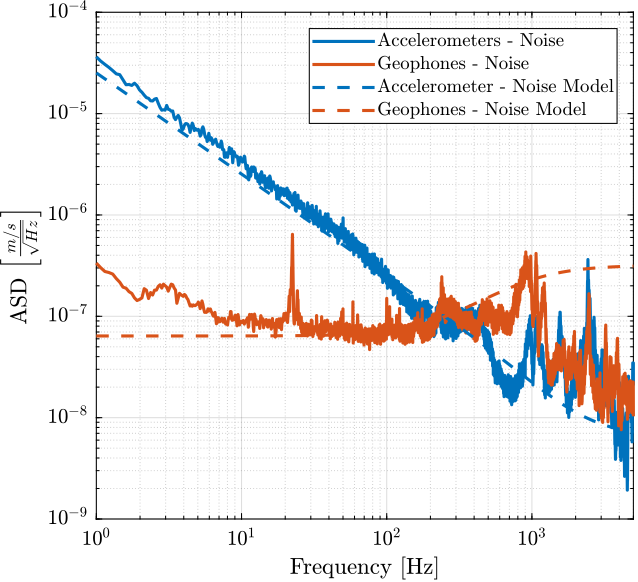
Noise Model
Transfer functions are adjusted in order to fit the ASD of the sensor noises (expressed in $[m/s/\sqrt{Hz}]$ for more easy fitting).
These transfer functions are defined below and compared with the measured ASD in Figure fig:noise_models_velocity.
N_acc = 1*(s/(2*pi*2000) + 1)^2/(s + 0.1*2*pi)/(s + 1e3*2*pi); % [m/sqrt(Hz)]
N_geo = 4e-4*(s/(2*pi*200) + 1)/(s + 1e3*2*pi); % [m/sqrt(Hz)]$\mathcal{H}_2$ Synthesis of the Complementary Filters
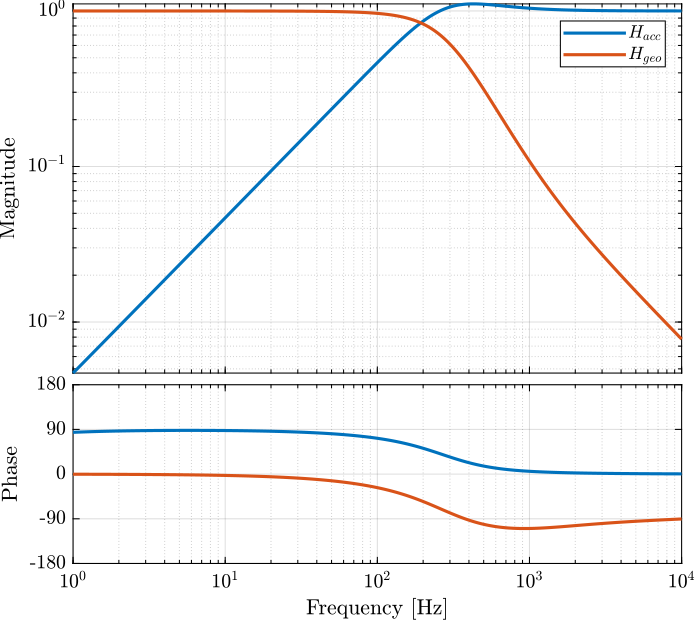
We now wish to synthesize two complementary filters to merge the geophone and the accelerometer signal in such a way that the fused signal has the lowest possible RMS noise.
To do so, we use the $\mathcal{H}_2$ synthesis where the transfer functions representing the noise density of both sensors are used as weights.
The generalized plant used for the synthesis is defined below.
P = [0 N_acc 1;
N_geo -N_acc 0];
And the $\mathcal{H}_2$ synthesis is done using the h2syn command.
[H_geo, ~, gamma] = h2syn(P, 1, 1);
H_acc = 1 - H_geo;The obtained complementary filters are shown in Figure fig:complementary_filters_velocity_H2.
