256 KiB
Nano-Hexapod - Test Bench
- Introduction
- Mounting Procedure
- Encoders fixed to the plates
- Decentralized High Authority Control with Integral Force Feedback
- Bibliography
This report is also available as a pdf.
Introduction ignore
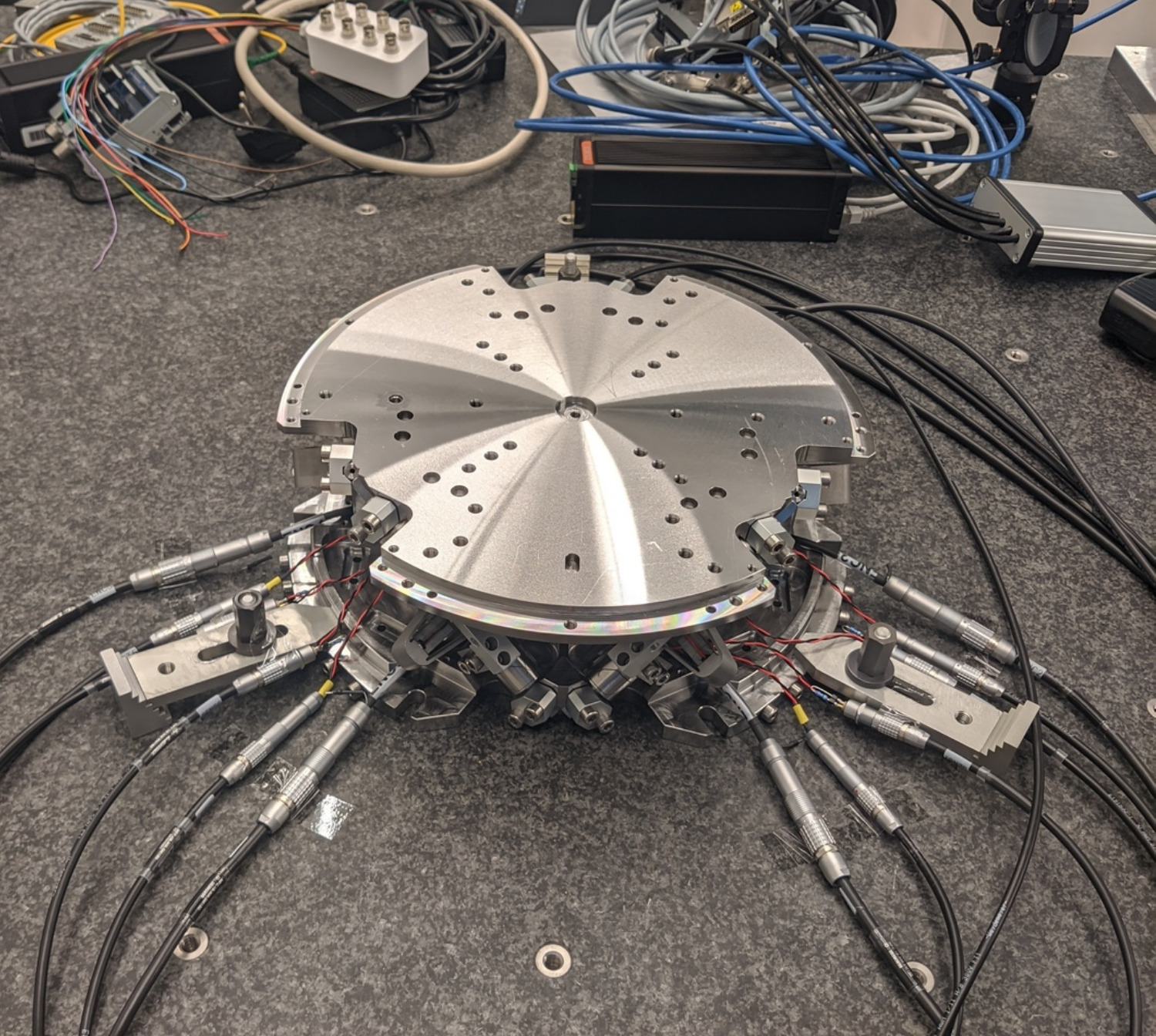
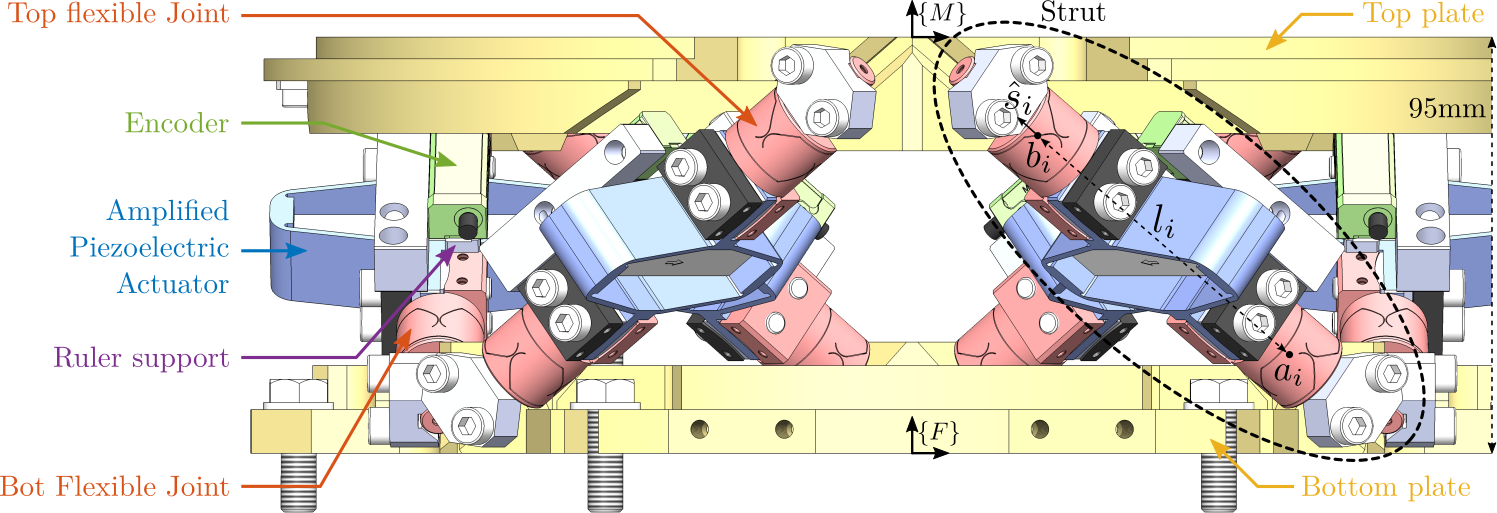
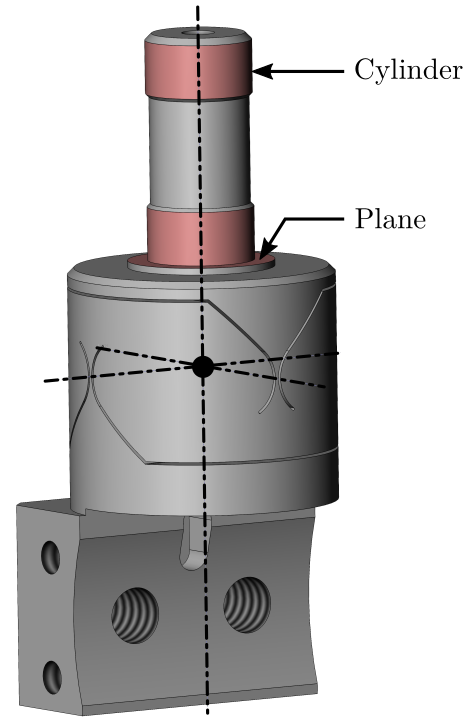
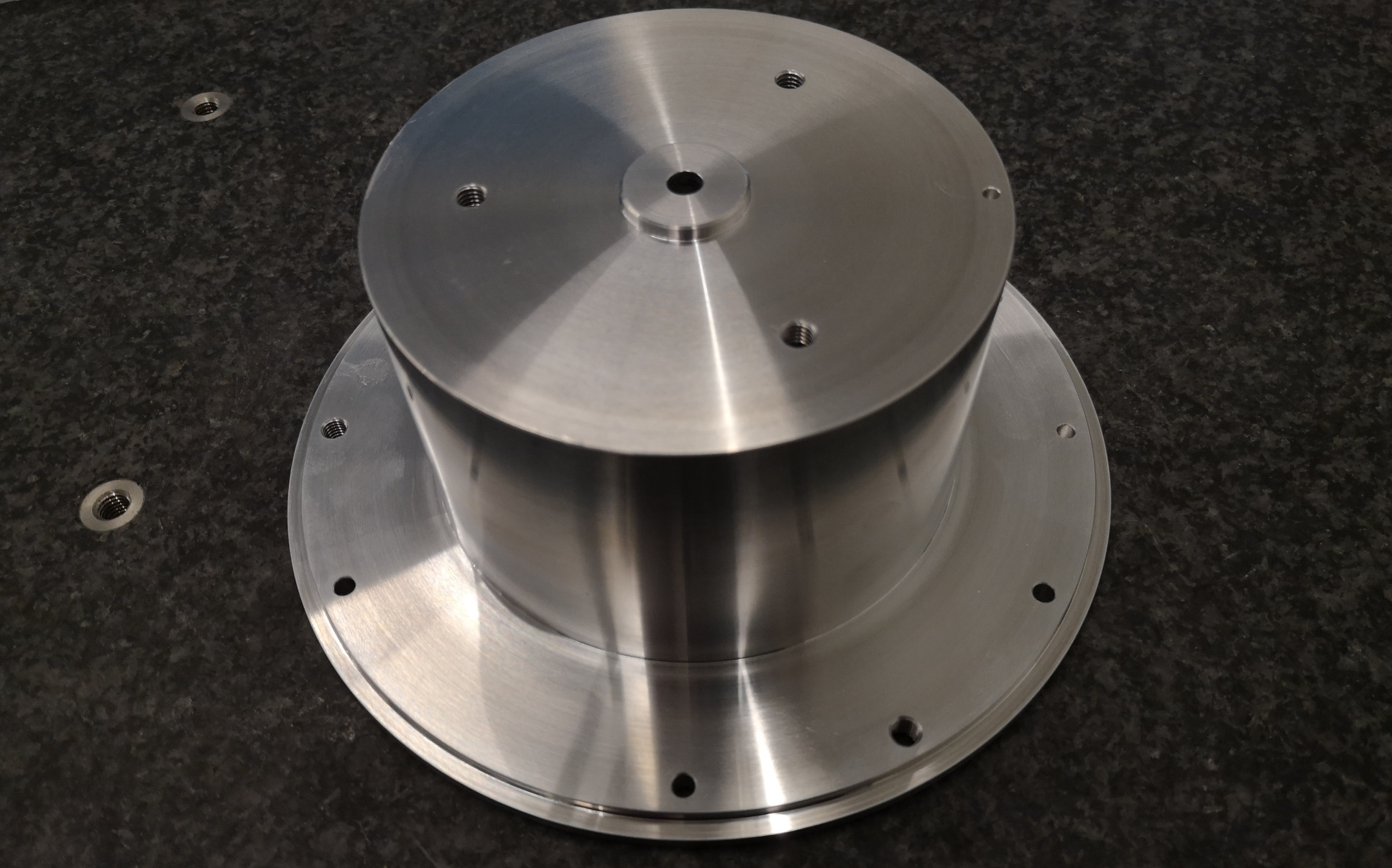
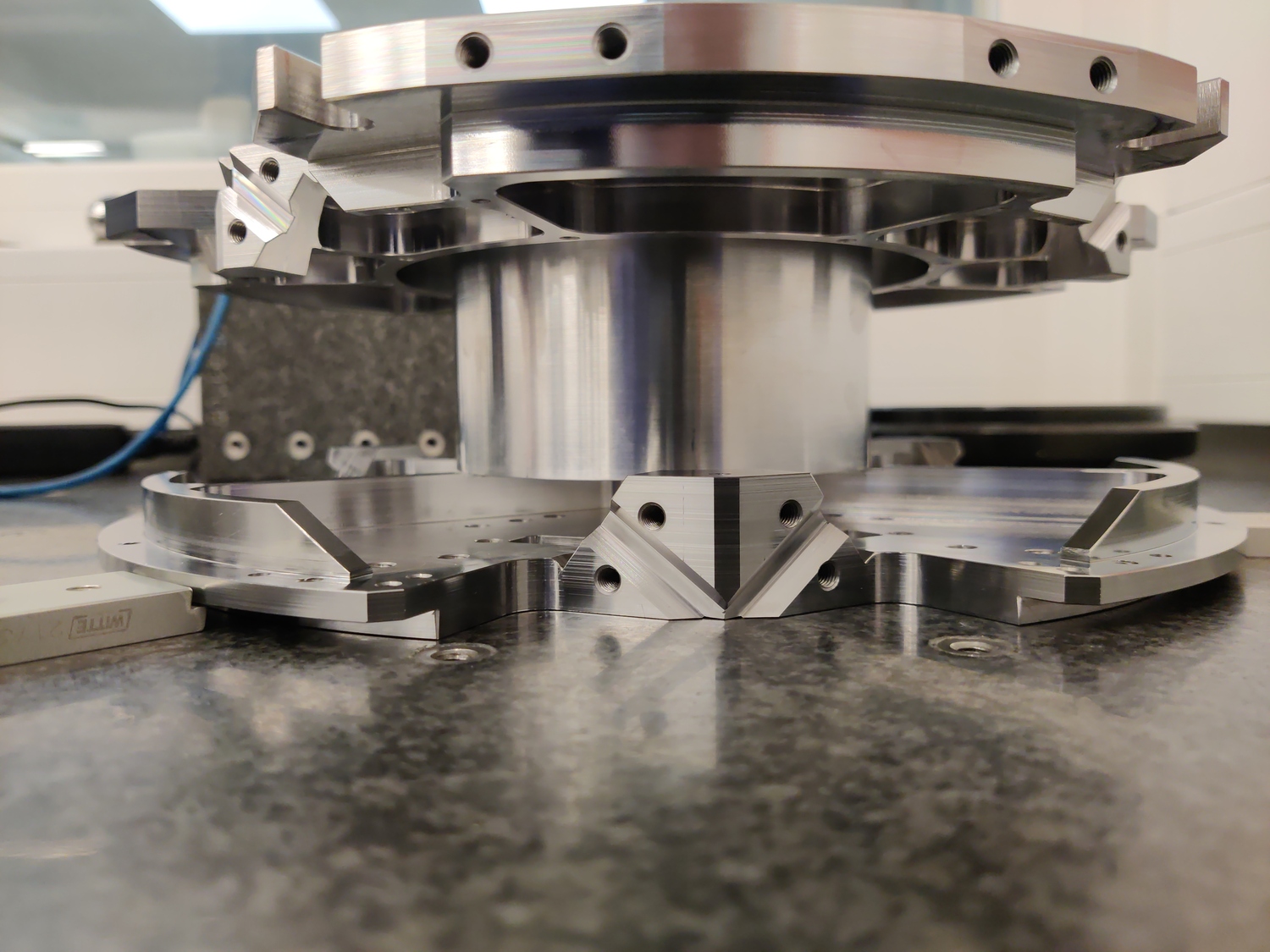
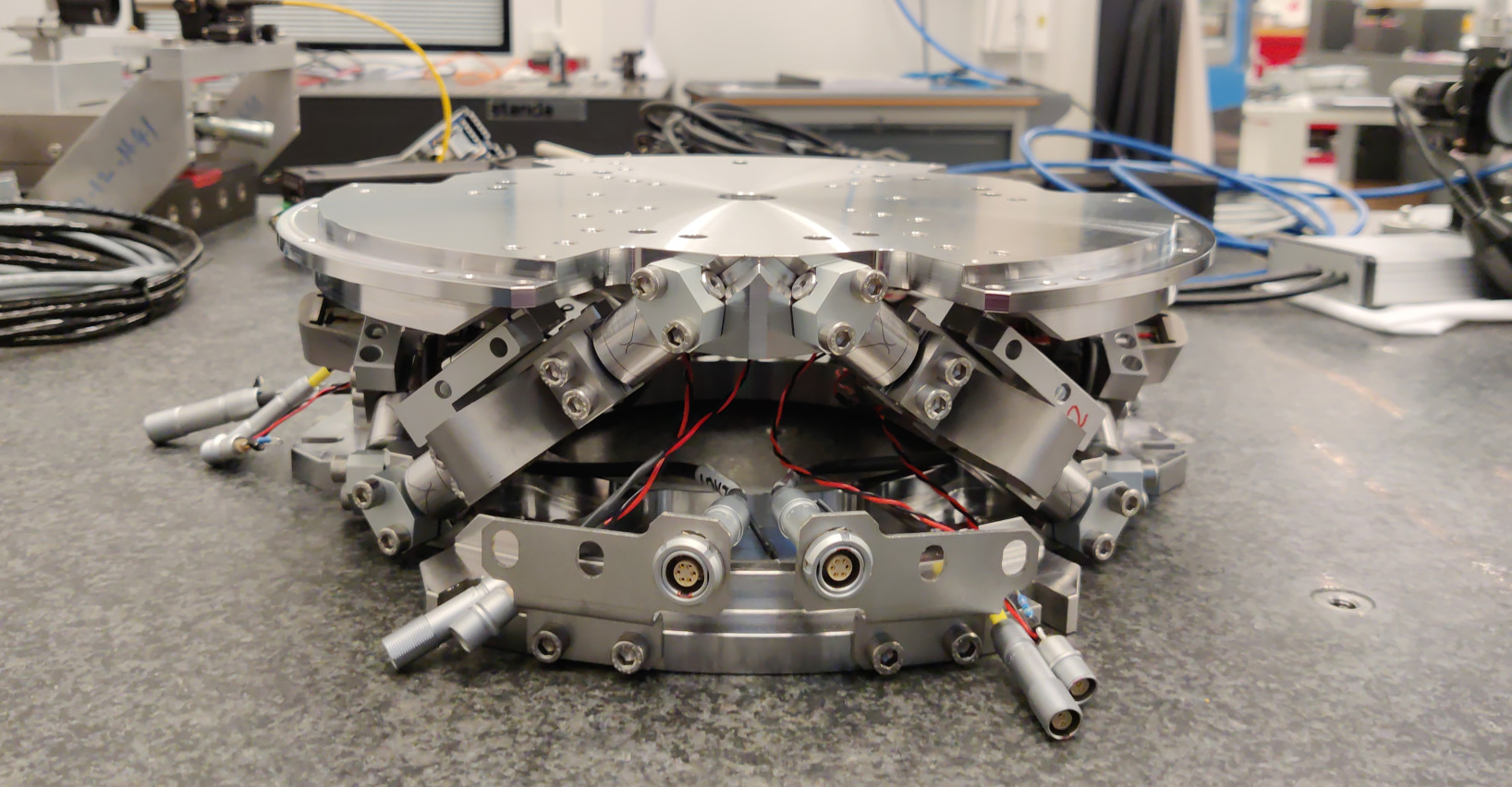
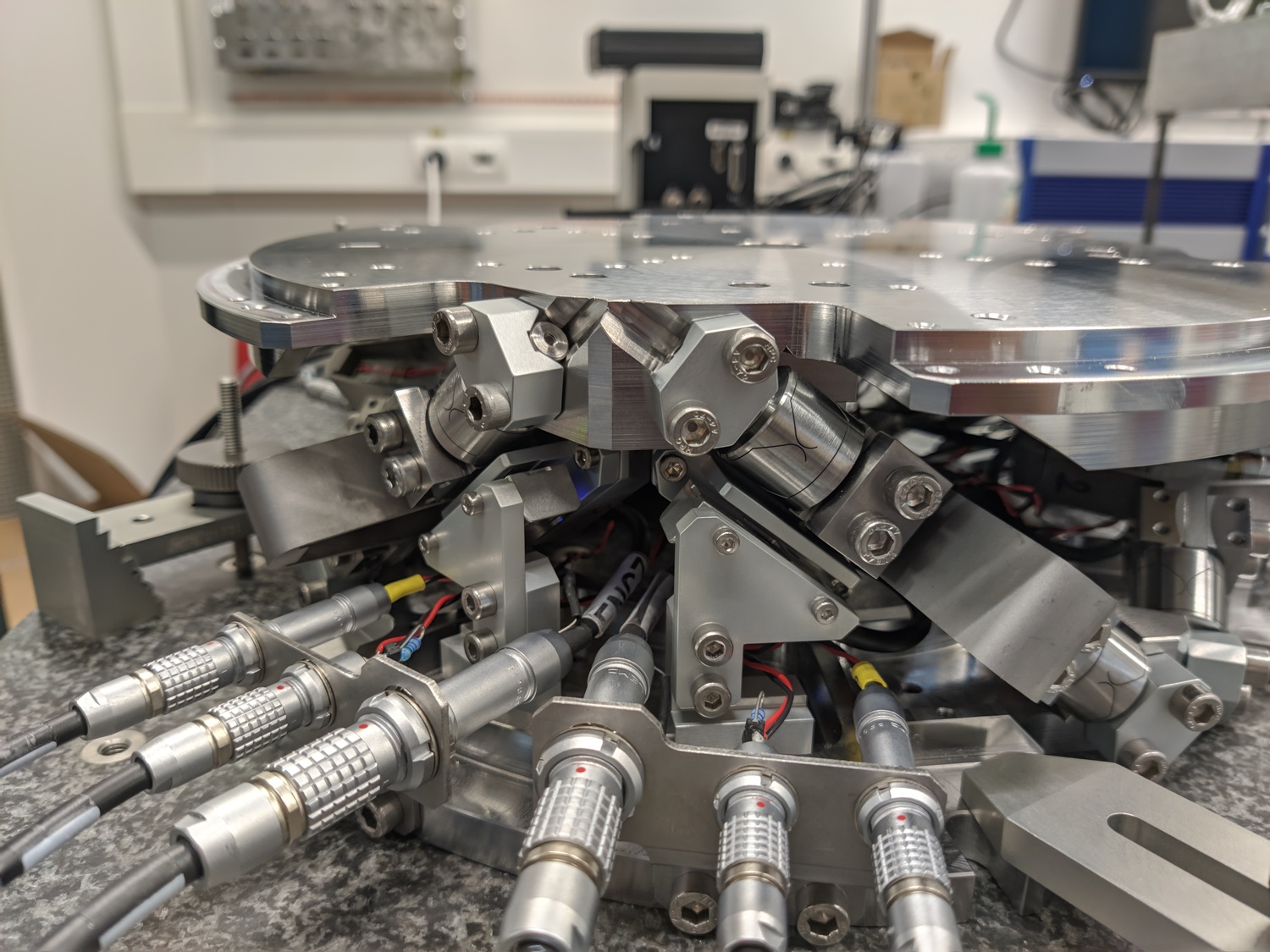
This document is dedicated to the experimental study of the nano-hexapod shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_picture_bench_granite_nano_hexapod.
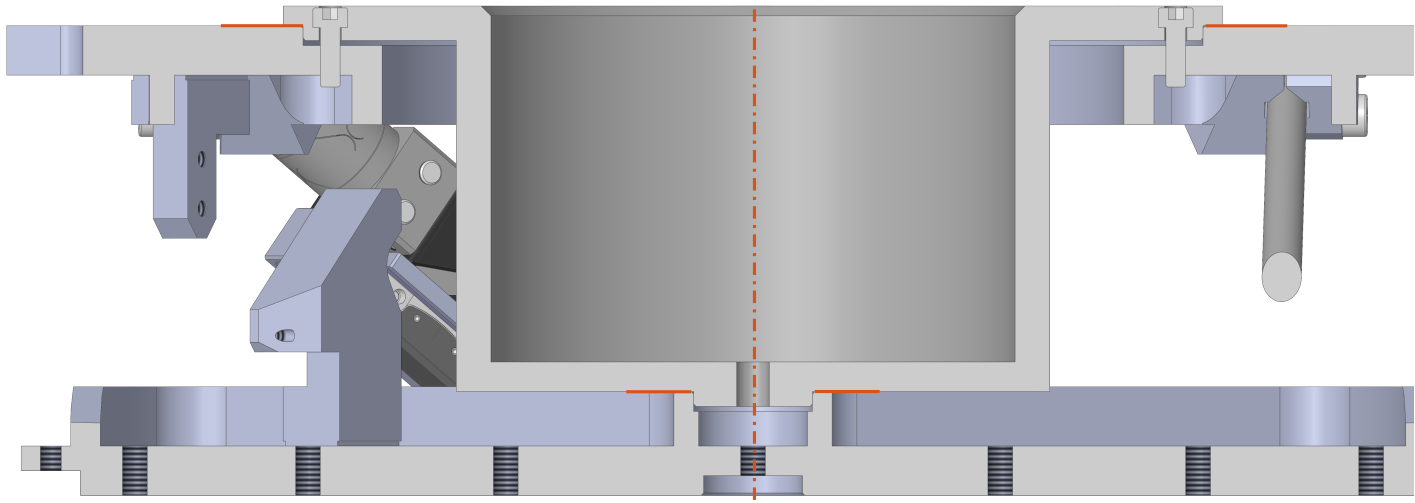
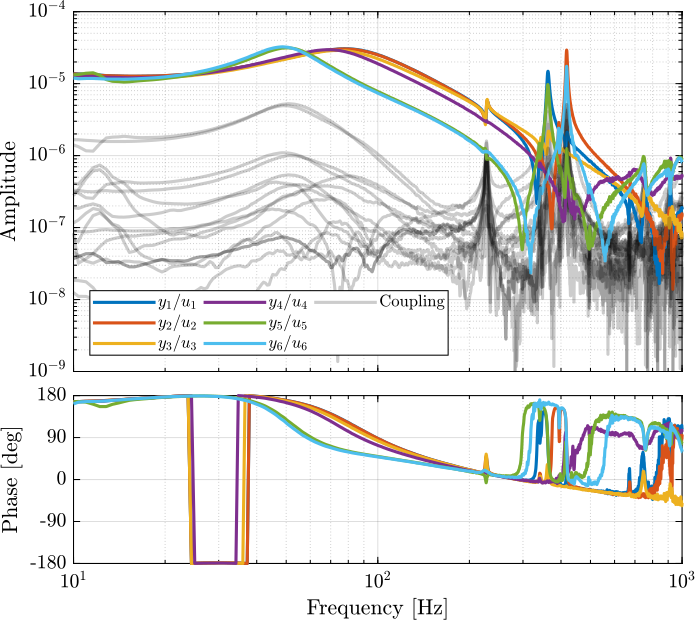
In Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_nano_hexapod_signals is shown a block diagram of the experimental setup. When possible, the notations are consistent with this diagram and summarized in Table ref:tab:list_signals.
\definecolor{instrumentation}{rgb}{0, 0.447, 0.741}
\definecolor{mechanics}{rgb}{0.8500, 0.325, 0.098}
\begin{tikzpicture}
% Blocs
\node[block={4.0cm}{3.0cm}, fill=mechanics!20!white] (nano_hexapod) {Mechanics};
\coordinate[] (inputF) at (nano_hexapod.west);
\coordinate[] (outputL) at ($(nano_hexapod.south east)!0.8!(nano_hexapod.north east)$);
\coordinate[] (outputF) at ($(nano_hexapod.south east)!0.2!(nano_hexapod.north east)$);
\node[block, left= 0.8 of inputF, fill=instrumentation!20!white, align=center] (F_stack) {\tiny Actuator \\ \tiny stacks};
\node[block, left= 0.8 of F_stack, fill=instrumentation!20!white] (PD200) {PD200};
\node[DAC, left= 0.8 of PD200, fill=instrumentation!20!white] (F_DAC) {DAC};
\node[block, right=0.8 of outputF, fill=instrumentation!20!white, align=center] (Fm_stack){\tiny Sensor \\ \tiny stack};
\node[ADC, right=0.8 of Fm_stack,fill=instrumentation!20!white] (Fm_ADC) {ADC};
\node[block, right=0.8 of outputL, fill=instrumentation!20!white] (encoder) {\tiny Encoder};
% Connections and labels
\draw[->] ($(F_DAC.west)+(-0.8,0)$) node[above right]{$\bm{u}$} node[below right]{$[V]$} -- node[sloped]{$/$} (F_DAC.west);
\draw[->] (F_DAC.east) -- node[midway, above]{$\tilde{\bm{u}}$}node[midway, below]{$[V]$} (PD200.west);
\draw[->] (PD200.east) -- node[midway, above]{$\bm{u}_a$}node[midway, below]{$[V]$} (F_stack.west);
\draw[->] (F_stack.east) -- (inputF) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}$}node[below left]{$[N]$};
\draw[->] (outputF) -- (Fm_stack.west) node[above left]{$\bm{\epsilon}$} node[below left]{$[m]$};
\draw[->] (Fm_stack.east) -- node[midway, above]{$\tilde{\bm{\tau}}_m$}node[midway, below]{$[V]$} (Fm_ADC.west);
\draw[->] (Fm_ADC.east) -- node[sloped]{$/$} ++(0.8, 0)coordinate(end) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}_m$}node[below left]{$[V]$};
\draw[->] (outputL) -- (encoder.west) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}$} node[below left]{$[m]$};
\draw[->] (encoder.east) -- node[sloped]{$/$} (encoder-|end) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$}node[below left]{$[m]$};
% Nano-Hexapod
\begin{scope}[on background layer]
\node[fit={(F_stack.west|-nano_hexapod.south) (Fm_stack.east|-nano_hexapod.north)}, fill=black!20!white, draw, inner sep=2pt] (system) {};
\node[above] at (system.north) {Nano-Hexapod};
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}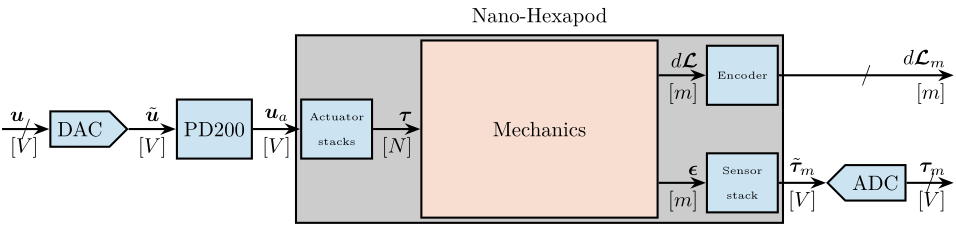
| Unit | Matlab | Vector | Elements | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Input (wanted DAC voltage) | [V] |
u |
$\bm{u}$ | $u_i$ |
| DAC Output Voltage | [V] |
u |
$\tilde{\bm{u}}$ | $\tilde{u}_i$ |
| PD200 Output Voltage | [V] |
ua |
$\bm{u}_a$ | $u_{a,i}$ |
| Actuator applied force | [N] |
tau |
$\bm{\tau}$ | $\tau_i$ |
| Strut motion | [m] |
dL |
$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}$ | $d\mathcal{L}_i$ |
| Encoder measured displacement | [m] |
dLm |
$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ | $d\mathcal{L}_{m,i}$ |
| Force Sensor strain | [m] |
epsilon |
$\bm{\epsilon}$ | $\epsilon_i$ |
| Force Sensor Generated Voltage | [V] |
taum |
$\tilde{\bm{\tau}}_m$ | $\tilde{\tau}_{m,i}$ |
| Measured Generated Voltage | [V] |
taum |
$\bm{\tau}_m$ | $\tau_{m,i}$ |
| Motion of the top platform | [m,rad] |
dX |
$d\bm{\mathcal{X}}$ | $d\mathcal{X}_i$ |
| Metrology measured displacement | [m,rad] |
dXm |
$d\bm{\mathcal{X}}_m$ | $d\mathcal{X}_{m,i}$ |
This document is divided in the following sections:
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_mounting: mounting of the nano-hexapod
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_encoders_plates: the same is done when the encoders are fixed to the plates.
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_decentralized_hac_iff: a decentralized HAC-LAC strategy is studied and implemented.
Mounting Procedure
<<sec:test_nhexa_mounting>>
Mounting Goals
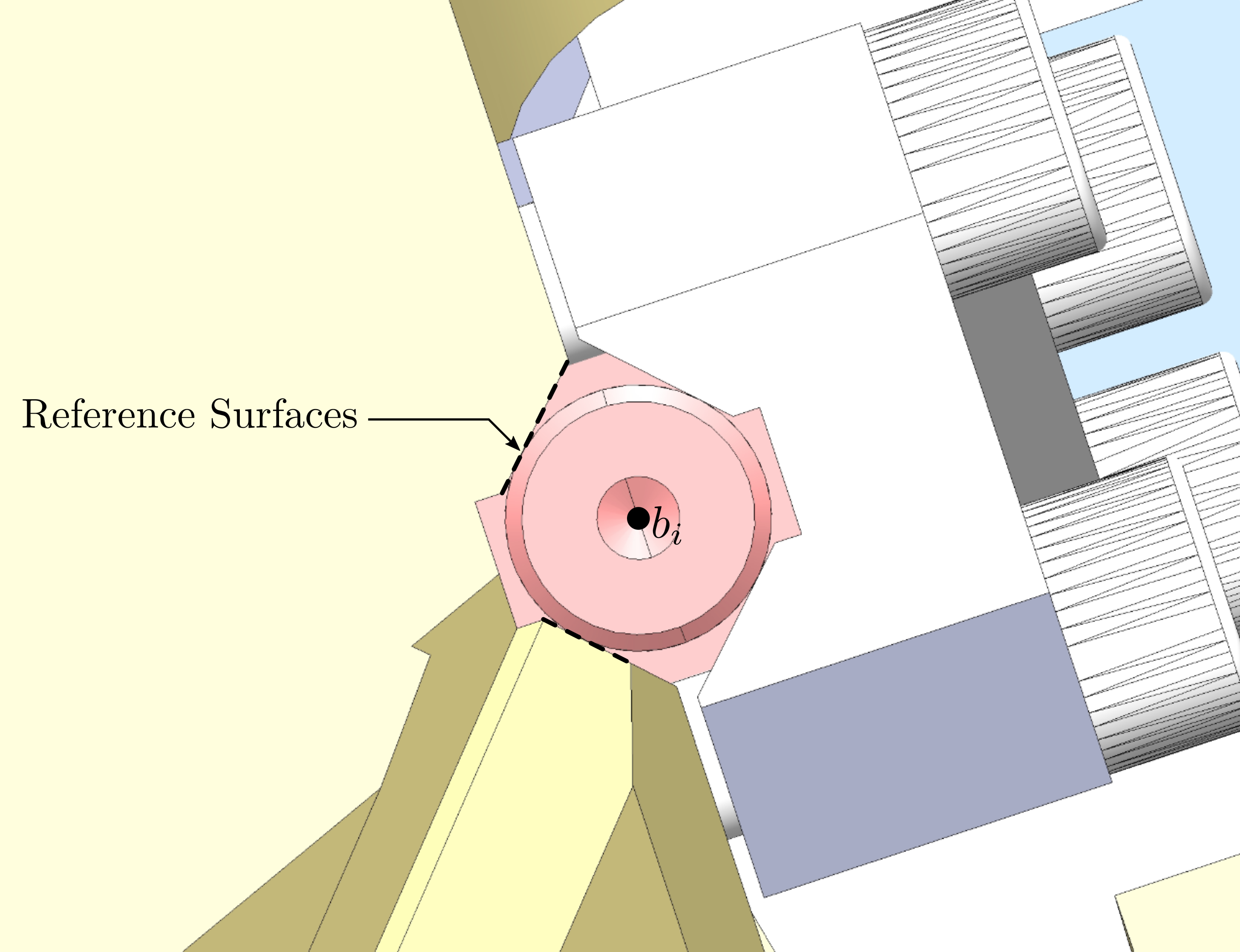
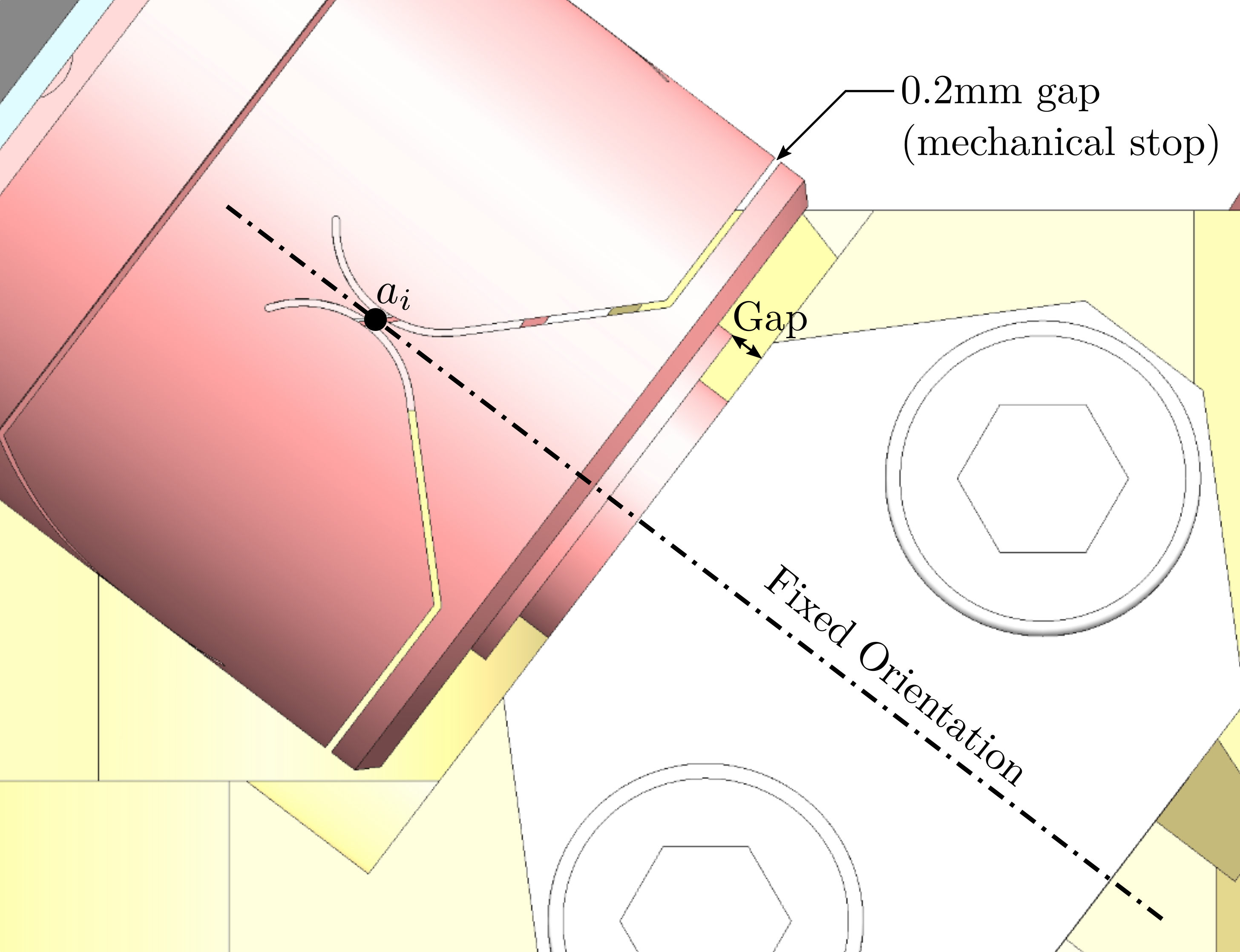