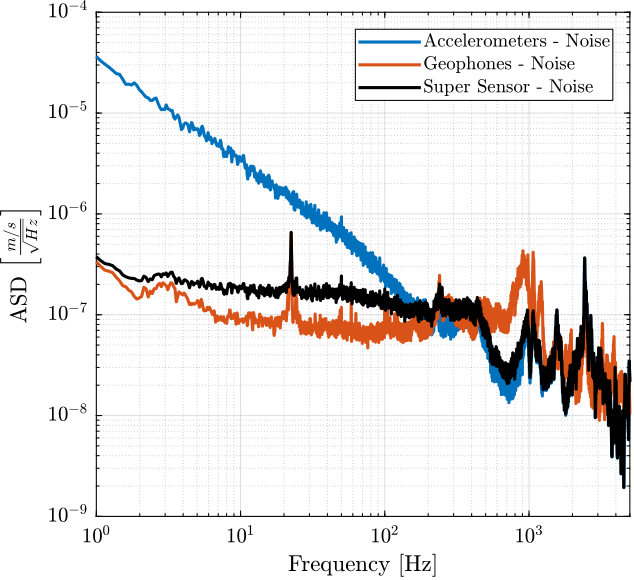
Results
Finally, the signals of both sensors are merged using the complementary filters and the super sensor noise is estimated and compared with the individual sensor noises in Figure fig:super_sensor_noise_asd_velocity.
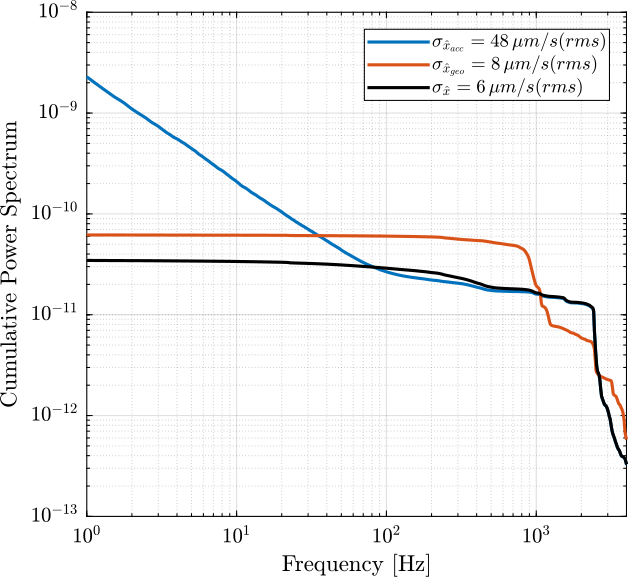
Finally, the Cumulative Power Spectrum is computed and compared in Figure fig:super_sensor_noise_cas_velocity.
[~, i_1Hz] = min(abs(f - 1)); CPS_acc = 1/pi*flip(-cumtrapz(2*pi*flip(f), flip((pN_acc.*(2*pi*f)).^2)));
CPS_geo = 1/pi*flip(-cumtrapz(2*pi*flip(f), flip((pN_geo.*(2*pi*f)).^2)));
CPS_SS = 1/pi*flip(-cumtrapz(2*pi*flip(f), flip((pN_acc.*(2*pi*f)).^2.*abs(squeeze(freqresp(H_acc, f, 'Hz'))).^2 + (pN_geo.*(2*pi*f)).^2.*abs(squeeze(freqresp(H_geo, f, 'Hz'))).^2)));Inertial Sensor Dynamics Uncertainty and the $\mathcal{H}_\infty$ Synthesis of complementary filters
<<sec:inertial_sensor_uncertainty>>
Introduction ignore
When merging two sensors, it is important to be sure that we correctly know the sensor dynamics near the merging frequency. Thus, identifying the uncertainty on the sensor dynamics is quite important to perform a robust merging.
Load Data
Data is loaded and offset is removed.
id = load('identification_noise_opt_iff.mat', 'd', 'acc_1', 'acc_2', 'geo_1', 'geo_2', 'f_meas', 'u', 't'); id.d = detrend(id.d, 0);
id.acc_1 = detrend(id.acc_1, 0);
id.acc_2 = detrend(id.acc_2, 0);
id.geo_1 = detrend(id.geo_1, 0);
id.geo_2 = detrend(id.geo_2, 0);
id.f_meas = detrend(id.f_meas, 0);Compute the dynamics of both sensors
The dynamics of inertial sensors are estimated (in $[V/m]$).
Ts = id.t(2) - id.t(1);
win = hann(ceil(10/Ts)); [tf_acc1_est, f] = tfestimate(id.d, id.acc_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_acc1_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.acc_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[tf_acc2_est, ~] = tfestimate(id.d, id.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_acc2_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.acc_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[tf_geo1_est, ~] = tfestimate(id.d, id.geo_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_geo1_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.geo_1, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[tf_geo2_est, ~] = tfestimate(id.d, id.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
[co_geo2_est, ~] = mscohere( id.d, id.geo_2, win, [], [], 1/Ts);The (nominal) models of the inertial sensors from the absolute displacement to the generated voltage are defined below:
G_acc = 1/(1 + s/2/pi/2000)
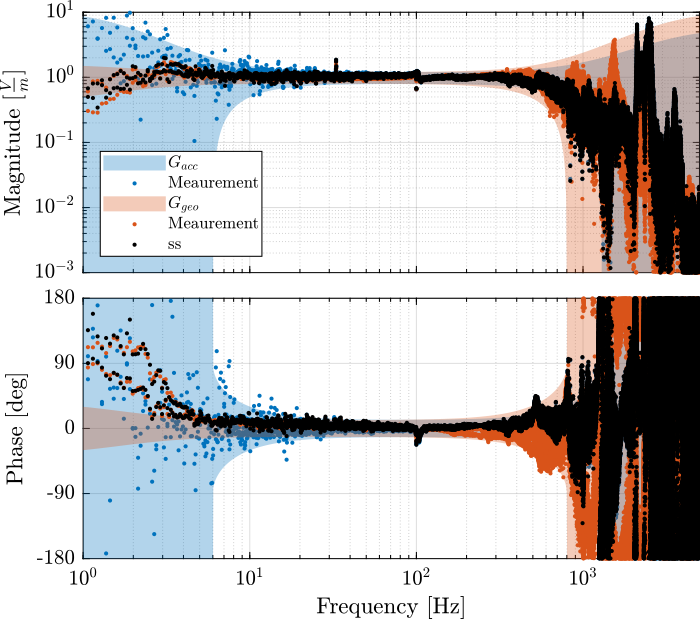
G_geo = -1200*s^2/(s^2 + 2*0.7*2*pi*2*s + (2*pi*2)^2);These models are very simplistic models, and we then take into account the un-modelled dynamics with dynamical uncertainty.
Dynamics uncertainty estimation
Weights representing the dynamical uncertainty of the sensors are defined below.
w_acc = createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 10, 'G1', 0.2, 'Gc', 1, 'w0', 6*2*pi) * ...
createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 1, 'G1', 5/0.2, 'Gc', 1/0.2, 'w0', 1300*2*pi);
w_geo = createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 0.6, 'G1', 0.2, 'Gc', 0.3, 'w0', 3*2*pi) * ...