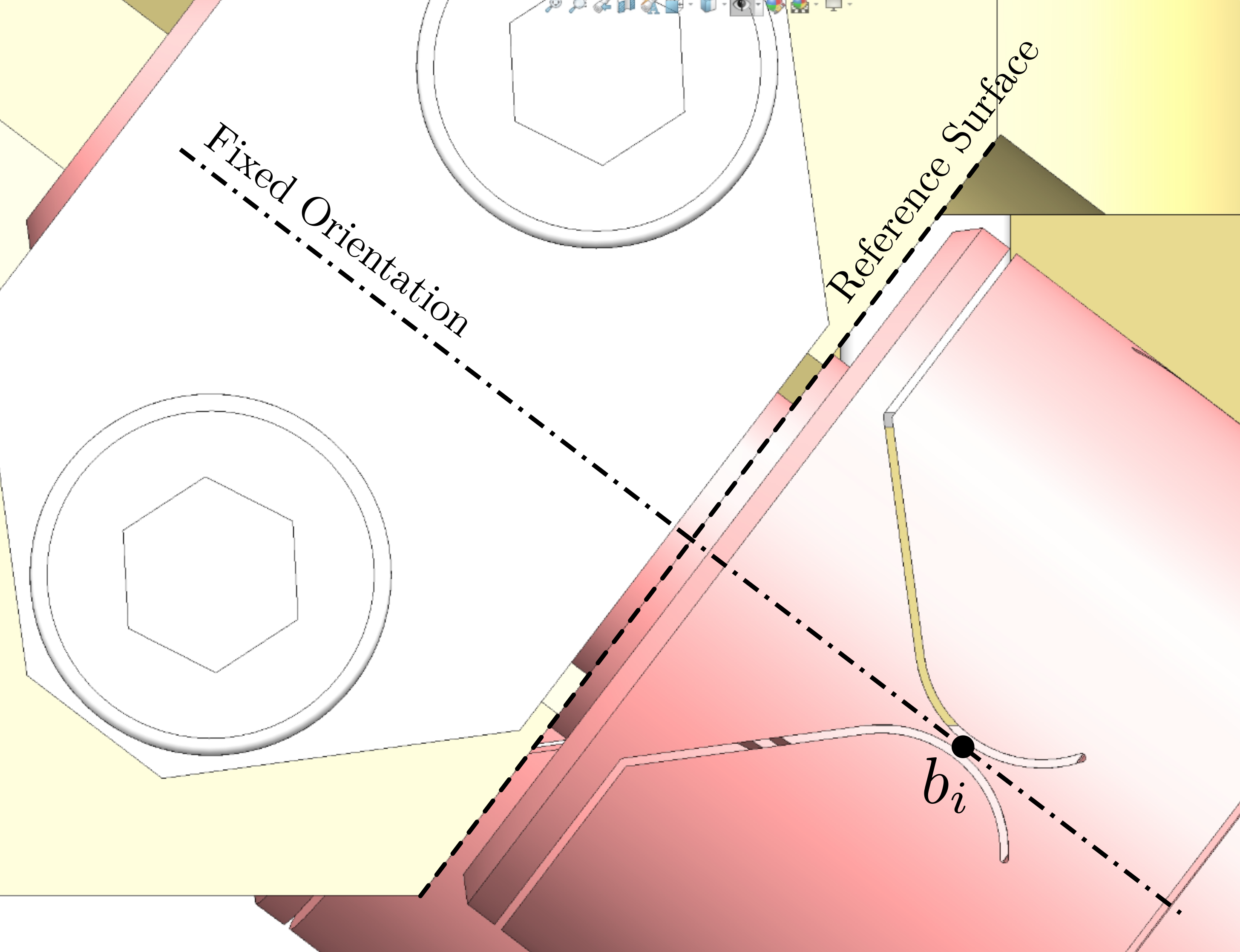
#+caption:Reference surfaces of the flexible joint interface with the plates
Mounting Bench

Mounting Procedure
- Fix the bottom plate with the cylindrical tool
- Put the top plate on the granite
- Put the cylindrical tool and bottom plate on top of the top plate (Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_mounting_tool_hexapod_bot_view). This position the bottom plate with respect to the top plate in X, Y, Z, Rx, Ry
- Put the pin to position/fix the Rz. Now the two plates should be position and clamped together
- Fix the 6 struts
- Remove the pin and the tool
- Put the nano-hexapod in place
Nano-Hexapod Mounting
<<sec:nano_hexapod_mounting>>
Introduction ignore
Plates
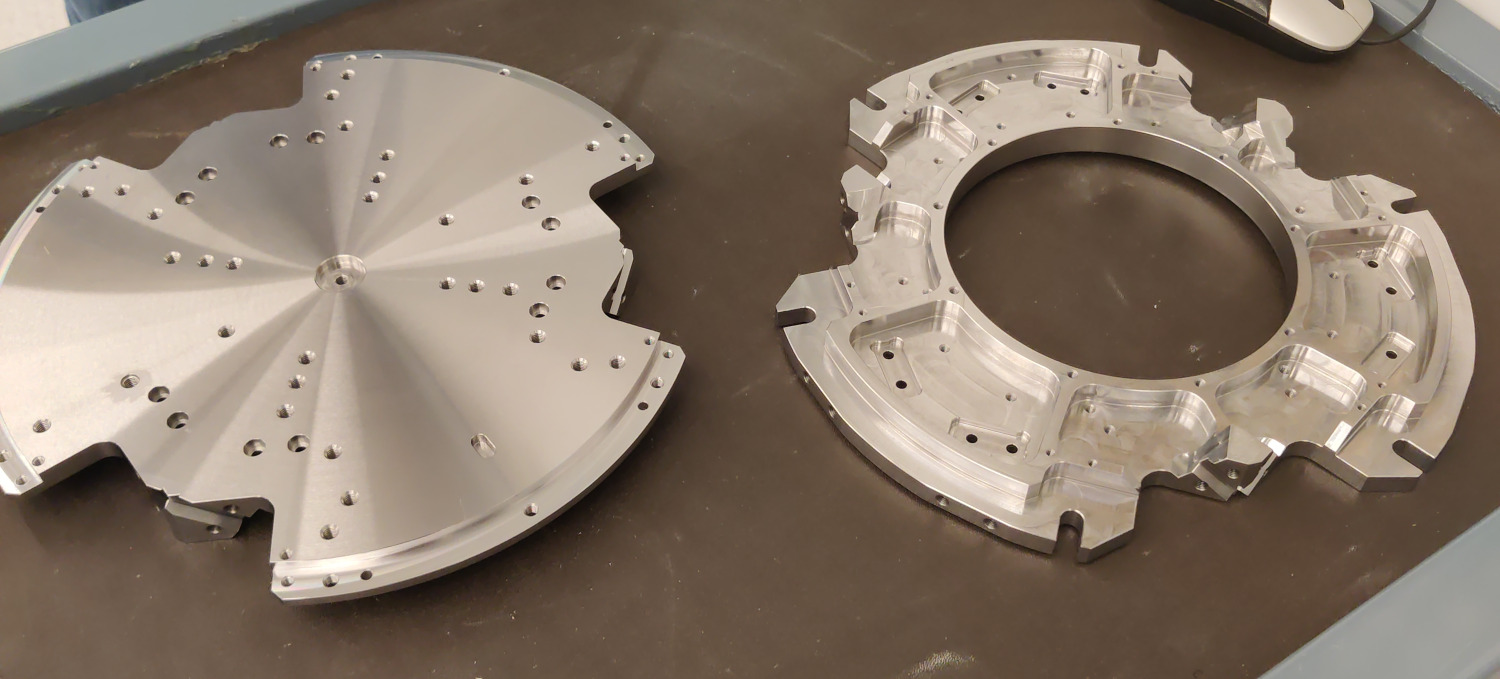


Mounting Tool
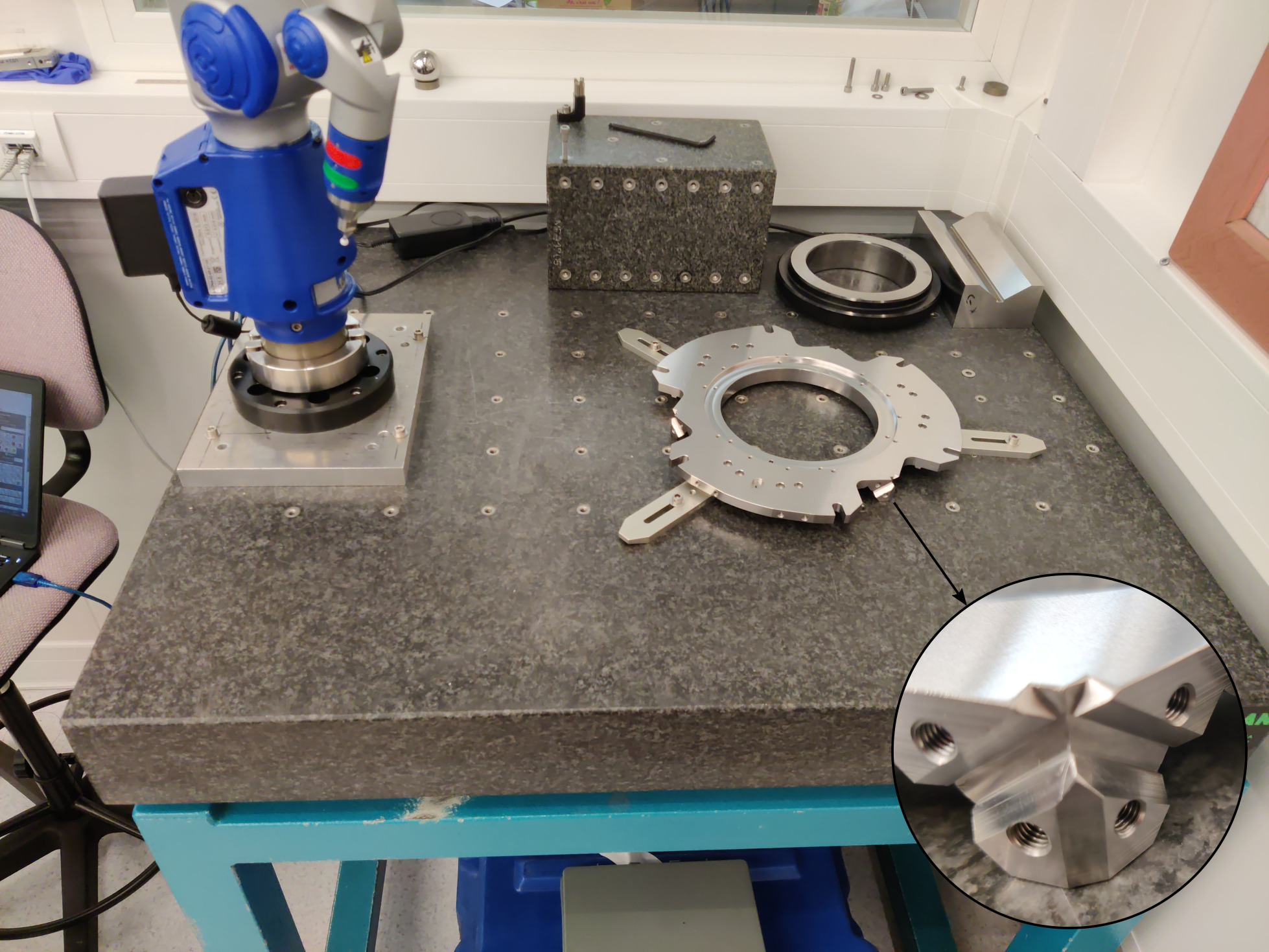
A mounting tool is used to position the top and bottom platforms. Then the struts can be mounted one by one. When all the struts are mounted, the "mounting tool" is disassembled and the nano-hexapod is considered to be mounted.
The main goal of this "mounting tool" is to position the "V" shapes of both plates such that they are coaxial.
The straightness is the diameter of the smallest cylinder containing all points of the axis.
| Strut nb | Meas 1 | Meas 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7um | 3um |
| 2 | 11um | 11um |
| 3 | 15um | 14um |
| 4 | 6um | 6um |
| 5 | 7um | 5um |
| 6 | 6um | 7um |
Using the FARO arm, the coaxiality of the "V" shapes have been measured to better than $15\,\mu m$! This means that the two cylinders corresponding to the flexible joints are both within a perfect cylinder with a diameter of $15\,\mu m$. This is probably better than that, but we reached the limit of the FARO arm's precision.
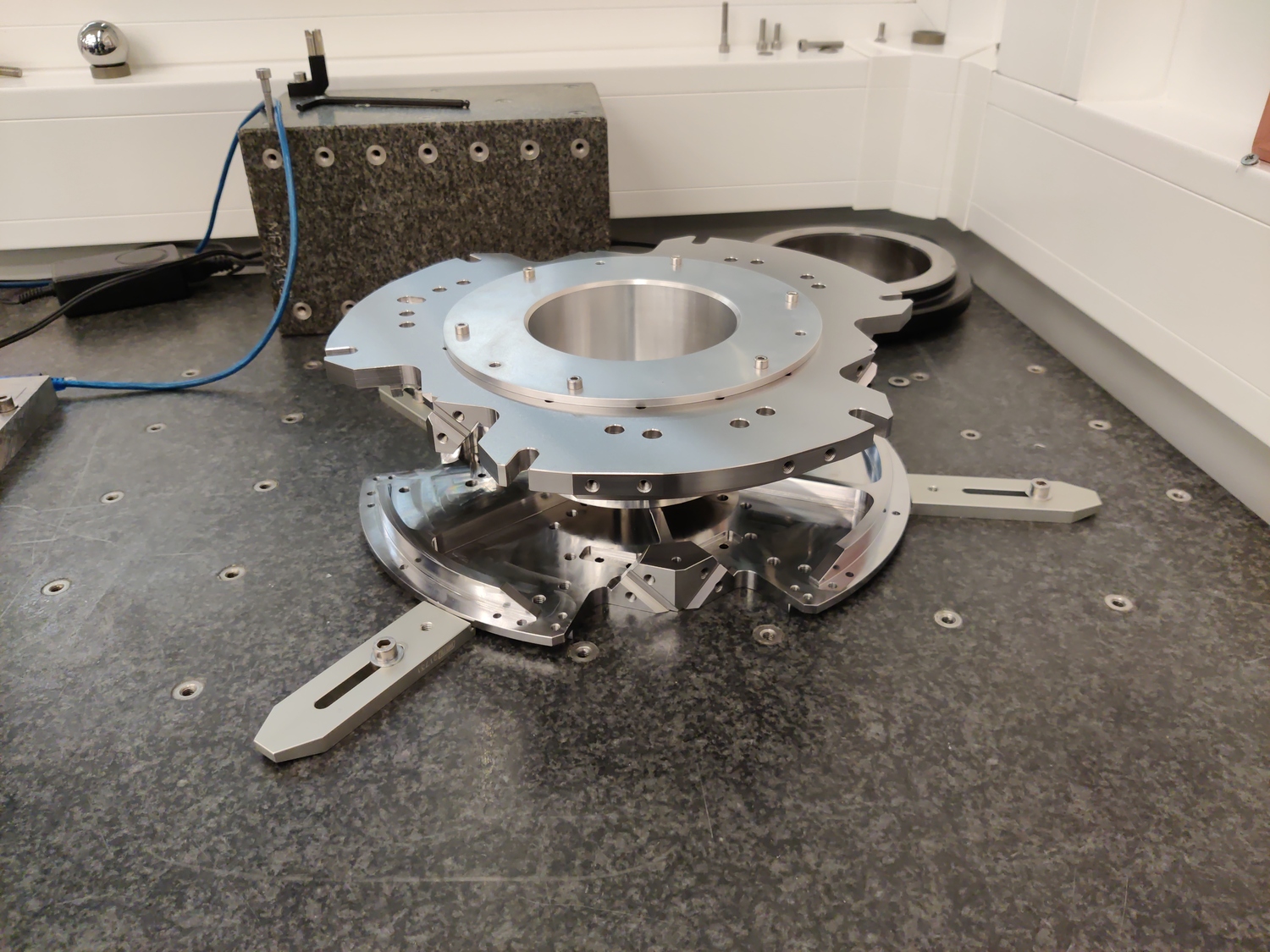

Mounted Hexapod
Encoders fixed to the plates
<<sec:test_nhexa_encoders_plates>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, the encoders are fixed to the plates rather than to the struts as shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_fixed_to_struts.
It is structured as follow:
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_plant_id: The dynamics of the nano-hexapod is identified.
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_comp_simscape: The identified dynamics is compared with the Simscape model.
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff: The Integral Force Feedback (IFF) control strategy is applied and the dynamics of the damped nano-hexapod is identified and compare with the Simscape model.
Identification of the dynamics
<<sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_plant_id>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, the dynamics of the nano-hexapod with the encoders fixed to the plates is identified.
First, the measurement data are loaded in Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_plant_id_setup, then the transfer function matrix from the actuators to the encoders are estimated in Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_plant_id_dvf. Finally, the transfer function matrix from the actuators to the force sensors is estimated in Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_plant_id_iff.
Data Loading and Spectral Analysis Setup
<<sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_plant_id_setup>>
The actuators are excited one by one using a low pass filtered white noise. For each excitation, the 6 force sensors and 6 encoders are measured and saved.
%% Load Identification Data
meas_data = {};
for i = 1:6
meas_data(i) = {load(sprintf('frf_exc_strut_%i_enc_plates_noise.mat', i), 't', 'Va', 'Vs', 'de')};
endTransfer function from Actuator to Encoder
<<sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_plant_id_dvf>>
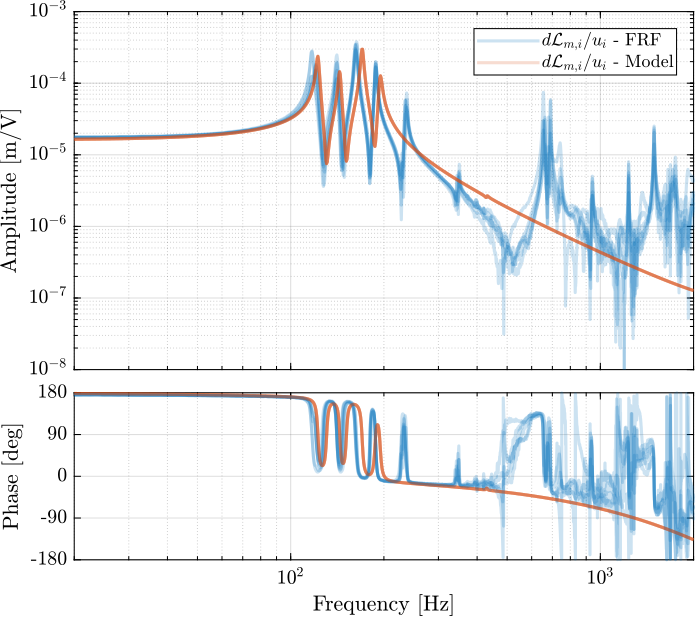
The 6x6 transfer function matrix from the excitation voltage $\bm{u}$ and the displacement $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ as measured by the encoders is estimated.
%% Transfer function from u to dLm
G_dL = zeros(length(f), 6, 6);
for i = 1:6
G_dL(:,:,i) = tfestimate(meas_data{i}.Va, meas_data{i}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);
endThe diagonal and off-diagonal terms of this transfer function matrix are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_dvf_frf.
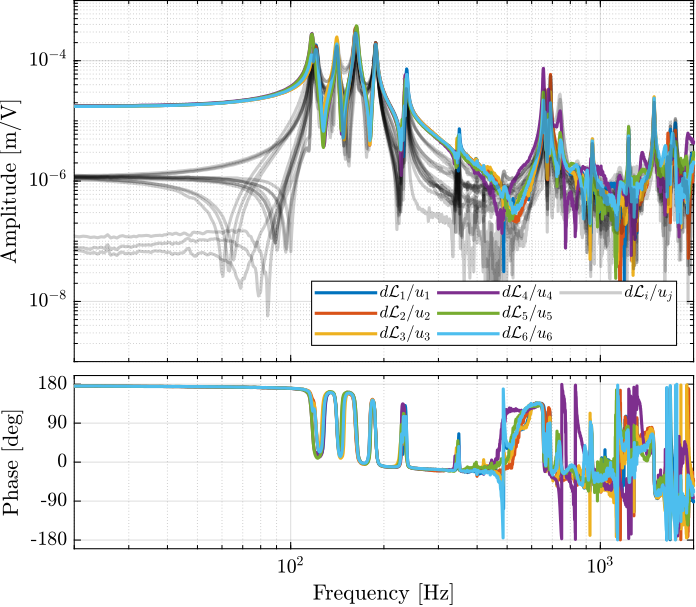
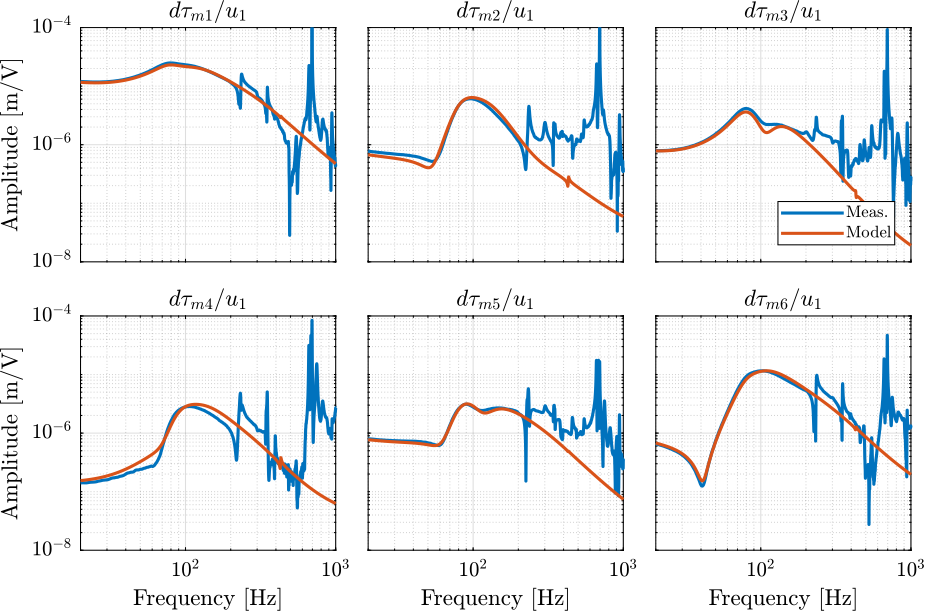
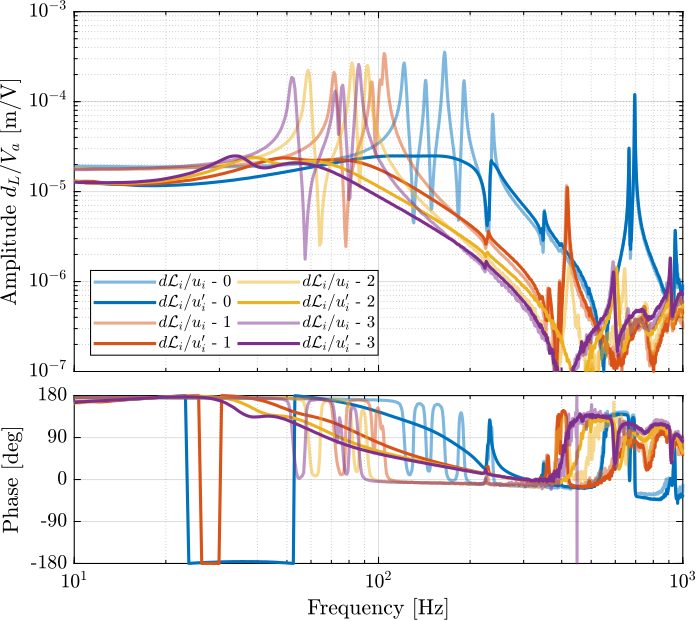
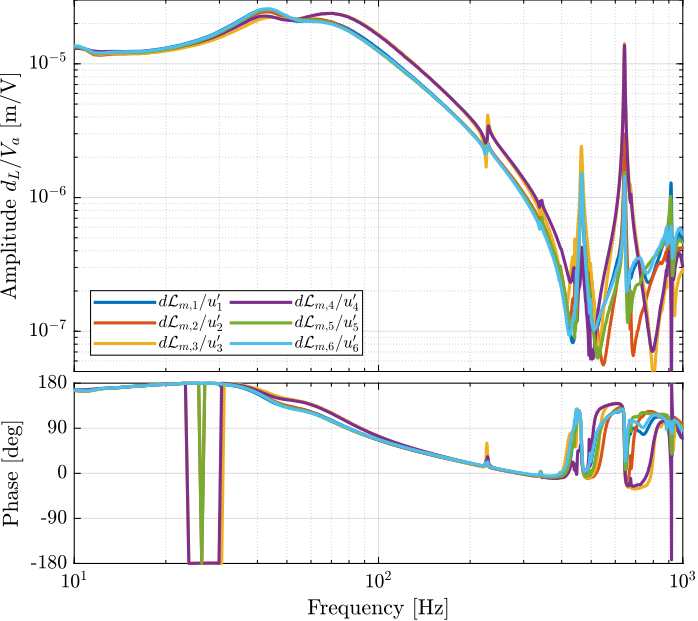
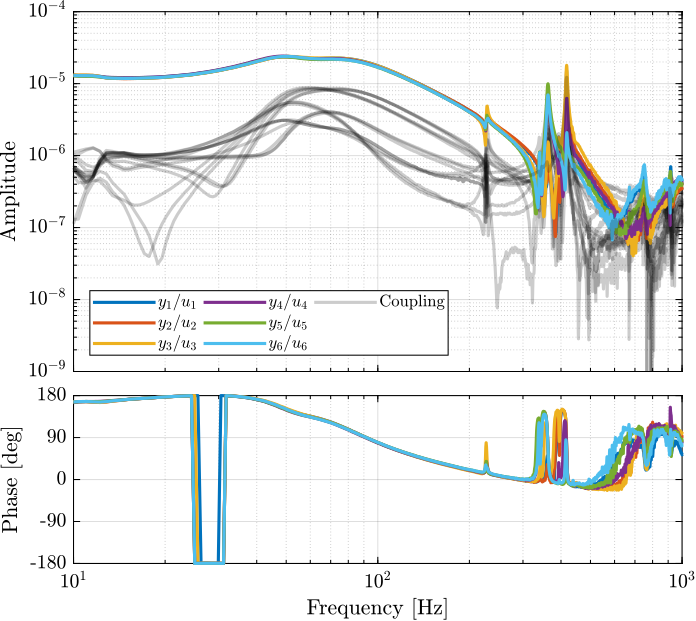
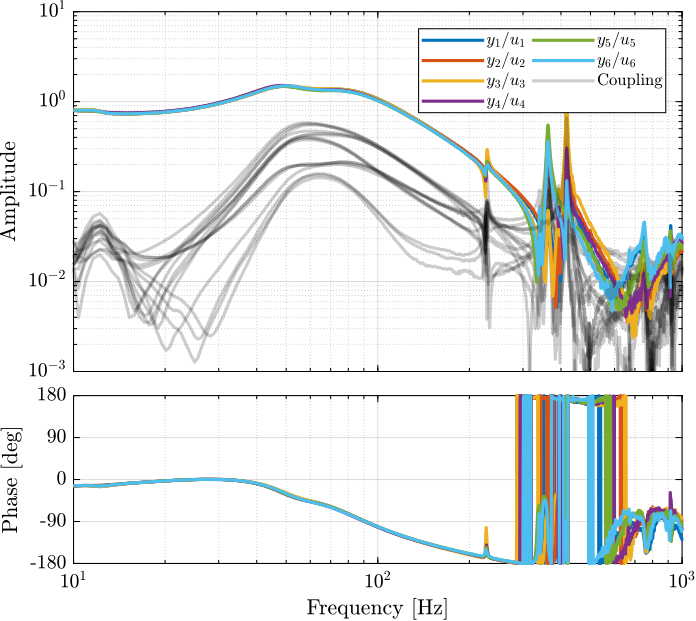
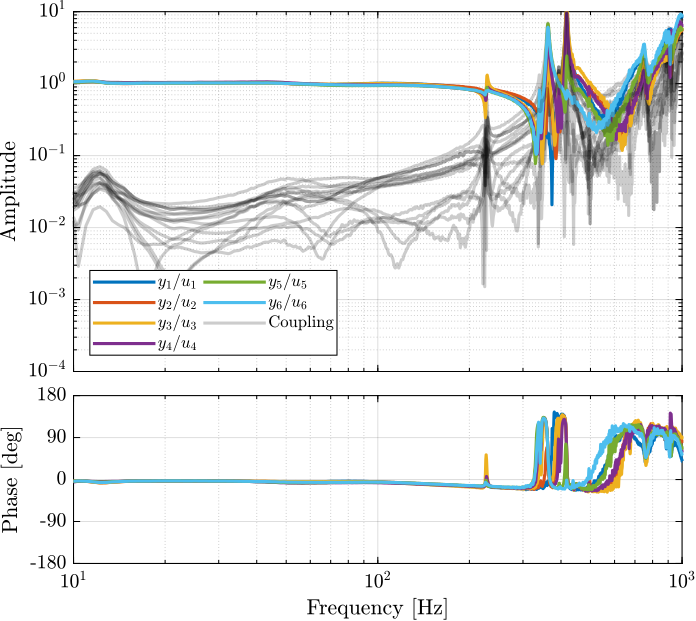
From Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_dvf_frf, we can draw few conclusions on the transfer functions from $\bm{u}$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ when the encoders are fixed to the plates:
- the decoupling is rather good at low frequency (below the first suspension mode). The low frequency gain is constant for the off diagonal terms, whereas when the encoders where fixed to the struts, the low frequency gain of the off-diagonal terms were going to zero (Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_struts_dvf_frf).
- the flexible modes of the struts at 226Hz and 337Hz are indeed shown in the transfer functions, but their amplitudes are rather low.
- the diagonal terms have alternating poles and zeros up to at least 600Hz: the flexible modes of the struts are not affecting the alternating pole/zero pattern. This what not the case when the encoders were fixed to the struts (Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_struts_dvf_frf).
Transfer function from Actuator to Force Sensor
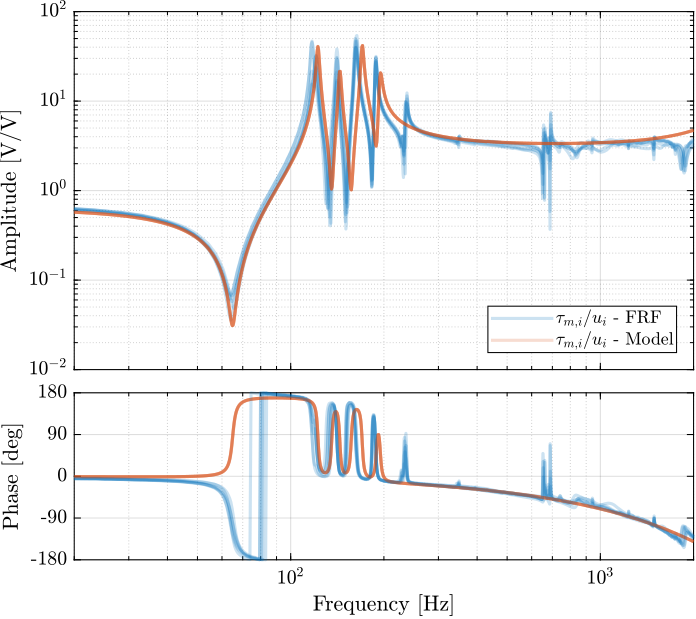
<<sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_plant_id_iff>> Then the 6x6 transfer function matrix from the excitation voltage $\bm{u}$ and the voltage $\bm{\tau}_m$ generated by the Force senors is estimated.
%% IFF Plant
G_tau = zeros(length(f), 6, 6);
for i = 1:6
G_tau(:,:,i) = tfestimate(meas_data{i}.Va, meas_data{i}.Vs, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);
endThe bode plot of the diagonal and off-diagonal terms are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff_frf.
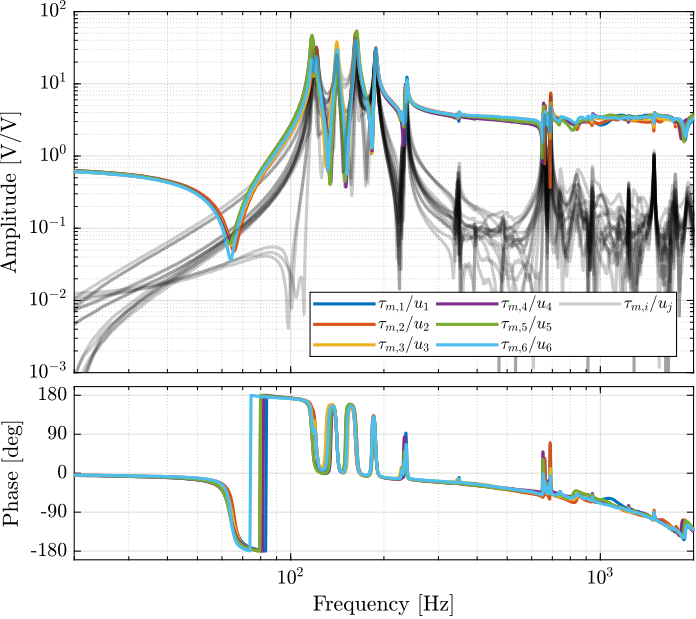
It is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff_comp_simscape_all that:
- The IFF plant has alternating poles and zeros
- The first flexible mode of the struts as 235Hz is appearing, and therefore is should be possible to add some damping to this mode using IFF
- The decoupling is quite good at low frequency (below the first model) as well as high frequency (above the last suspension mode, except near the flexible modes of the top plate)
Save Identified Plants
The identified dynamics is saved for further use.
save('data_frf/identified_plants_enc_plates.mat', 'f', 'Ts', 'G_tau', 'G_dL')Comparison with the Simscape Model
<<sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_comp_simscape>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, the measured dynamics done in Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_plant_id is compared with the dynamics estimated from the Simscape model.
Identification with the Simscape Model
The nano-hexapod is initialized with the APA taken as 2dof models.
%% Initialize Nano-Hexapod
n_hexapod = initializeNanoHexapodFinal('flex_bot_type', '4dof', ...
'flex_top_type', '4dof', ...
'motion_sensor_type', 'plates', ...
'actuator_type', '2dof');
support.type = 1; % On top of vibration table
payload.type = 0; % No PayloadThen the transfer function from $\bm{u}$ to $\bm{\tau}_m$ is identified using the Simscape model.
%% Identify the transfer function from u to taum
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/du'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Actuator Inputs
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fm'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Force Sensors
G_tau = exp(-s*frf_ol.Ts)*linearize(mdl, io, 0.0, options);Now, the dynamics from the DAC voltage $\bm{u}$ to the encoders $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ is estimated using the Simscape model.
%% Identify the DVtransfer function from u to dLm
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/du'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Actuator Inputs
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/dL'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Encoders
G_dL = exp(-s*frf_ol.Ts)*linearize(mdl, io, 0.0, options);The identified dynamics is saved for further use.
save('data_frf/simscape_plants_enc_plates.mat', 'G_tau', 'G_dL');Dynamics from Actuator to Force Sensors
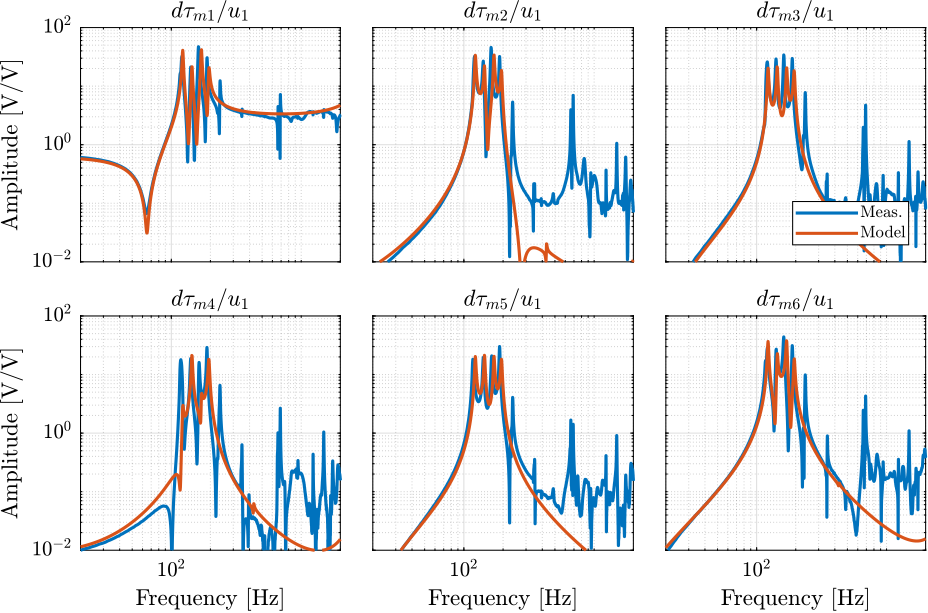
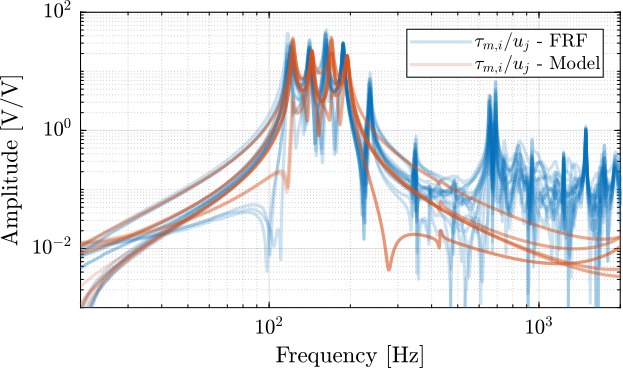
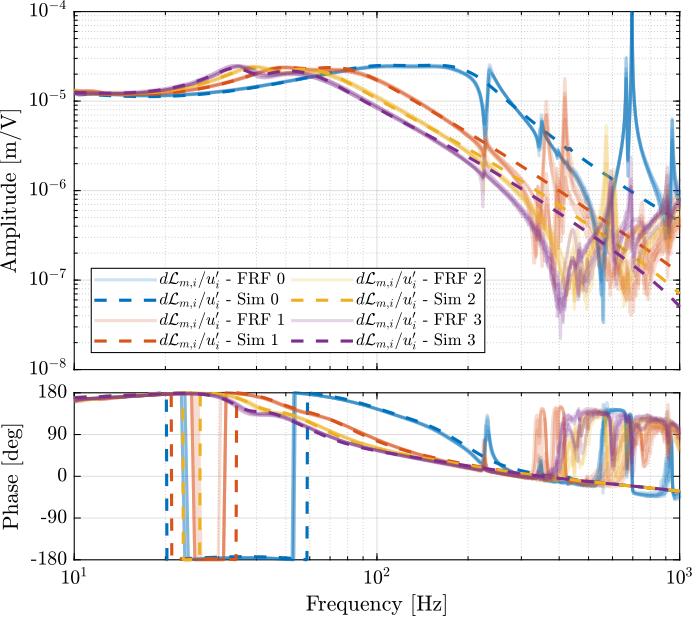
The identified dynamics is compared with the measured FRF:
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff_comp_simscape_all: the individual transfer function from $u_1$ (the DAC voltage for the first actuator) to the force sensors of all 6 struts are compared
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff_comp_simscape: all the diagonal elements are compared
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff_comp_offdiag_simscape: all the off-diagonal elements are compared
Dynamics from Actuator to Encoder
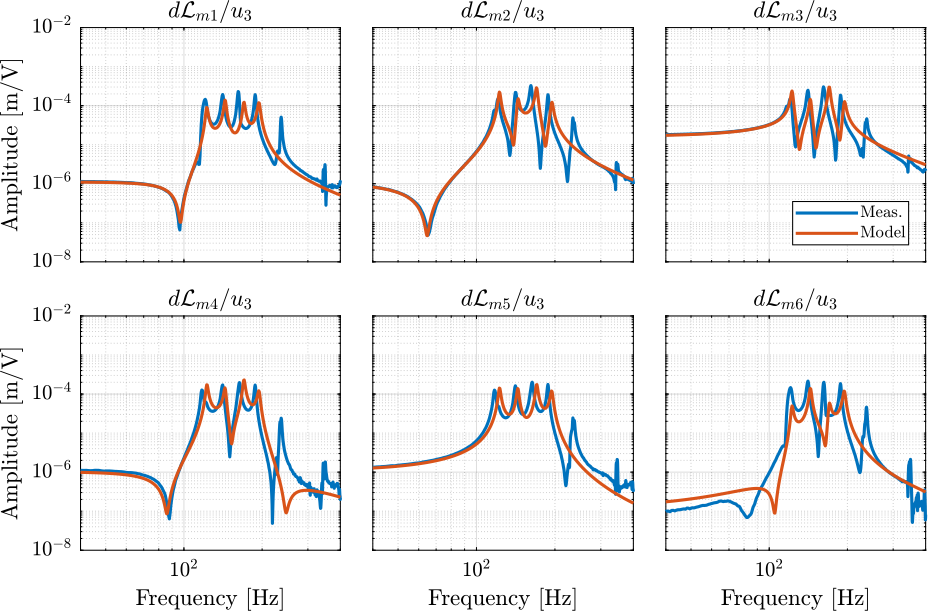
The identified dynamics is compared with the measured FRF:
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_dvf_comp_simscape_all: the individual transfer function from $u_3$ (the DAC voltage for the actuator number 3) to the six encoders
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_dvf_comp_simscape: all the diagonal elements are compared
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_dvf_comp_offdiag_simscape: all the off-diagonal elements are compared
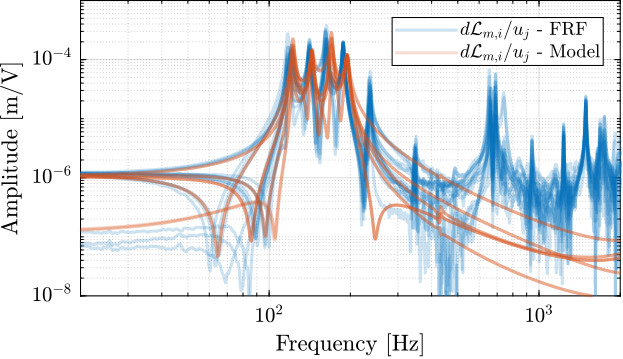
Conclusion
The Simscape model is quite accurate for the transfer function matrices from $\bm{u}$ to $\bm{\tau}_m$ and from $\bm{u}$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ except at frequencies of the flexible modes of the top-plate. The Simscape model can therefore be used to develop the control strategies.
Integral Force Feedback
<<sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, the Integral Force Feedback (IFF) control strategy is applied to the nano-hexapod in order to add damping to the suspension modes.
The control architecture is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_control_architecture_iff:
- $\bm{\tau}_m$ is the measured voltage of the 6 force sensors
- $\bm{K}_{\text{IFF}}$ is the $6 \times 6$ diagonal controller
- $\bm{u}$ is the plant input (voltage generated by the 6 DACs)
- $\bm{u}^\prime$ is the new plant inputs with added damping
\begin{tikzpicture}
% Blocs
\node[block={3.0cm}{2.0cm}] (P) {Plant};
\coordinate[] (inputF) at ($(P.south west)!0.5!(P.north west)$);
\coordinate[] (outputF) at ($(P.south east)!0.7!(P.north east)$);
\coordinate[] (outputL) at ($(P.south east)!0.3!(P.north east)$);
\node[block, above=0.4 of P] (Kiff) {$\bm{K}_\text{IFF}$};
\node[addb, left= of inputF] (addF) {};
% Connections and labels
\draw[->] (outputF) -- ++(1, 0) node[below left]{$\bm{\tau}_m$};
\draw[->] (outputL) -- ++(1, 0) node[below left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$};
\draw[->] ($(outputF) + (0.6, 0)$)node[branch]{} |- (Kiff.east);
\draw[->] (Kiff.west) -| (addF.north);
\draw[->] (addF.east) -- (inputF) node[above left]{$\bm{u}$};
\draw[<-] (addF.west) -- ++(-1, 0) node[above right]{$\bm{u}^\prime$};
\end{tikzpicture}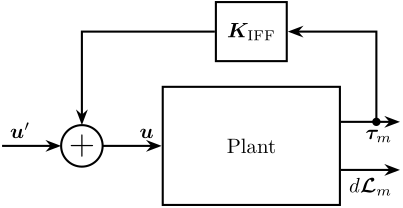
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_enc_struts_effect_iff_plant
Effect of IFF on the plant - Simscape Model
<<sec:test_nhexa_enc_struts_effect_iff_plant>>
The nano-hexapod is initialized with 2DoF APA and the encoders fixed to the struts.
%% Initialize the Simscape model in closed loop
n_hexapod = initializeNanoHexapodFinal('flex_bot_type', '4dof', ...
'flex_top_type', '4dof', ...
'motion_sensor_type', 'plates', ...
'actuator_type', '2dof', ...
'controller_type', 'iff');
support.type = 1; % On top of vibration table
payload.type = 0; % No PayloadThe same controller as the one developed when the encoder were fixed to the struts is used.
%% Optimal IFF controller
load('Kiff_struts_no_payload.mat', 'Kiff');The transfer function from $\bm{u}^\prime$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ is identified.
%% Identify the (damped) transfer function from u to dLm for different values of the IFF gain
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/du'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Actuator Inputs
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/dL'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Plate Displacement (encoder)
%% Transfer function from u to dL (IFF)
G_dL = exp(-s*frf_ol.Ts)*linearize(mdl, io, 0.0, options);It is first verified that the system is stable:
isstable(G_dL)1
The identified dynamics is saved for further use.