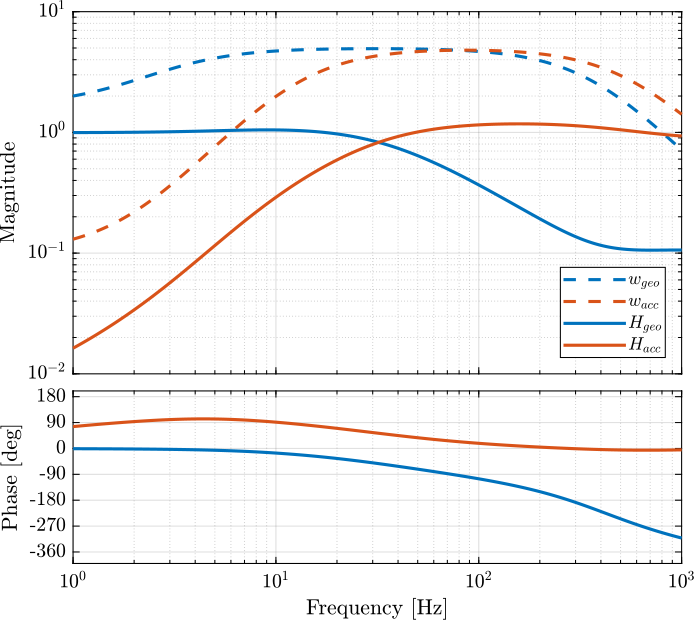
createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 1, 'G1', 10/0.2, 'Gc', 1/0.2, 'w0', 800*2*pi);The measured dynamics are compared with the modelled one as well as the modelled uncertainty in Figure fig:dyn_uncertainty_acc for the accelerometers and in Figure fig:dyn_uncertainty_geo for the geophones.
$\mathcal{H}_\infty$ Synthesis of Complementary Filters
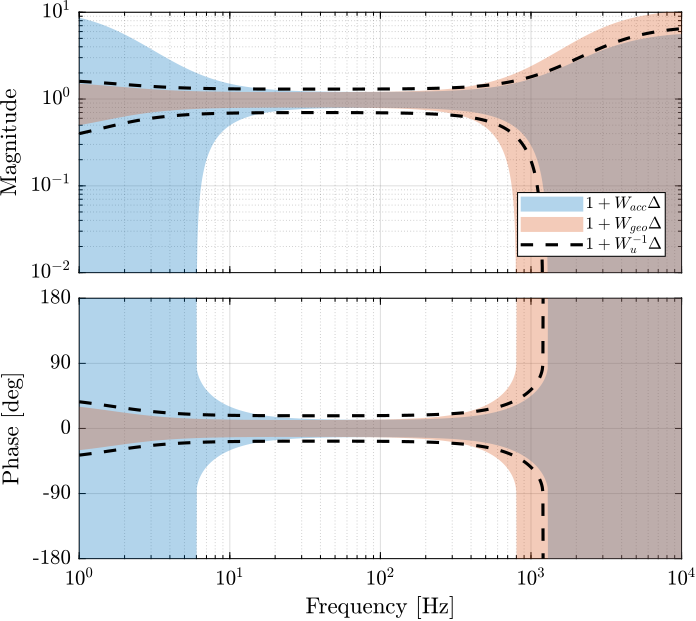
A last weight is now defined that represents the maximum dynamical uncertainty that is allowed for the super sensor.
wu = inv(createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 0.7, 'G1', 0.3, 'Gc', 0.4, 'w0', 3*2*pi) * ...