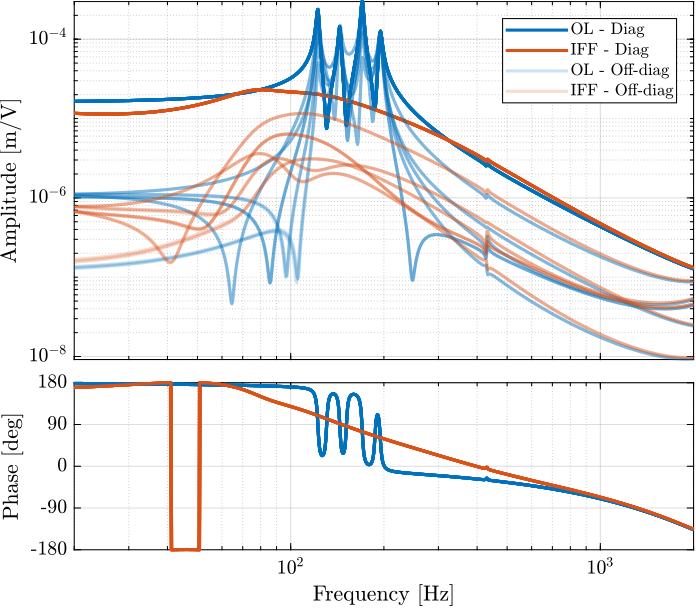
save('data_frf/simscape_plants_enc_plates_iff.mat', 'G_dL');The diagonal and off-diagonal terms of the $6 \times 6$ transfer function matrices identified are compared in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff_gains_effect_dvf_plant. It is shown, as was the case when the encoders were fixed to the struts, that the IFF control strategy is very effective in damping the suspension modes of the nano-hexapod.
Effect of IFF on the plant - FRF
The IFF control strategy is experimentally implemented. The (damped) transfer function from $\bm{u}^\prime$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ is experimentally identified.
The identification data are loaded:
%% Load Identification Data
meas_iff_plates = {};
for i = 1:6
meas_iff_plates(i) = {load(sprintf('frf_exc_iff_strut_%i_enc_plates_noise.mat', i), 't', 'Va', 'Vs', 'de', 'u')};
endAnd the parameters used for the transfer function estimation are defined below.
% Sampling Time [s]
Ts = (meas_iff_plates{1}.t(end) - (meas_iff_plates{1}.t(1)))/(length(meas_iff_plates{1}.t)-1);
% Hannning Windows
win = hanning(ceil(1/Ts));
% And we get the frequency vector
[~, f] = tfestimate(meas_iff_plates{1}.Va, meas_iff_plates{1}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);
The estimation is performed using the tfestimate command.
%% Estimation of the transfer function matrix from u to dL when IFF is applied
G_dL = zeros(length(f), 6, 6);
for i = 1:6
G_dL(:,:,i) = tfestimate(meas_iff_plates{i}.Va, meas_iff_plates{i}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);
endThe experimentally identified plant is saved for further use.
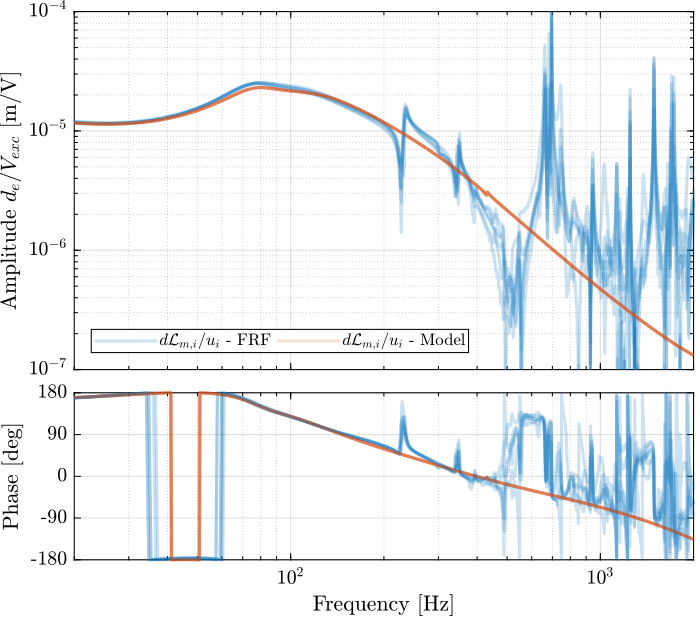
save('matlab/data_frf/damped_plant_enc_plates.mat', 'f', 'Ts', 'G_dL')save('data_frf/damped_plant_enc_plates.mat', 'f', 'Ts', 'G_dL')The obtained diagonal and off-diagonal elements of the transfer function from $\bm{u}^\prime$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plant_plates_effect_iff both without and with IFF.
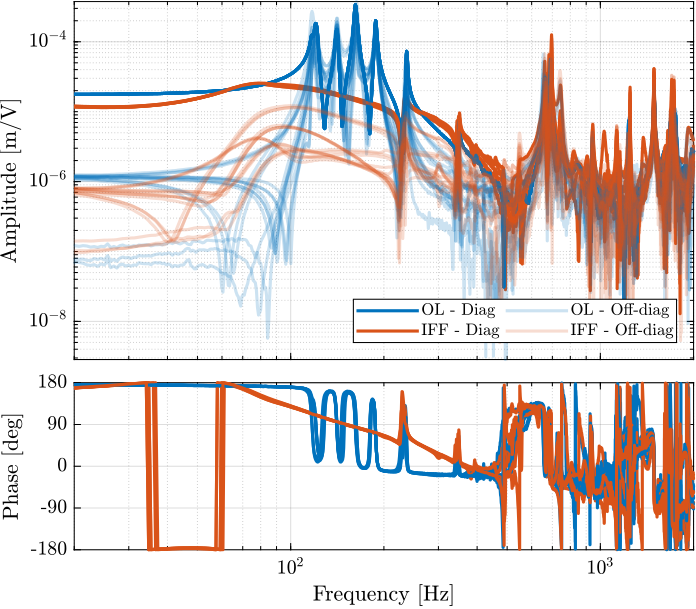
As was predicted with the Simscape model, the IFF control strategy is very effective in damping the suspension modes of the nano-hexapod. Little damping is also applied on the first flexible mode of the strut at 235Hz. However, no damping is applied on other modes, such as the flexible modes of the top plate.
Comparison of the measured FRF and the Simscape model
Let's now compare the obtained damped plants obtained experimentally with the one extracted from Simscape:
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_opt_iff_comp_simscape_all: the individual transfer function from $u_1^\prime$ to the six encoders are comapred
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_damped_iff_plates_plant_comp_diagonal: all the diagonal elements are compared
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_damped_iff_plates_plant_comp_off_diagonal: all the off-diagonal elements are compared
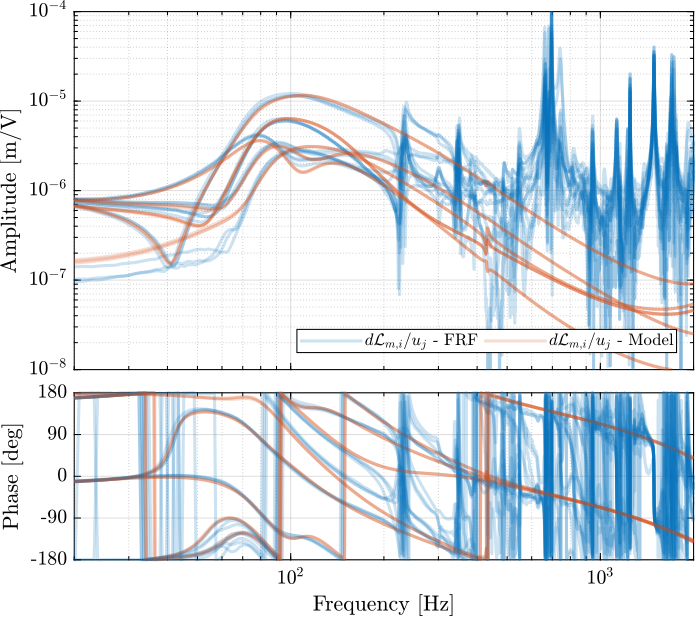
From Figures ref:fig:test_nhexa_damped_iff_plates_plant_comp_diagonal and ref:fig:test_nhexa_damped_iff_plates_plant_comp_off_diagonal, it is clear that the Simscape model very well represents the dynamics of the nano-hexapod. This is true to around 400Hz, then the dynamics depends on the flexible modes of the top plate which are not modelled.
Effect of Payload mass on the Dynamics
<<sec:test_nhexa_added_mass>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, the encoders are fixed to the plates, and we identify the dynamics for several payloads. The added payload are half cylinders, and three layers can be added for a total of around 40kg (Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_picture_added_3_masses).
First the dynamics from $\bm{u}$ to $d\mathcal{L}_m$ and $\bm{\tau}_m$ is identified. Then, the Integral Force Feedback controller is developed and applied as shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_nano_hexapod_signals_iff. Finally, the dynamics from $\bm{u}^\prime$ to $d\mathcal{L}_m$ is identified and the added damping can be estimated.
\definecolor{instrumentation}{rgb}{0, 0.447, 0.741}
\definecolor{mechanics}{rgb}{0.8500, 0.325, 0.098}
\definecolor{control}{rgb}{0.4660, 0.6740, 0.1880}
\begin{tikzpicture}
% Blocs
\node[block={4.0cm}{3.0cm}, fill=mechanics!20!white] (nano_hexapod) {Mechanics};
\coordinate[] (inputF) at (nano_hexapod.west);
\coordinate[] (outputL) at ($(nano_hexapod.south east)!0.8!(nano_hexapod.north east)$);
\coordinate[] (outputF) at ($(nano_hexapod.south east)!0.2!(nano_hexapod.north east)$);
\node[block, left= 0.8 of inputF, fill=instrumentation!20!white, align=center] (F_stack) {\tiny Actuator \\ \tiny stacks};
\node[block, left= 0.8 of F_stack, fill=instrumentation!20!white] (PD200) {PD200};
\node[DAC, left= 0.8 of PD200, fill=instrumentation!20!white] (F_DAC) {DAC};
\node[block, right=0.8 of outputF, fill=instrumentation!20!white, align=center] (Fm_stack){\tiny Sensor \\ \tiny stack};
\node[ADC, right=0.8 of Fm_stack,fill=instrumentation!20!white] (Fm_ADC) {ADC};
\node[block, right=0.8 of outputL, fill=instrumentation!20!white] (encoder) {\tiny Encoder};
\node[addb, left= 0.8 of F_DAC, fill=control!20!white] (add_iff) {};
\node[block, below=0.8 of add_iff, fill=control!20!white] (Kiff) {\tiny $K_{\text{IFF}}(s)$};
% Connections and labels
\draw[->] (add_iff.east) node[above right]{$\bm{u}$} node[below right]{$[V]$} -- node[sloped]{$/$} (F_DAC.west);
\draw[->] (F_DAC.east) -- node[midway, above]{$\tilde{\bm{u}}$}node[midway, below]{$[V]$} (PD200.west);
\draw[->] (PD200.east) -- node[midway, above]{$\bm{u}_a$}node[midway, below]{$[V]$} (F_stack.west);
\draw[->] (F_stack.east) -- (inputF) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}$}node[below left]{$[N]$};
\draw[->] (outputF) -- (Fm_stack.west) node[above left]{$\bm{\epsilon}$} node[below left]{$[m]$};
\draw[->] (Fm_stack.east) -- node[midway, above]{$\tilde{\bm{\tau}}_m$}node[midway, below]{$[V]$} (Fm_ADC.west);
\draw[->] (Fm_ADC.east) -- node[sloped]{$/$} ++(0.8, 0)coordinate(end) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}_m$}node[below left]{$[V]$};
\draw[->] (outputL) -- (encoder.west) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}$} node[below left]{$[m]$};
\draw[->] (encoder.east) -- node[sloped]{$/$} (encoder-|end) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$}node[below left]{$[m]$};
\draw[->] ($(Fm_ADC.east)+(0.14,0)$) node[branch]{} -- node[sloped]{$/$} ++(0, -1.8) -| (Kiff.south);
\draw[->] (Kiff.north) -- node[sloped]{$/$} (add_iff.south);
\draw[->] ($(add_iff.west)+(-0.8,0)$) node[above right]{$\bm{u}^\prime$} node[below right]{$[V]$} -- node[sloped]{$/$} (add_iff.west);
% Nano-Hexapod
\begin{scope}[on background layer]
\node[fit={(F_stack.west|-nano_hexapod.south) (Fm_stack.east|-nano_hexapod.north)}, fill=black!20!white, draw, inner sep=2pt] (system) {};
\node[above] at (system.north) {Nano-Hexapod};
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}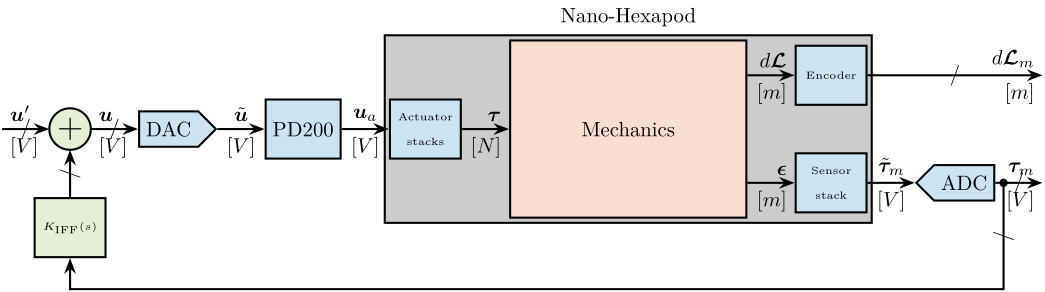
Measured Frequency Response Functions
The following data are loaded:
Va: the excitation voltage (corresponding to $u_i$)Vs: the generated voltage by the 6 force sensors (corresponding to $\bm{\tau}_m$)de: the measured motion by the 6 encoders (corresponding to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$)
%% Load Identification Data
meas_added_mass = {};
for i_mass = i_masses
for i_strut = 1:6
meas_added_mass(i_strut, i_mass+1) = {load(sprintf('frf_data_exc_strut_%i_realigned_vib_table_%im.mat', i_strut, i_mass), 't', 'Va', 'Vs', 'de')};
end
end
The window win and the frequency vector f are defined.
% Sampling Time [s]
Ts = (meas_added_mass{1,1}.t(end) - (meas_added_mass{1,1}.t(1)))/(length(meas_added_mass{1,1}.t)-1);
% Hannning Windows
win = hanning(ceil(1/Ts));
% And we get the frequency vector
[~, f] = tfestimate(meas_added_mass{1,1}.Va, meas_added_mass{1,1}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);Finally the $6 \times 6$ transfer function matrices from $\bm{u}$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ and from $\bm{u}$ to $\bm{\tau}_m$ are identified:
%% DVF Plant (transfer function from u to dLm)
G_dL = {};
for i_mass = i_masses
G_dL(i_mass+1) = {zeros(length(f), 6, 6)};
for i_strut = 1:6
G_dL{i_mass+1}(:,:,i_strut) = tfestimate(meas_added_mass{i_strut, i_mass+1}.Va, meas_added_mass{i_strut, i_mass+1}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);
end
end
%% IFF Plant (transfer function from u to taum)
G_tau = {};
for i_mass = i_masses
G_tau(i_mass+1) = {zeros(length(f), 6, 6)};
for i_strut = 1:6
G_tau{i_mass+1}(:,:,i_strut) = tfestimate(meas_added_mass{i_strut, i_mass+1}.Va, meas_added_mass{i_strut, i_mass+1}.Vs, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);
end
endThe identified dynamics are then saved for further use.
save('data_frf/frf_vib_table_m.mat', 'f', 'Ts', 'G_tau', 'G_dL')Rigidification of the added payloads
- figure
%% Load Identification Data
meas_added_mass = {};
for i_strut = 1:6
meas_added_mass(i_strut) = {load(sprintf('frf_data_exc_strut_%i_spindle_1m_solid.mat', i_strut), 't', 'Va', 'Vs', 'de')};
end
The window win and the frequency vector f are defined.
% Sampling Time [s]
Ts = (meas_added_mass{1}.t(end) - (meas_added_mass{1}.t(1)))/(length(meas_added_mass{1}.t)-1);
% Hannning Windows
win = hanning(ceil(1/Ts));
% And we get the frequency vector
[~, f] = tfestimate(meas_added_mass{1}.Va, meas_added_mass{1}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);Finally the $6 \times 6$ transfer function matrices from $\bm{u}$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ and from $\bm{u}$ to $\bm{\tau}_m$ are identified:
%% DVF Plant (transfer function from u to dLm)
G_dL = zeros(length(f), 6, 6);
for i_strut = 1:6
G_dL(:,:,i_strut) = tfestimate(meas_added_mass{i_strut}.Va, meas_added_mass{i_strut}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);
end
%% IFF Plant (transfer function from u to taum)
G_tau = zeros(length(f), 6, 6);
for i_strut = 1:6
G_tau(:,:,i_strut) = tfestimate(meas_added_mass{i_strut}.Va, meas_added_mass{i_strut}.Vs, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);
endTransfer function from Actuators to Encoders
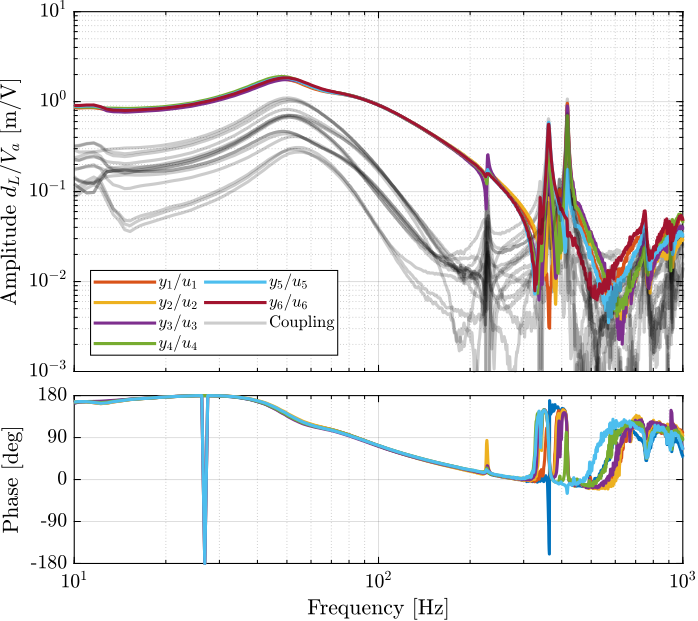
The transfer functions from $\bm{u}$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_{m}$ are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_comp_plant_payloads_dvf.
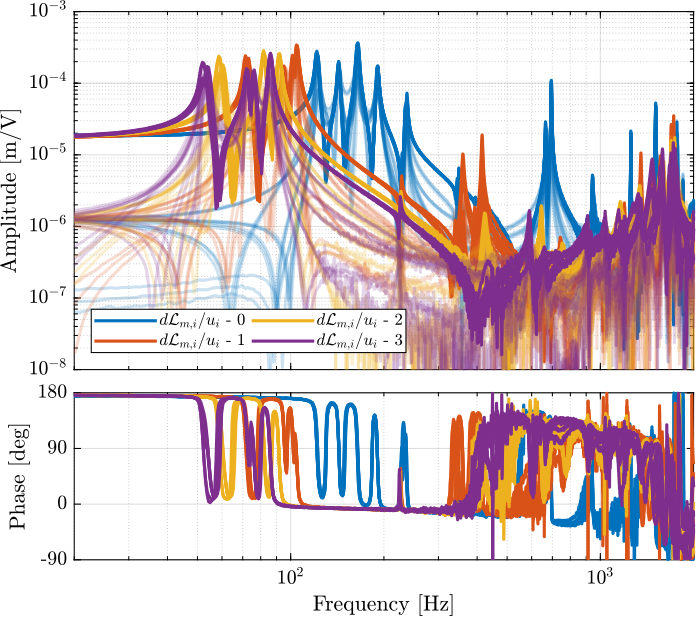
From Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_comp_plant_payloads_dvf, we can observe few things:
- The obtained dynamics is changing a lot between the case without mass and when there is at least one added mass.
- Between 1, 2 and 3 added masses, the dynamics is not much different, and it would be easier to design a controller only for these cases.
- The flexible modes of the top plate is first decreased a lot when the first mass is added (from 700Hz to 400Hz). This is due to the fact that the added mass is composed of two half cylinders which are not fixed together. Therefore is adds a lot of mass to the top plate without adding a lot of rigidity in one direction. When more than 1 mass layer is added, the half cylinders are added with some angles such that rigidity are added in all directions (see Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_picture_added_3_masses). In that case, the frequency of these flexible modes are increased. In practice, the payload should be one solid body, and we should not see a massive decrease of the frequency of this flexible mode.
- Flexible modes of the top plate are becoming less problematic as masses are added.
- First flexible mode of the strut at 230Hz is not much decreased when mass is added. However, its apparent amplitude is much decreased.
Transfer function from Actuators to Force Sensors
The transfer functions from $\bm{u}$ to $\bm{\tau}_{m}$ are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_comp_plant_payloads_iff.
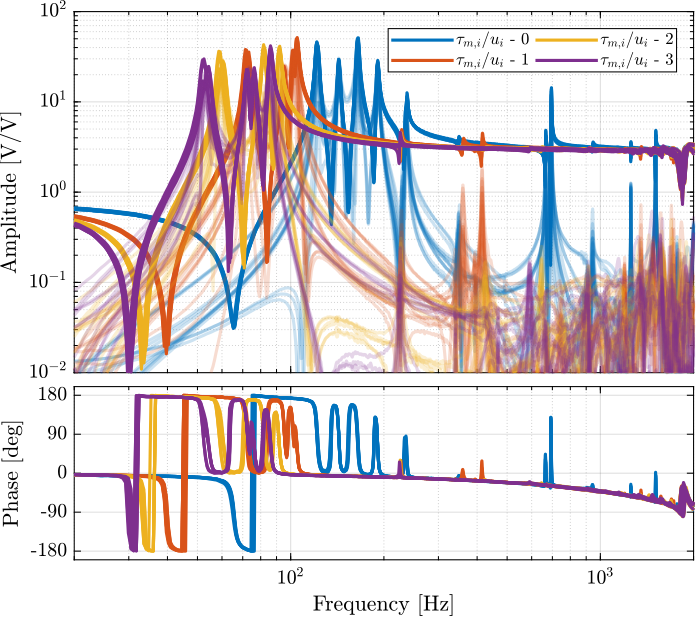
From Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_comp_plant_payloads_iff, we can see that for all added payloads, the transfer function from $\bm{u}$ to $\bm{\tau}_{m}$ always has alternating poles and zeros.
Coupling of the transfer function from Actuator to Encoders
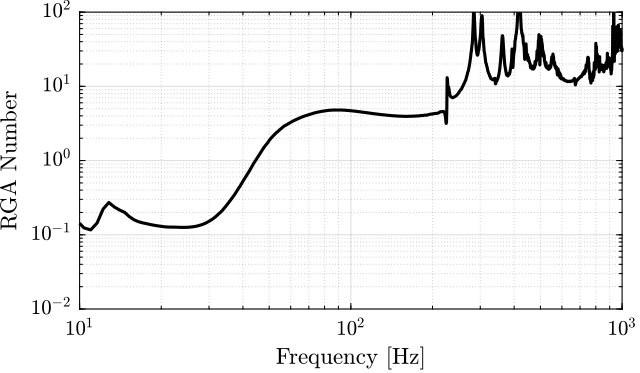
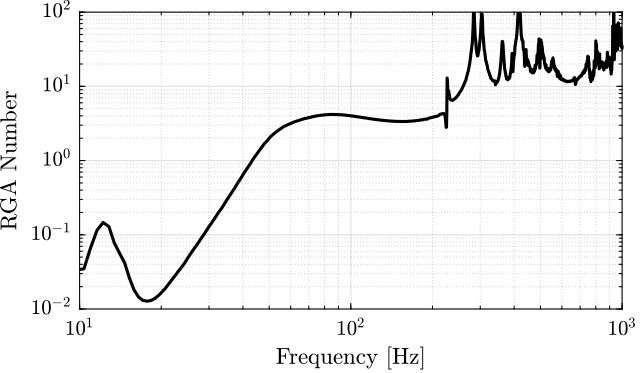
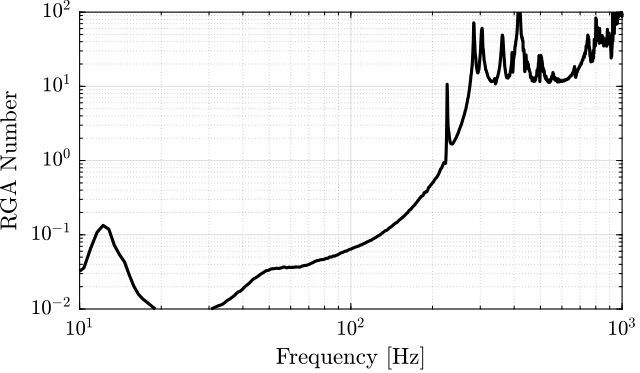
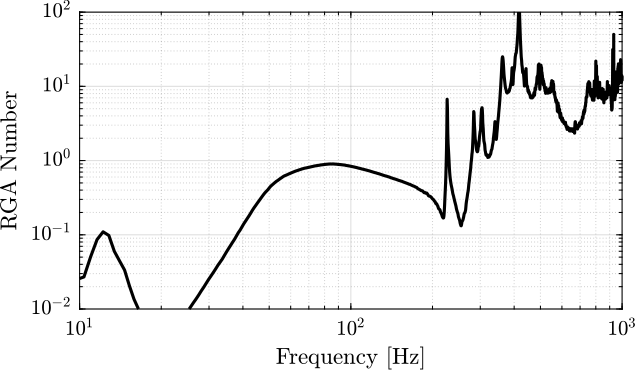
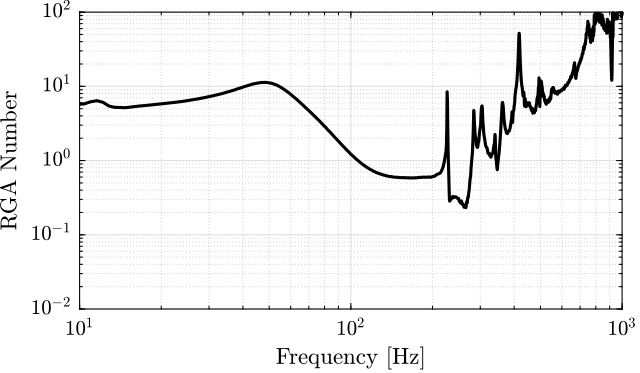
The RGA-number, which is a measure of the interaction in the system, is computed for the transfer function matrix from $\bm{u}$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ for all the payloads. The obtained numbers are compared in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_rga_num_ol_masses.
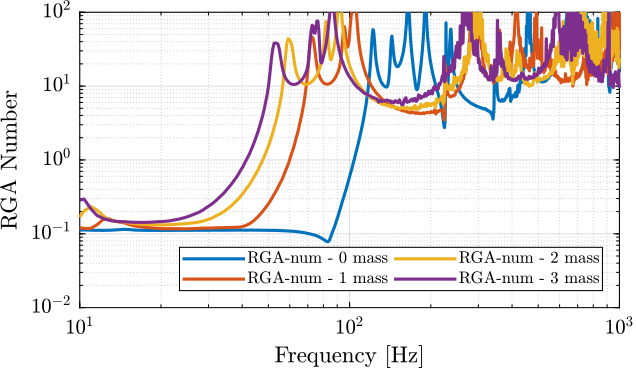
From Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_rga_num_ol_masses, it is clear that the coupling is quite large starting from the first suspension mode of the nano-hexapod. Therefore, is the payload's mass is increase, the coupling in the system start to become unacceptably large at lower frequencies.
Comparison with the Simscape model
<<sec:test_nhexa_added_mass_simscape>>
Introduction ignore
Let's now compare the identified dynamics with the Simscape model. We wish to verify if the Simscape model is still accurate for all the tested payloads.
System Identification
Let's initialize the simscape model with the nano-hexapod fixed on top of the vibration table.
%% Initialize Nano-Hexapod
n_hexapod = initializeNanoHexapodFinal('flex_bot_type', '4dof', ...
'flex_top_type', '4dof', ...
'motion_sensor_type', 'plates', ...
'actuator_type', '2dof');
support.type = 1; % On top of vibration tableFirst perform the identification for the transfer functions from $\bm{u}$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$:
%% Identify the DVF Plant (transfer function from u to dLm)
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/du'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Actuator Inputs
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/dL'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Encoders
%% Identification for all the added payloads
G_dL = {};
for i = i_masses
fprintf('i = %i\n', i)
payload.type = i; % Change the payload on the nano-hexapod
G_dL(i+1) = {exp(-s*frf_ol.Ts)*linearize(mdl, io, 0.0, options)};
end%% Identify the IFF Plant (transfer function from u to taum)
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/du'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Actuator Inputs
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fm'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Force Sensors
%% Identification for all the added payloads
G_tau = {};
for i = 0:3
fprintf('i = %i\n', i)
payload.type = i; % Change the payload on the nano-hexapod
G_tau(i+1) = {exp(-s*frf_ol.Ts)*linearize(mdl, io, 0.0, options)};
endThe identified dynamics are then saved for further use.
save('data_frf/sim_vib_table_m.mat', 'G_tau', 'G_dL')Transfer function from Actuators to Encoders
The measured FRF and the identified dynamics from $u_i$ to $d\mathcal{L}_{m,i}$ are compared in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_comp_masses_model_exp_dvf. A zoom near the "suspension" modes is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_comp_masses_model_exp_dvf_zoom.
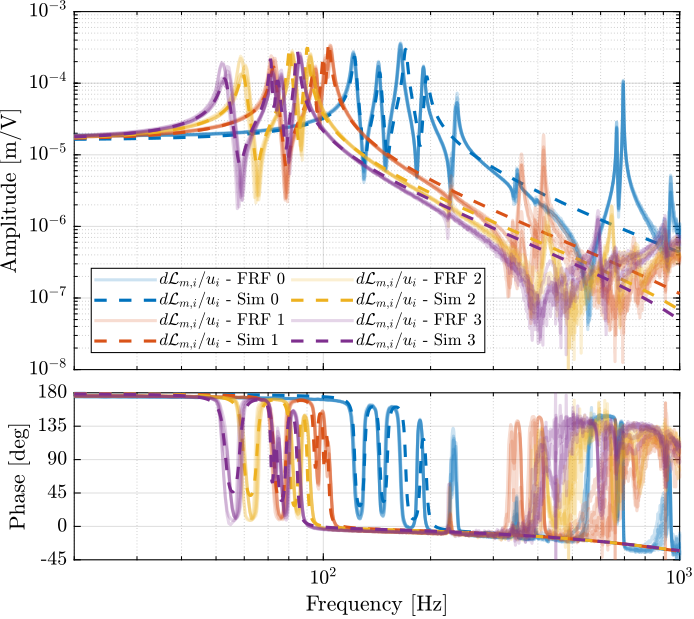
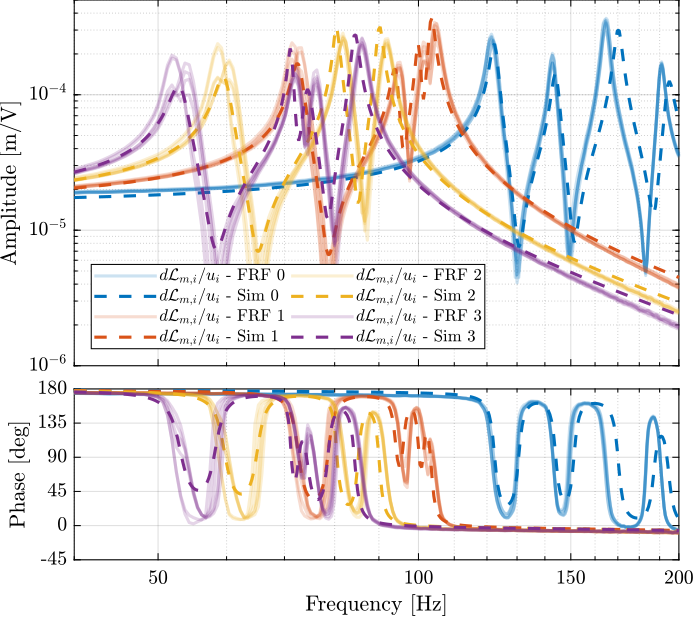
The Simscape model is very accurately representing the measured dynamics up. Only the flexible modes of the struts and of the top plate are not represented here as these elements are modelled as rigid bodies.
Transfer function from Actuators to Force Sensors
The measured FRF and the identified dynamics from $u_i$ to $\tau_{m,i}$ are compared in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_comp_masses_model_exp_iff. A zoom near the "suspension" modes is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_comp_masses_model_exp_iff_zoom.
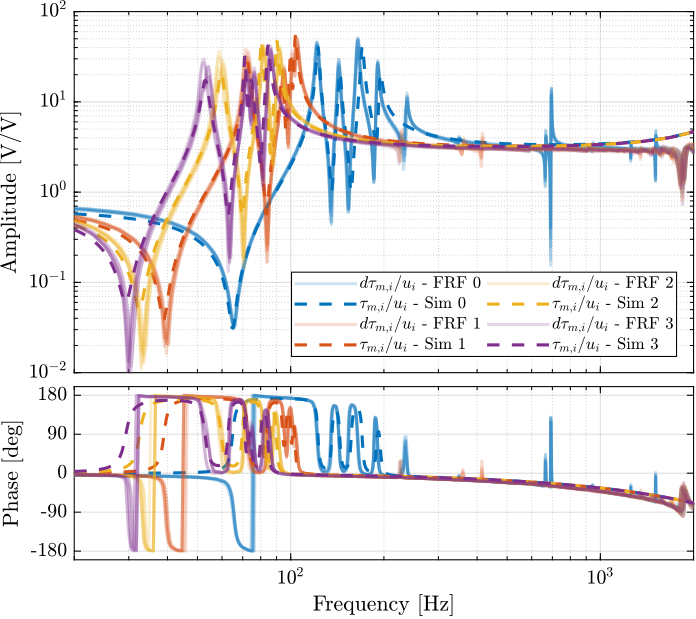
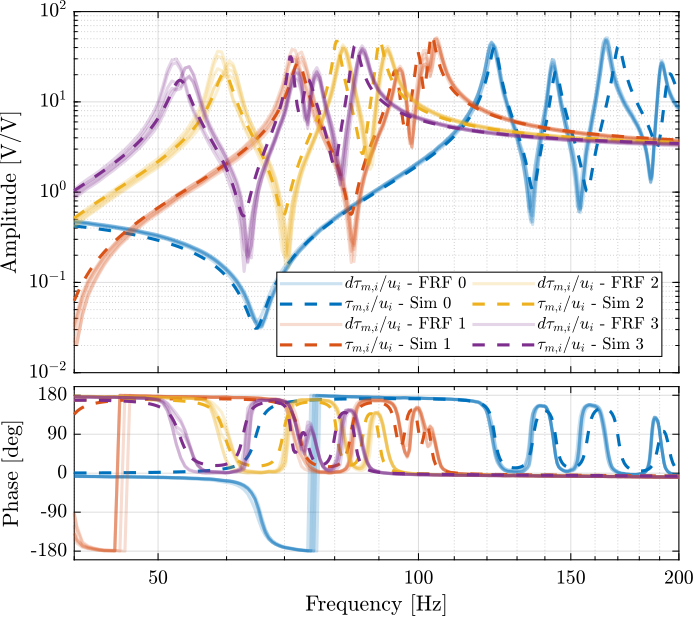
Integral Force Feedback Controller
<<sec:test_nhexa_robust_iff>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, we wish to develop the Integral Force Feedback controller that is robust with respect to the added payload.
Robust IFF Controller
Based on the measured FRF from $\bm{u}$ to $\bm{\tau}_{m}$, the following IFF controller is developed:
%% IFF Controller
Kiff_g1 = -(1/(s + 2*pi*20))*... % LPF: provides integral action above 20[Hz]
(s/(s + 2*pi*20))*... % HPF: limit low frequency gain
(1/(1 + s/2/pi/400)); % LPF: more robust to high frequency resonancesThen, the Root Locus plot of Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_iff_root_locus_masses is used to estimate the optimal gain. This Root Locus plot is computed from the Simscape model.
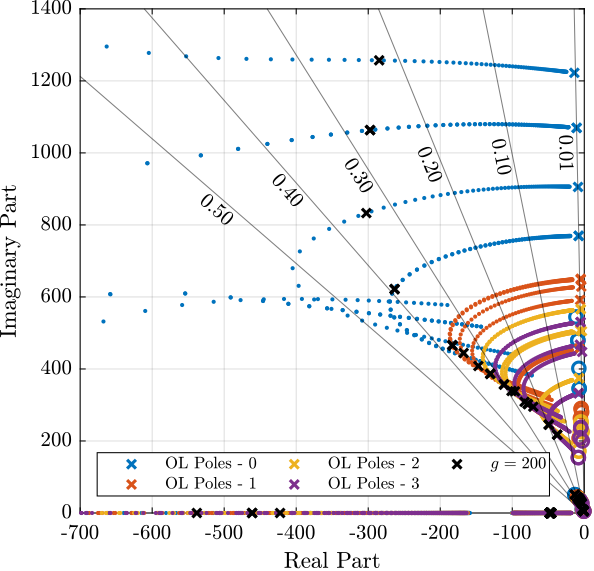
The found optimal IFF controller is:
%% Optimal controller
g_opt = 2e2;
Kiff = g_opt*Kiff_g1*eye(6);It is saved for further use.
save('data_sim/Kiff_robust_opt.mat', 'Kiff')The corresponding experimental loop gains are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_iff_loop_gain_masses.
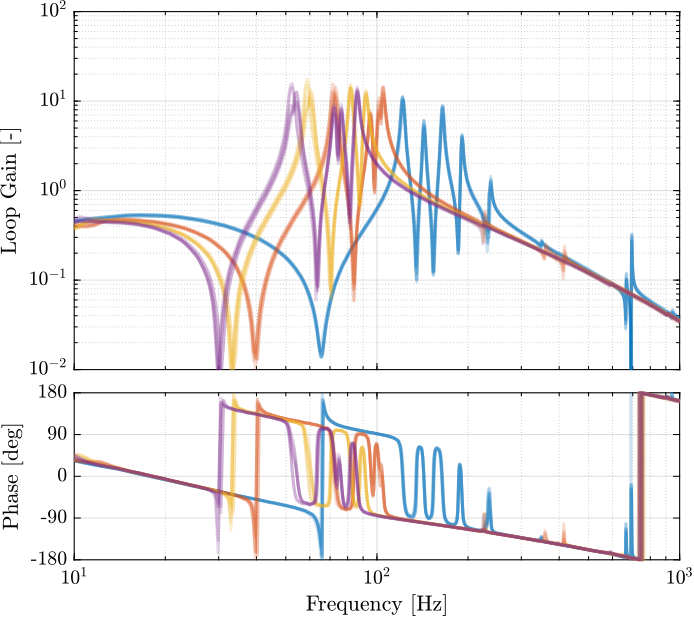
Based on the above analysis:
- The same IFF controller can be used to damp the suspension modes for all payload conditions
- The IFF controller should be robust
Estimated Damped Plant from the Simscape model
Let's initialize the simscape model with the nano-hexapod fixed on top of the vibration table.
%% Initialize the Simscape model in closed loop
n_hexapod = initializeNanoHexapodFinal('flex_bot_type', '4dof', ...
'flex_top_type', '4dof', ...
'motion_sensor_type', 'plates', ...
'actuator_type', '2dof', ...
'controller_type', 'iff');
support.type = 1; % On top of vibration tableAnd Load the IFF controller.
Finally, let's identify the damped plant from $\bm{u}^\prime$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ for all payloads.
%% Identify the (damped) transfer function from u to dLm
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/du'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Actuator Inputs
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/dL'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Plate Displacement (encoder)
%% Identify for all add masses
G_dL = {};
for i = i_masses
payload.type = i;
G_dL(i+1) = {exp(-s*frf_ol.Ts)*linearize(mdl, io, 0.0, options)};
endThe identified dynamics are then saved for further use.
save('data_frf/sim_iff_vib_table_m.mat', 'G_dL');%% Load the identified dynamics
sim_iff = load('sim_iff_vib_table_m.mat', 'G_dL');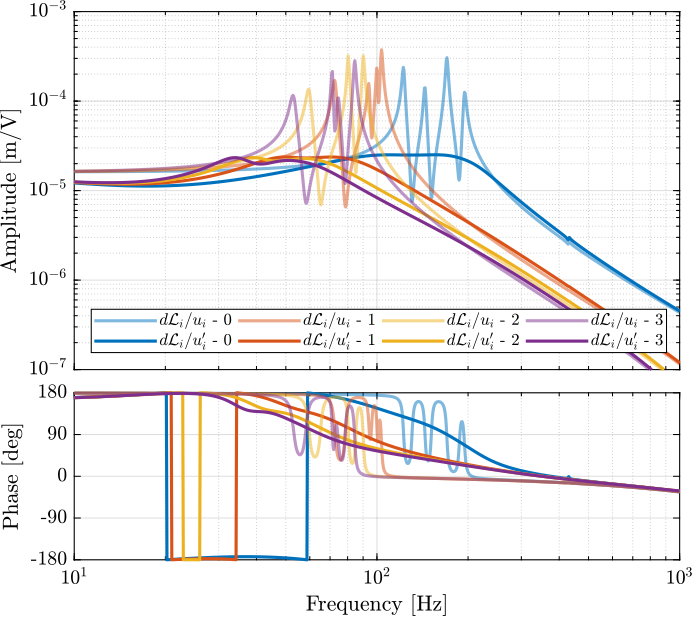
Compute the identified FRF with IFF
Several experimental identifications are done in order to identify the dynamics from $\bm{u}^\prime$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ with the robust IFF controller implemented and with various payloads.
The following data are loaded:
Va: the excitation voltage for the damped plant (corresponding to $u^\prime_i$)de: the measured motion by the 6 encoders (corresponding to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$)
%% Load Identification Data
meas_added_mass = {};
for i_mass = i_masses
for i_strut = 1:6
meas_iff_mass(i_strut, i_mass+1) = {load(sprintf('frf_data_exc_strut_%i_iff_vib_table_%im.mat', i_strut, i_mass), 't', 'Va', 'de')};
end
end
The window win and the frequency vector f are defined.