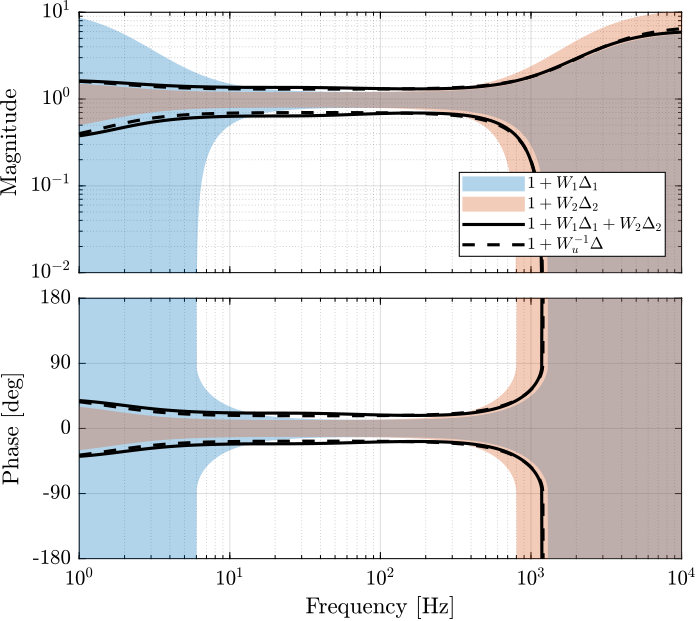
createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 1, 'G1', 6/0.3, 'Gc', 1/0.3, 'w0', 1200*2*pi));This dynamical uncertainty is compared with the two sensor uncertainties in Figure fig:uncertainty_weight_and_sensor_uncertainties.
The generalized plant used for the synthesis is defined:
P = [wu*w_acc -wu*w_acc;
0 wu*w_geo;
1 0];
And the $\mathcal{H}_\infty$ synthesis using the hinfsyn command is performed.
[H_geo, ~, gamma, ~] = hinfsyn(P, 1, 1,'TOLGAM', 0.001, 'METHOD', 'ric', 'DISPLAY', 'on'); Test bounds: 0.8556 <= gamma <= 1.34
gamma X>=0 Y>=0 rho(XY)<1 p/f
1.071e+00 0.0e+00 0.0e+00 0.000e+00 p
9.571e-01 0.0e+00 0.0e+00 9.436e-16 p
9.049e-01 0.0e+00 0.0e+00 1.084e-15 p
8.799e-01 0.0e+00 0.0e+00 1.191e-16 p
8.677e-01 0.0e+00 0.0e+00 6.905e-15 p
8.616e-01 0.0e+00 0.0e+00 0.000e+00 p
8.586e-01 1.1e-17 0.0e+00 6.917e-16 p
8.571e-01 0.0e+00 0.0e+00 6.991e-17 p
8.564e-01 0.0e+00 0.0e+00 1.492e-16 p
Best performance (actual): 0.8563
The complementary filter is defined as follows:
H_acc = 1 - H_geo;The bode plot of the obtained complementary filters is shown in Figure
Obtained Super Sensor Dynamical Uncertainty
The obtained super sensor dynamical uncertainty is shown in Figure fig:super_sensor_uncertainty_h_infinity.
Optimal and Robust sensor fusion using the $\mathcal{H}_2/\mathcal{H}_\infty$ synthesis
<<sec:optimal_sensor_fusion>>
Introduction ignore
Noise and Dynamical uncertainty weights
N_acc = (s/(2*pi*2000) + 1)^2/(s + 0.1*2*pi)/(s + 1e3*2*pi)/(1 + s/2/pi/1e3); % [m/sqrt(Hz)]
N_geo = 4e-4*((s + 2*pi)/(2*pi*200) + 1)/(s + 1e3*2*pi)/(1 + s/2/pi/1e3); % [m/sqrt(Hz)] w_acc = createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 10, 'G1', 0.2, 'Gc', 1, 'w0', 6*2*pi) * ...
createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 1, 'G1', 5/0.2, 'Gc', 1/0.2, 'w0', 1300*2*pi);
w_geo = createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 0.6, 'G1', 0.2, 'Gc', 0.3, 'w0', 3*2*pi) * ...
createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 1, 'G1', 10/0.2, 'Gc', 1/0.2, 'w0', 800*2*pi); wu = inv(createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 0.7, 'G1', 0.3, 'Gc', 0.4, 'w0', 3*2*pi) * ...
createWeight('n', 2, 'G0', 1, 'G1', 6/0.3, 'Gc', 1/0.3, 'w0', 1200*2*pi)); P = [wu*w_acc -wu*w_acc;
0 wu*w_geo;
N_acc -N_acc;
0 N_geo;
1 0];And the mixed $\mathcal{H}_2/\mathcal{H}_\infty$ synthesis is performed.