% Sampling Time [s]
Ts = (meas_iff_mass{1,1}.t(end) - (meas_iff_mass{1,1}.t(1)))/(length(meas_iff_mass{1,1}.t)-1);
% Hannning Windows
win = hanning(ceil(1/Ts));
% And we get the frequency vector
[~, f] = tfestimate(meas_iff_mass{1,1}.Va, meas_iff_mass{1,1}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);Finally the $6 \times 6$ transfer function matrix from $\bm{u}^\prime$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ is estimated:
%% DVF Plant (transfer function from u to dLm)
G_dL = {};
for i_mass = i_masses
G_dL(i_mass+1) = {zeros(length(f), 6, 6)};
for i_strut = 1:6
G_dL{i_mass+1}(:,:,i_strut) = tfestimate(meas_iff_mass{i_strut, i_mass+1}.Va, meas_iff_mass{i_strut, i_mass+1}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);
end
endThe identified dynamics are then saved for further use.
save('mat/frf_iff_vib_table_m.mat', 'f', 'Ts', 'G_dL');Comparison of the measured FRF and the Simscape model
The following figures are computed:
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_damped_iff_plant_meas_frf: the measured damped FRF are displayed
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_comp_undamped_damped_plant_meas_frf: the open-loop and damped FRF are compared (diagonal elements)
- Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_comp_iff_plant_frf_sim: the obtained damped FRF is compared with the identified damped from using the Simscape model
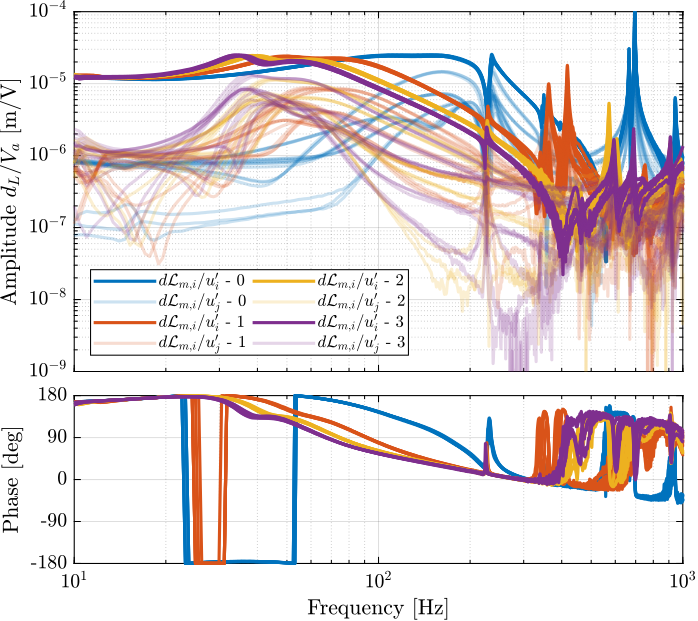
The IFF control strategy effectively damps all the suspensions modes of the nano-hexapod whatever the payload is. The obtained plant is easier to control (provided the flexible modes of the top platform are well damped).
Change of coupling with IFF
Let's see how the Integral Force Feedback is changing the interaction in the system.
To study that, the RGA-number are computed both for the undamped plant and for the damped plant using IFF.
Both are compared in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_rga_num_ol_iff_masses.
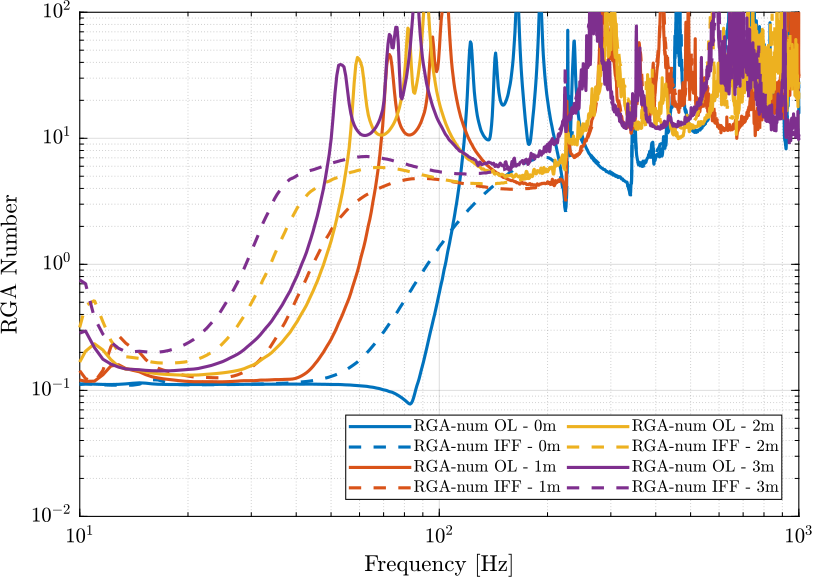
From Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_picture_unbalanced_payload, it is clear that the interaction in the system is largest near the resonances. The Integral Force Feedback controller, by reducing the amplitude at the resonances, also reduces the coupling near these resonances. It however increases the coupling bellow the frequency of the suspension modes.
Un-Balanced mass
Introduction
In this section, we wish to see if a payload with a center of mass not aligned with the symmetry axis of the nano-hexapod could cause any issue.
To study that, the payload shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_picture_unbalanced_payload is used.
Compute the identified FRF with IFF
The following data are loaded:
Va: the excitation voltage for the damped plant (corresponding to $u^\prime_i$)de: the measured motion by the 6 encoders (corresponding to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$)
%% Load Identification Data
meas_added_mass = {zeros(6,1)};
for i_strut = 1:6
meas_iff_mass(i_strut) = {load(sprintf('frf_data_exc_strut_%i_iff_vib_table_1m_unbalanced.mat', i_strut), 't', 'Va', 'de')};
end
The window win and the frequency vector f are defined.
% Sampling Time [s]
Ts = (meas_iff_mass{1}.t(end) - (meas_iff_mass{1}.t(1)))/(length(meas_iff_mass{1}.t)-1);
% Hannning Windows
win = hanning(ceil(1/Ts));
% And we get the frequency vector
[~, f] = tfestimate(meas_iff_mass{1}.Va, meas_iff_mass{1}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);Finally the $6 \times 6$ transfer function matrix from $\bm{u}^\prime$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ is estimated:
%% DVF Plant (transfer function from u to dLm)
G_dL = zeros(length(f), 6, 6);
for i_strut = 1:6
G_dL(:,:,i_strut) = tfestimate(meas_iff_mass{i_strut}.Va, meas_iff_mass{i_strut}.de, win, Noverlap, Nfft, 1/Ts);
endThe identified dynamics are then saved for further use.
save('data_frf/frf_iff_unbalanced_vib_table_m.mat', 'f', 'Ts', 'G_dL');Effect of an unbalanced payload
The transfer functions from $u_i$ to $d\mathcal{L}_i$ are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_frf_damp_unbalanced_mass. Due to the unbalanced payload, the system is not symmetrical anymore, and therefore each of the diagonal elements are not equal. This is due to the fact that each strut is not affected by the same inertia.
Conclusion
In this section, the dynamics of the nano-hexapod with the encoders fixed to the plates is studied.
It has been found that:
- The measured dynamics is in agreement with the dynamics of the simscape model, up to the flexible modes of the top plate. See figures ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff_comp_simscape and ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff_comp_offdiag_simscape for the transfer function to the force sensors and Figures ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_dvf_comp_simscape and ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plates_dvf_comp_offdiag_simscape for the transfer functions to the encoders
- The Integral Force Feedback strategy is very effective in damping the suspension modes of the nano-hexapod (Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_enc_plant_plates_effect_iff).
- The transfer function from $\bm{u}^\prime$ to $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$ show nice dynamical properties and is a much better candidate for the high-authority-control than when the encoders were fixed to the struts. At least up to the flexible modes of the top plate, the diagonal elements of the transfer function matrix have alternating poles and zeros, and the phase is moving smoothly. Only the flexible modes of the top plates seems to be problematic for control.
Decentralized High Authority Control with Integral Force Feedback
<<sec:test_nhexa_decentralized_hac_iff>>
Introduction ignore
In this section is studied the HAC-IFF architecture for the Nano-Hexapod. More precisely:
- The LAC control is a decentralized integral force feedback as studied in Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff
- The HAC control is a decentralized controller working in the frame of the struts
The corresponding control architecture is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_control_architecture_hac_iff_struts with:
- $\bm{r}_{\mathcal{X}_n}$: the $6 \times 1$ reference signal in the cartesian frame
- $\bm{r}_{d\mathcal{L}}$: the $6 \times 1$ reference signal transformed in the frame of the struts thanks to the inverse kinematic
- $\bm{\epsilon}_{d\mathcal{L}}$: the $6 \times 1$ length error of the 6 struts
- $\bm{u}^\prime$: input of the damped plant
- $\bm{u}$: generated DAC voltages
- $\bm{\tau}_m$: measured force sensors
- $d\bm{\mathcal{L}}_m$: measured displacement of the struts by the encoders
\definecolor{instrumentation}{rgb}{0, 0.447, 0.741}
\definecolor{mechanics}{rgb}{0.8500, 0.325, 0.098}
\definecolor{control}{rgb}{0.4660, 0.6740, 0.1880}
\begin{tikzpicture}
% Blocs
\node[block={3.0cm}{2.0cm}, fill=black!20!white] (P) {Plant};
\coordinate[] (inputF) at ($(P.south west)!0.5!(P.north west)$);
\coordinate[] (outputF) at ($(P.south east)!0.2!(P.north east)$);
\coordinate[] (outputL) at ($(P.south east)!0.8!(P.north east)$);
\node[block, below=0.4 of P, fill=control!20!white] (Kiff) {$\bm{K}_\text{IFF}$};
\node[block, left=0.8 of inputF, fill=instrumentation!20!white] (pd200) {\tiny PD200};
\node[addb, left=0.8 of pd200, fill=control!20!white] (addF) {};
\node[block, left=0.8 of addF, fill=control!20!white] (K) {$\bm{K}_\mathcal{L}$};
\node[addb={+}{}{-}{}{}, left=0.8 of K, fill=control!20!white] (subr) {};
\node[block, align=center, left= of subr, fill=control!20!white] (J) {\tiny Inverse\\\tiny Kinematics};
% Connections and labels
\draw[->] (outputF) -- ++(1.0, 0) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}_m$};
\draw[->] ($(outputF) + (0.6, 0)$)node[branch]{} |- (Kiff.east);
\draw[->] (Kiff.west) -| (addF.south);
\draw[->] (addF.east) -- (pd200.west) node[above left]{$\bm{u}$};
\draw[->] (pd200.east) -- (inputF) node[above left]{$\bm{u}_a$};
\draw[->] (outputL) -- ++(1.0, 0) node[below left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}_m}$};
\draw[->] ($(outputL) + (0.6, 0)$)node[branch]{} -- ++(0, 1) -| (subr.north);
\draw[->] (subr.east) -- (K.west) node[above left]{$\bm{\epsilon}_{d\mathcal{L}}$};
\draw[->] (K.east) -- (addF.west) node[above left]{$\bm{u}^\prime$};
\draw[->] (J.east) -- (subr.west) node[above left]{$\bm{r}_{d\mathcal{L}}$};
\draw[<-] (J.west)node[above left]{$\bm{r}_{\mathcal{X}_n}$} -- ++(-1, 0);
\end{tikzpicture}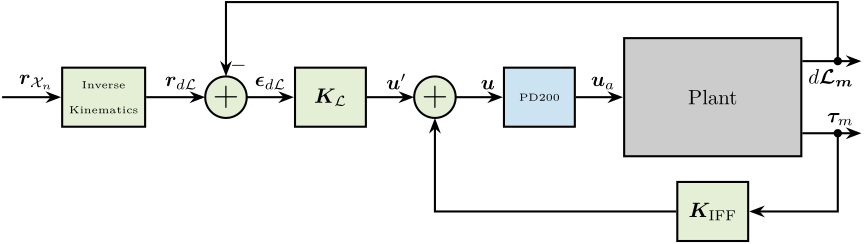
This part is structured as follow:
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_hac_iff_struts_ref_track: some reference tracking tests are performed
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_hac_iff_struts_controller: the decentralized high authority controller is tuned using the Simscape model and is implemented and tested experimentally
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_interaction_analysis: an interaction analysis is performed, from which the best decoupling strategy can be determined
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_robust_hac_design: Robust High Authority Controller are designed
Reference Tracking - Trajectories
<<sec:test_nhexa_hac_iff_struts_ref_track>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, several trajectories representing the wanted pose (position and orientation) of the top platform with respect to the bottom platform are defined.
These trajectories will be used to test the HAC-LAC architecture.
In order to transform the wanted pose to the wanted displacement of the 6 struts, the inverse kinematic is required. As a first approximation, the Jacobian matrix $\bm{J}$ can be used instead of using the full inverse kinematic equations.
Therefore, the control architecture with the input trajectory $\bm{r}_{\mathcal{X}_n}$ is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_control_architecture_hac_iff_L.
\definecolor{instrumentation}{rgb}{0, 0.447, 0.741}
\definecolor{mechanics}{rgb}{0.8500, 0.325, 0.098}
\definecolor{control}{rgb}{0.4660, 0.6740, 0.1880}
\begin{tikzpicture}
% Blocs
\node[block={3.0cm}{2.0cm}, fill=black!20!white] (P) {Plant};
\coordinate[] (inputF) at ($(P.south west)!0.5!(P.north west)$);
\coordinate[] (outputF) at ($(P.south east)!0.2!(P.north east)$);
\coordinate[] (outputL) at ($(P.south east)!0.8!(P.north east)$);
\node[block, below=0.4 of P, fill=control!20!white] (Kiff) {$\bm{K}_\text{IFF}$};
\node[block, left=0.8 of inputF, fill=instrumentation!20!white] (pd200) {\tiny PD200};
\node[addb, left=0.8 of pd200, fill=control!20!white] (addF) {};
\node[block, left=0.8 of addF, fill=control!20!white] (K) {$\bm{K}_\mathcal{L}$};
\node[addb={+}{}{-}{}{}, left=0.8 of K, fill=control!20!white] (subr) {};
\node[block, align=center, left= of subr, fill=control!20!white] (J) {$\bm{J}$};
% Connections and labels
\draw[->] (outputF) -- ++(1.0, 0) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}_m$};
\draw[->] ($(outputF) + (0.6, 0)$)node[branch]{} |- (Kiff.east);
\draw[->] (Kiff.west) -| (addF.south);
\draw[->] (addF.east) -- (pd200.west) node[above left]{$\bm{u}$};
\draw[->] (pd200.east) -- (inputF) node[above left]{$\bm{u}_a$};
\draw[->] (outputL) -- ++(1.0, 0) node[below left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}_m}$};
\draw[->] ($(outputL) + (0.6, 0)$)node[branch]{} -- ++(0, 1) -| (subr.north);
\draw[->] (subr.east) -- (K.west) node[above left]{$\bm{\epsilon}_{d\mathcal{L}}$};
\draw[->] (K.east) -- (addF.west) node[above left]{$\bm{u}^\prime$};
\draw[->] (J.east) -- (subr.west) node[above left]{$\bm{r}_{d\mathcal{L}}$};
\draw[<-] (J.west)node[above left]{$\bm{r}_{\mathcal{X}_n}$} -- ++(-1, 0);
\end{tikzpicture}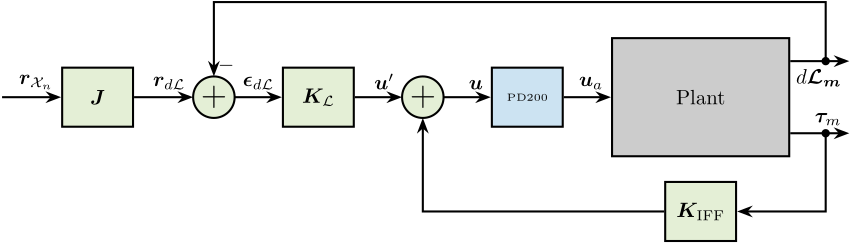
In the following sections, several reference trajectories are defined:
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_yz_scans: simple scans in the Y-Z plane
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_tilt_scans: scans in tilt are performed
- Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_nass_scans: scans with X-Y-Z translations in order to draw the word "NASS"
Y-Z Scans
<<sec:test_nhexa_yz_scans>>
A function generateYZScanTrajectory has been developed in order to easily generate scans in the Y-Z plane.
For instance, the following generated trajectory is represented in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_yz_scan_example_trajectory_yz_plane.
%% Generate the Y-Z trajectory scan
Rx_yz = generateYZScanTrajectory(...
'y_tot', 4e-6, ... % Length of Y scans [m]
'z_tot', 4e-6, ... % Total Z distance [m]
'n', 5, ... % Number of Y scans
'Ts', 1e-3, ... % Sampling Time [s]
'ti', 1, ... % Time to go to initial position [s]
'tw', 0, ... % Waiting time between each points [s]
'ty', 0.6, ... % Time for a scan in Y [s]
'tz', 0.2); % Time for a scan in Z [s]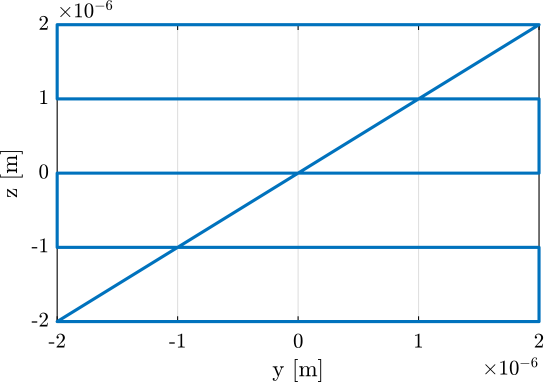
The Y and Z positions as a function of time are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_yz_scan_example_trajectory.
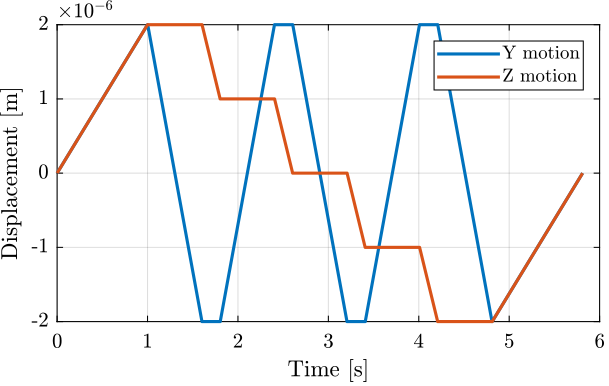
Using the Jacobian matrix, it is possible to compute the wanted struts lengths as a function of time:
\begin{equation} \bm{r}_{d\mathcal{L}} = \bm{J} \bm{r}_{\mathcal{X}_n} \end{equation}%% Compute the reference in the frame of the legs
dL_ref = [J*Rx_yz(:, 2:7)']';The reference signal for the strut length is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_yz_scan_example_trajectory_struts.
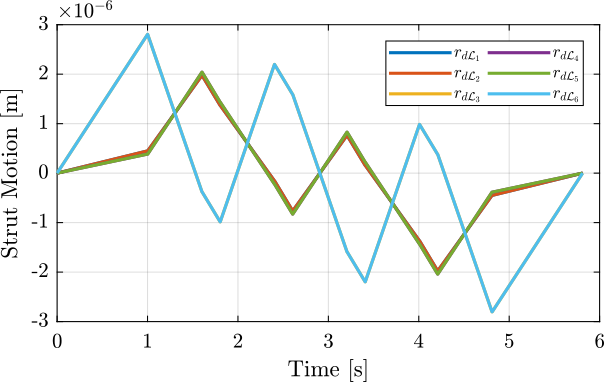
Tilt Scans
<<sec:test_nhexa_tilt_scans>>
A function generalSpiralAngleTrajectory has been developed in order to easily generate $R_x,R_y$ tilt scans.
For instance, the following generated trajectory is represented in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_tilt_scan_example_trajectory.
%% Generate the "tilt-spiral" trajectory scan
R_tilt = generateSpiralAngleTrajectory(...
'R_tot', 20e-6, ... % Total Tilt [ad]
'n_turn', 5, ... % Number of scans
'Ts', 1e-3, ... % Sampling Time [s]
't_turn', 1, ... % Turn time [s]
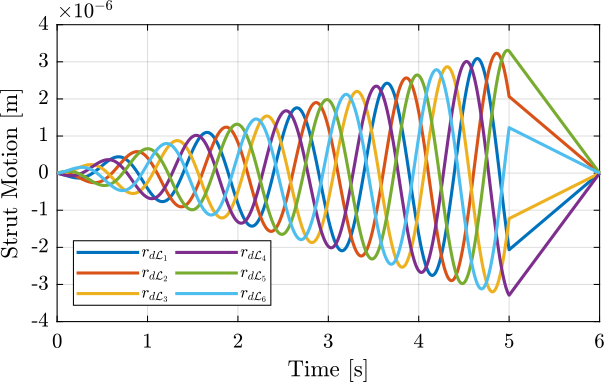
't_end', 1); % End time to go back to zero [s]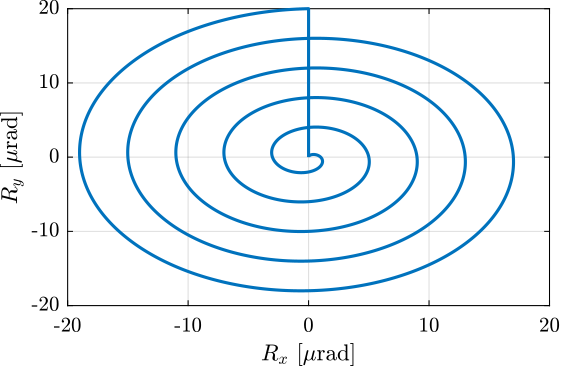
The reference signal for the strut length is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_tilt_scan_example_trajectory_struts.