[H_geo, ~] = h2hinfsyn(ss(P), 1, 1, 2, [0, 1], 'HINFMAX', 1, 'H2MAX', Inf, 'DKMAX', 100, 'TOL', 1e-3, 'DISPLAY', 'on'); H_acc = 1 - H_geo;Obtained Super Sensor Noise
freqs = logspace(0, 4, 1000);
PSD_Sgeo = abs(squeeze(freqresp(N_geo, freqs, 'Hz'))).^2;
PSD_Sacc = abs(squeeze(freqresp(N_acc, freqs, 'Hz'))).^2;
PSD_Hss = abs(squeeze(freqresp(N_acc*H_acc, freqs, 'Hz'))).^2 + ...
abs(squeeze(freqresp(N_geo*H_geo, freqs, 'Hz'))).^2;Obtained Super Sensor Dynamical Uncertainty
Experimental Super Sensor Dynamical Uncertainty
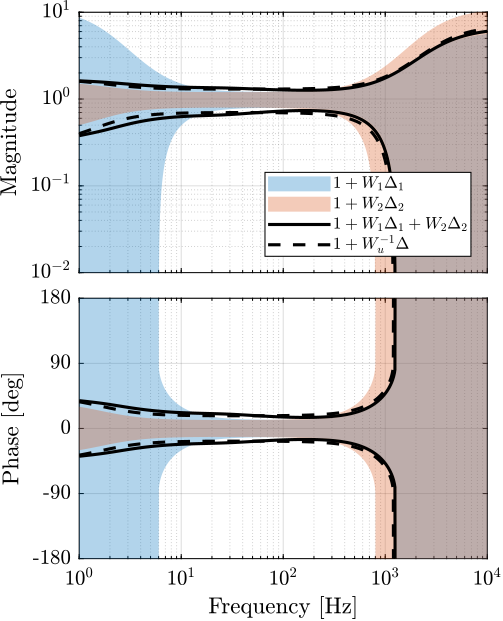
The super sensor dynamics is shown in Figure fig:super_sensor_optimal_uncertainty.
Experimental Super Sensor Noise
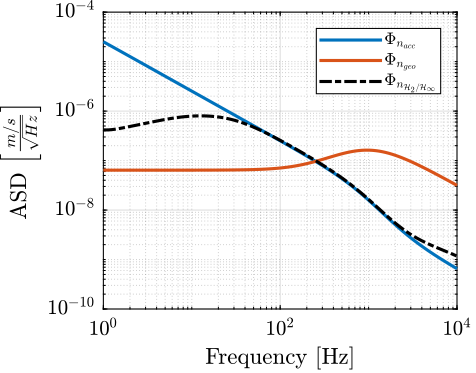
The obtained super sensor noise is shown in Figure fig:super_sensor_optimal_noise.
Matlab Functions
<<sec:matlab_functions>>
createWeight
<<sec:createWeight>>
This Matlab function is accessible here.
function [W] = createWeight(args)
% createWeight -
%
% Syntax: [in_data] = createWeight(in_data)
%
% Inputs:
% - n - Weight Order
% - G0 - Low frequency Gain
% - G1 - High frequency Gain
% - Gc - Gain of W at frequency w0
% - w0 - Frequency at which |W(j w0)| = Gc
%
% Outputs:
% - W - Generated Weight
arguments
args.n (1,1) double {mustBeInteger, mustBePositive} = 1
args.G0 (1,1) double {mustBeNumeric, mustBePositive} = 0.1
args.G1 (1,1) double {mustBeNumeric, mustBePositive} = 10
args.Gc (1,1) double {mustBeNumeric, mustBePositive} = 1
args.w0 (1,1) double {mustBeNumeric, mustBePositive} = 1
end
mustBeBetween(args.G0, args.Gc, args.G1);
s = tf('s');
W = (((1/args.w0)*sqrt((1-(args.G0/args.Gc)^(2/args.n))/(1-(args.Gc/args.G1)^(2/args.n)))*s + (args.G0/args.Gc)^(1/args.n))/((1/args.G1)^(1/args.n)*(1/args.w0)*sqrt((1-(args.G0/args.Gc)^(2/args.n))/(1-(args.Gc/args.G1)^(2/args.n)))*s + (1/args.Gc)^(1/args.n)))^args.n;
end
% Custom validation function
function mustBeBetween(a,b,c)
if ~((a > b && b > c) || (c > b && b > a))
eid = 'createWeight:inputError';
msg = 'Gc should be between G0 and G1.';
throwAsCaller(MException(eid,msg))
end
end
plotMagUncertainty
<<sec:plotMagUncertainty>>
This Matlab function is accessible here.
function [p] = plotMagUncertainty(W, freqs, args)
% plotMagUncertainty -
%
% Syntax: [p] = plotMagUncertainty(W, freqs, args)
%
% Inputs:
% - W - Multiplicative Uncertainty Weight
% - freqs - Frequency Vector [Hz]
% - args - Optional Arguments:
% - G
% - color_i
% - opacity
%
% Outputs:
% - p - Plot Handle
arguments
W
freqs double {mustBeNumeric, mustBeNonnegative}
args.G = tf(1)
args.color_i (1,1) double {mustBeInteger, mustBePositive} = 1
args.opacity (1,1) double {mustBeNumeric, mustBeNonnegative} = 0.3
args.DisplayName char = ''
end
% Get defaults colors
colors = get(groot, 'defaultAxesColorOrder');
p = patch([freqs flip(freqs)], ...
[abs(squeeze(freqresp(args.G, freqs, 'Hz'))).*(1 + abs(squeeze(freqresp(W, freqs, 'Hz')))); ...
flip(abs(squeeze(freqresp(args.G, freqs, 'Hz'))).*max(1 - abs(squeeze(freqresp(W, freqs, 'Hz'))), 1e-6))], 'w', ...
'DisplayName', args.DisplayName);
p.FaceColor = colors(args.color_i, :);
p.EdgeColor = 'none';
p.FaceAlpha = args.opacity;
end
plotPhaseUncertainty
<<sec:plotPhaseUncertainty>>
This Matlab function is accessible here.
function [p] = plotPhaseUncertainty(W, freqs, args)
% plotPhaseUncertainty -
%
% Syntax: [p] = plotPhaseUncertainty(W, freqs, args)
%
% Inputs:
% - W - Multiplicative Uncertainty Weight
% - freqs - Frequency Vector [Hz]
% - args - Optional Arguments:
% - G
% - color_i
% - opacity
%
% Outputs:
% - p - Plot Handle
arguments
W
freqs double {mustBeNumeric, mustBeNonnegative}
args.G = tf(1)
args.color_i (1,1) double {mustBeInteger, mustBePositive} = 1
args.opacity (1,1) double {mustBeNumeric, mustBePositive} = 0.3
args.DisplayName char = ''
end
% Get defaults colors
colors = get(groot, 'defaultAxesColorOrder');
% Compute Phase Uncertainty
Dphi = 180/pi*asin(abs(squeeze(freqresp(W, freqs, 'Hz'))));
Dphi(abs(squeeze(freqresp(W, freqs, 'Hz'))) > 1) = 360;
% Compute Plant Phase
G_ang = 180/pi*angle(squeeze(freqresp(args.G, freqs, 'Hz')));
p = patch([freqs flip(freqs)], [G_ang+Dphi; flip(G_ang-Dphi)], 'w', ...
'DisplayName', args.DisplayName);
p.FaceColor = colors(args.color_i, :);
p.EdgeColor = 'none';
p.FaceAlpha = args.opacity;
endBibliography ignore
bibliography:ref.bib