"NASS" reference path
<<sec:test_nhexa_nass_scans>> In this section, a reference path that "draws" the work "NASS" is developed.
First, a series of points representing each letter are defined. Between each letter, a negative Z motion is performed.
%% List of points that draws "NASS"
ref_path = [ ...
0, 0,0; % Initial Position
0,0,1; 0,4,1; 3,0,1; 3,4,1; % N
3,4,0; 4,0,0; % Transition
4,0,1; 4,3,1; 5,4,1; 6,4,1; 7,3,1; 7,2,1; 4,2,1; 4,3,1; 5,4,1; 6,4,1; 7,3,1; 7,0,1; % A
7,0,0; 8,0,0; % Transition
8,0,1; 11,0,1; 11,2,1; 8,2,1; 8,4,1; 11,4,1; % S
11,4,0; 12,0,0; % Transition
12,0,1; 15,0,1; 15,2,1; 12,2,1; 12,4,1; 15,4,1; % S
15,4,0;
];
%% Center the trajectory arround zero
ref_path = ref_path - (max(ref_path) - min(ref_path))/2;
%% Define the X-Y-Z cuboid dimensions containing the trajectory
X_max = 10e-6;
Y_max = 4e-6;
Z_max = 2e-6;
ref_path = ([X_max, Y_max, Z_max]./max(ref_path)).*ref_path; % [m]
Then, using the generateXYZTrajectory function, the $6 \times 1$ trajectory signal is computed.
%% Generating the trajectory
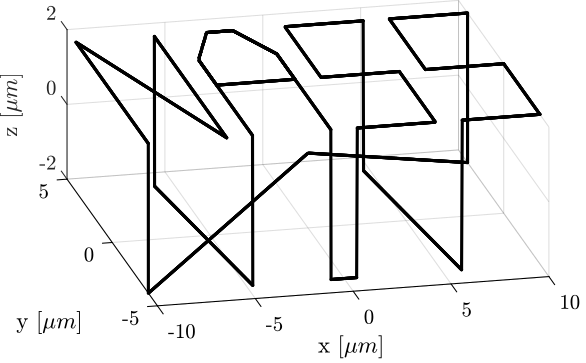
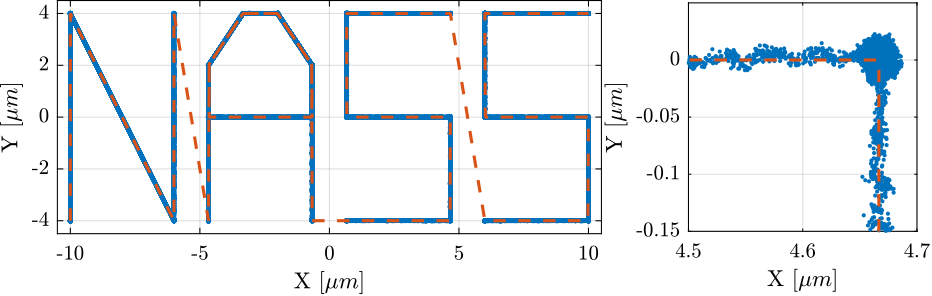
Rx_nass = generateXYZTrajectory('points', ref_path);The trajectory in the X-Y plane is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_ref_track_test_nass (the transitions between the letters are removed).
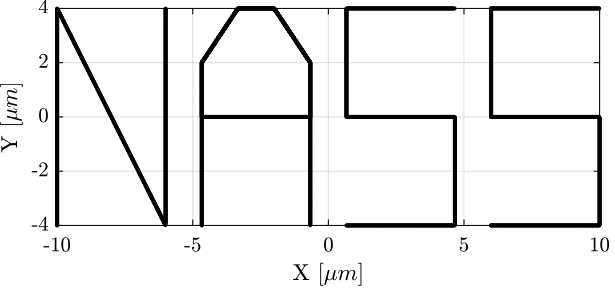
It can also be better viewed in a 3D representation as in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_ref_track_test_nass_3d.
First Basic High Authority Controller
<<sec:test_nhexa_hac_iff_struts_controller>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, a simple decentralized high authority controller $\bm{K}_{\mathcal{L}}$ is developed to work without any payload.
The diagonal controller is tuned using classical Loop Shaping in Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_hac_iff_no_payload_tuning. The stability is verified in Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_hac_iff_no_payload_stability using the Simscape model.
HAC Controller
<<sec:test_nhexa_hac_iff_no_payload_tuning>>
Let's first try to design a first decentralized controller with:
- a bandwidth of 100Hz
- sufficient phase margin
- simple and understandable components
After some very basic and manual loop shaping, A diagonal controller is developed. Each diagonal terms are identical and are composed of:
- A lead around 100Hz
- A first order low pass filter starting at 200Hz to add some robustness to high frequency modes
- A notch at 700Hz to cancel the flexible modes of the top plate
- A pure integrator
%% Lead to increase phase margin
a = 2; % Amount of phase lead / width of the phase lead / high frequency gain
wc = 2*pi*100; % Frequency with the maximum phase lead [rad/s]
H_lead = (1 + s/(wc/sqrt(a)))/(1 + s/(wc*sqrt(a)));
%% Low Pass filter to increase robustness
H_lpf = 1/(1 + s/2/pi/200);
%% Notch at the top-plate resonance
gm = 0.02;
xi = 0.3;
wn = 2*pi*700;
H_notch = (s^2 + 2*gm*xi*wn*s + wn^2)/(s^2 + 2*xi*wn*s + wn^2);
%% Decentralized HAC
Khac_iff_struts = -(1/(2.87e-5)) * ... % Gain
H_lead * ... % Lead
H_notch * ... % Notch
(2*pi*100/s) * ... % Integrator
eye(6); % 6x6 DiagonalThis controller is saved for further use.
save('data_sim/Khac_iff_struts.mat', 'Khac_iff_struts')The experimental loop gain is computed and shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_loop_gain_hac_iff_struts.
L_hac_iff_struts = pagemtimes(permute(frf_iff.G_dL{1}, [2 3 1]), squeeze(freqresp(Khac_iff_struts, frf_iff.f, 'Hz')));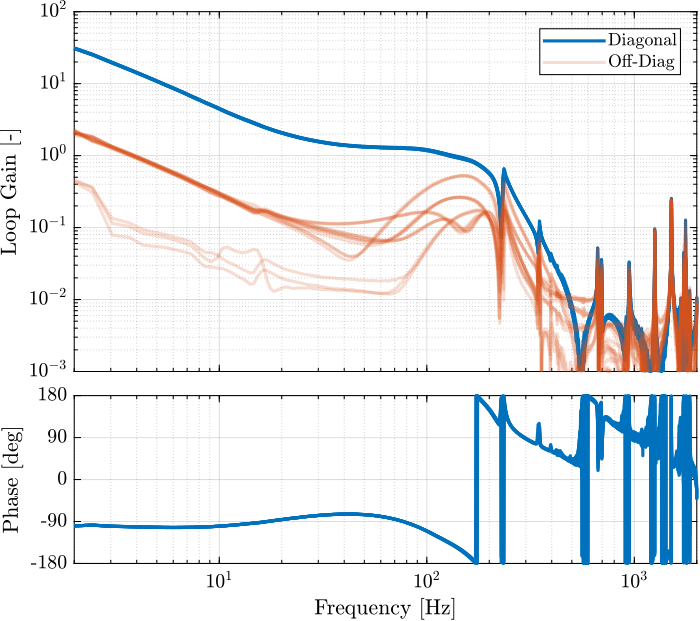
Verification of the Stability using the Simscape model
<<sec:test_nhexa_hac_iff_no_payload_stability>>
The HAC-IFF control strategy is implemented using Simscape.
%% Initialize the Simscape model in closed loop
n_hexapod = initializeNanoHexapodFinal('flex_bot_type', '4dof', ...
'flex_top_type', '4dof', ...
'motion_sensor_type', 'plates', ...
'actuator_type', 'flexible', ...
'controller_type', 'hac-iff-struts');%% Identify the (damped) transfer function from u to dLm
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/du'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Actuator Inputs
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/dL'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Plate Displacement (encoder)We identify the closed-loop system.
%% Identification
Gd_iff_hac_opt = linearize(mdl, io, 0.0, options);And verify that it is indeed stable.
%% Verify the stability
isstable(Gd_iff_hac_opt)1
Experimental Validation
Both the Integral Force Feedback controller (developed in Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_enc_plates_iff) and the high authority controller working in the frame of the struts (developed in Section ref:sec:test_nhexa_hac_iff_struts_controller) are implemented experimentally.
Two reference tracking experiments are performed to evaluate the stability and performances of the implemented control.
%% Load the experimental data
load('hac_iff_struts_yz_scans.mat', 't', 'de')The position of the top-platform is estimated using the Jacobian matrix:
%% Pose of the top platform from the encoder values
load('jacobian.mat', 'J');
Xe = [inv(J)*de']';%% Generate the Y-Z trajectory scan
Rx_yz = generateYZScanTrajectory(...
'y_tot', 4e-6, ... % Length of Y scans [m]
'z_tot', 8e-6, ... % Total Z distance [m]
'n', 5, ... % Number of Y scans
'Ts', 1e-3, ... % Sampling Time [s]
'ti', 1, ... % Time to go to initial position [s]
'tw', 0, ... % Waiting time between each points [s]
'ty', 0.6, ... % Time for a scan in Y [s]
'tz', 0.2); % Time for a scan in Z [s]The reference path as well as the measured position are partially shown in the Y-Z plane in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_yz_scans_exp_results_first_K.
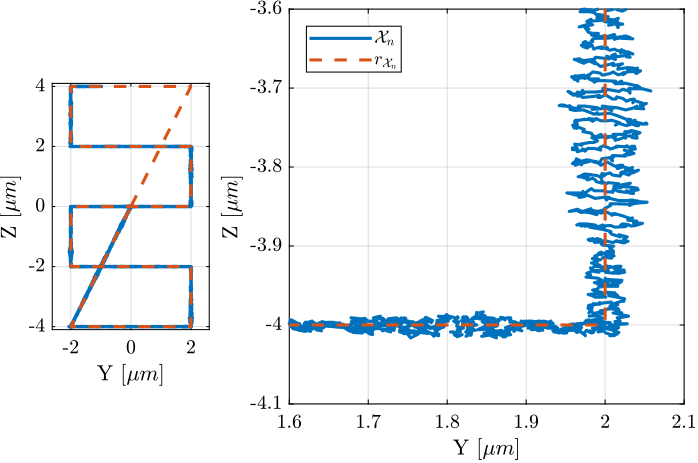
It is clear from Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_yz_scans_exp_results_first_K that the position of the nano-hexapod effectively tracks to reference signal. However, oscillations with amplitudes as large as 50nm can be observe.
It turns out that the frequency of these oscillations is 100Hz which is corresponding to the crossover frequency of the High Authority Control loop. This clearly indicates poor stability margins. In the next section, the controller is re-designed to improve the stability margins.
Controller with increased stability margins
The High Authority Controller is re-designed in order to improve the stability margins.
%% Lead
a = 5; % Amount of phase lead / width of the phase lead / high frequency gain
wc = 2*pi*110; % Frequency with the maximum phase lead [rad/s]
H_lead = (1 + s/(wc/sqrt(a)))/(1 + s/(wc*sqrt(a)));
%% Low Pass Filter
H_lpf = 1/(1 + s/2/pi/300);
%% Notch
gm = 0.02;
xi = 0.5;
wn = 2*pi*700;
H_notch = (s^2 + 2*gm*xi*wn*s + wn^2)/(s^2 + 2*xi*wn*s + wn^2);
%% HAC Controller
Khac_iff_struts = -2.2e4 * ... % Gain
H_lead * ... % Lead
H_lpf * ... % Lead
H_notch * ... % Notch
(2*pi*100/s) * ... % Integrator
eye(6); % 6x6 DiagonalThe bode plot of the new loop gain is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_hac_iff_plates_exp_loop_gain_redesigned_K.
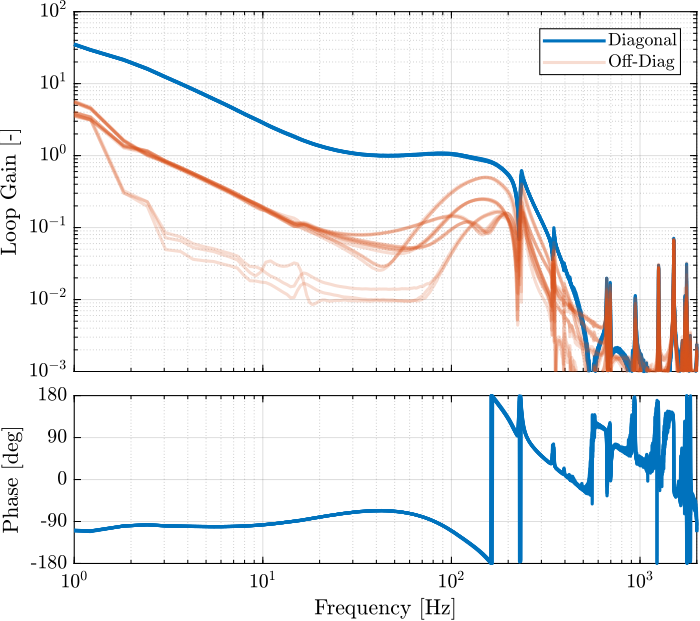
This new controller is implemented experimentally and several tracking tests are performed.
%% Load Measurements
load('hac_iff_more_lead_nass_scan.mat', 't', 'de')The pose of the top platform is estimated from the encoder position using the Jacobian matrix.
%% Compute the pose of the top platform
load('jacobian.mat', 'J');
Xe = [inv(J)*de']';The measured motion as well as the trajectory are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_nass_scans_first_test_exp.
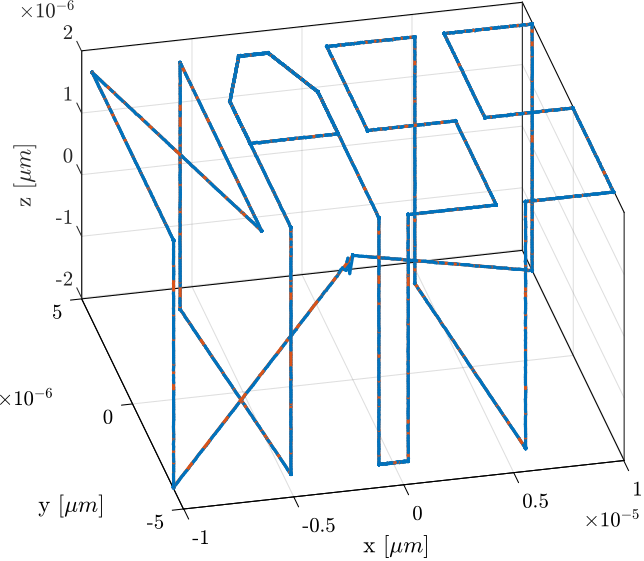
The trajectory and measured motion are also shown in the X-Y plane in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_ref_track_nass_exp_hac_iff_struts.
The orientation errors during all the scans are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_nass_ref_rx_ry.
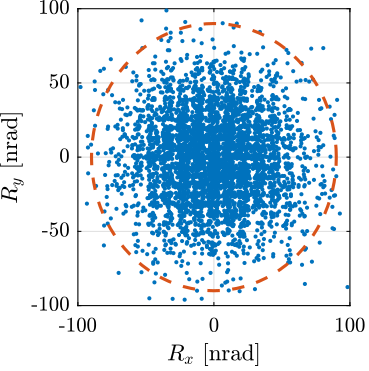
Using the updated High Authority Controller, the nano-hexapod can follow trajectories with high accuracy (the position errors are in the order of 50nm peak to peak, and the orientation errors 300nrad peak to peak).
Interaction Analysis and Decoupling
<<sec:test_nhexa_interaction_analysis>>
Introduction ignore
In this section, the interaction in the identified plant is estimated using the Relative Gain Array (RGA) Chap. 3.4.
Then, several decoupling strategies are compared for the nano-hexapod.
The RGA Matrix is defined as follow:
\begin{equation} \text{RGA}(G(f)) = G(f) \times (G(f)^{-1})^T \end{equation}Then, the RGA number is defined:
\begin{equation} \text{RGA-num}(f) = \| \text{I - RGA(G(f))} \|_{\text{sum}} \end{equation}In this section, the plant with 2 added mass is studied.
Parameters
wc = 100; % Wanted crossover frequency [Hz]
[~, i_wc] = min(abs(frf_iff.f - wc)); % Indice corresponding to wc%% Plant to be decoupled
frf_coupled = frf_iff.G_dL{2};
G_coupled = sim_iff.G_dL{2};No Decoupling (Decentralized)
<<sec:test_nhexa_interaction_decentralized>>
\begin{tikzpicture}
\node[block] (G) {$\bm{G}$};
% Connections and labels
\draw[<-] (G.west) -- ++(-1.8, 0) node[above right]{$\bm{\tau}$};
\draw[->] (G.east) -- ++( 1.8, 0) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}$};
\begin{scope}[on background layer]
\node[fit={(G.south west) (G.north east)}, fill=black!10!white, draw, dashed, inner sep=16pt] (Gdec) {};
\node[below right] at (Gdec.north west) {$\bm{G}_{\text{dec}}$};
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}
Static Decoupling
<<sec:test_nhexa_interaction_static>>
\begin{tikzpicture}
\node[block] (G) {$\bm{G}$};
\node[block, left=0.8 of G] (Ginv) {$\bm{\hat{G}}(j0)^{-1}$};
% Connections and labels
\draw[<-] (Ginv.west) -- ++(-1.8, 0) node[above right]{$\bm{u}$};
\draw[->] (Ginv.east) -- (G.west) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}$};
\draw[->] (G.east) -- ++( 1.8, 0) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}$};
\begin{scope}[on background layer]
\node[fit={(Ginv.south west) (G.north east)}, fill=black!10!white, draw, dashed, inner sep=16pt] (Gx) {};
\node[below right] at (Gx.north west) {$\bm{G}_{\text{static}}$};
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}
The DC gain is evaluated from the model as be have bad low frequency identification.
| -62011.5 | 3910.6 | 4299.3 | 660.7 | -4016.5 | -4373.6 |
| 3914.4 | -61991.2 | -4356.8 | -4019.2 | 640.2 | 4281.6 |
| -4020.0 | -4370.5 | -62004.5 | 3914.6 | 4295.8 | 653.8 |
| 660.9 | 4292.4 | 3903.3 | -62012.2 | -4366.5 | -4008.9 |
| 4302.8 | 655.6 | -4025.8 | -4377.8 | -62006.0 | 3919.7 |
| -4377.9 | -4013.2 | 668.6 | 4303.7 | 3906.8 | -62019.3 |
Decoupling at the Crossover
<<sec:test_nhexa_interaction_crossover>>
\begin{tikzpicture}
\node[block] (G) {$\bm{G}$};
\node[block, left=0.8 of G] (Ginv) {$\bm{\hat{G}}(j\omega_c)^{-1}$};
% Connections and labels
\draw[<-] (Ginv.west) -- ++(-1.8, 0) node[above right]{$\bm{u}$};
\draw[->] (Ginv.east) -- (G.west) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}$};
\draw[->] (G.east) -- ++( 1.8, 0) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}$};
\begin{scope}[on background layer]
\node[fit={(Ginv.south west) (G.north east)}, fill=black!10!white, draw, dashed, inner sep=16pt] (Gx) {};
\node[below right] at (Gx.north west) {$\bm{G}_{\omega_c}$};
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}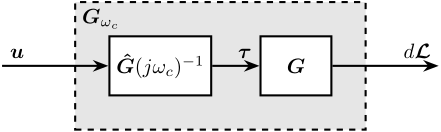
| 67229.8 | 3769.3 | -13704.6 | -23084.8 | -6318.2 | 23378.7 |
| 3486.2 | 67708.9 | 23220.0 | -6314.5 | -22699.8 | -14060.6 |
| -5731.7 | 22471.7 | 66701.4 | 3070.2 | -13205.6 | -21944.6 |
| -23305.5 | -14542.6 | 2743.2 | 70097.6 | 24846.8 | -5295.0 |
| -14882.9 | -22957.8 | -5344.4 | 25786.2 | 70484.6 | 2979.9 |
| 24353.3 | -5195.2 | -22449.0 | -14459.2 | 2203.6 | 69484.2 |
%% Compute RGA Matrix
RGA_wc = zeros(size(frf_coupled));
for i = 1:length(frf_iff.f)
RGA_wc(i,:,:) = squeeze(G_dL_wc(i,:,:)).*inv(squeeze(G_dL_wc(i,:,:))).';
end
%% Compute RGA-number
RGA_wc_sum = zeros(size(RGA_wc, 1), 1);
for i = 1:size(RGA_wc, 1)
RGA_wc_sum(i) = sum(sum(abs(eye(6) - squeeze(RGA_wc(i,:,:)))));
end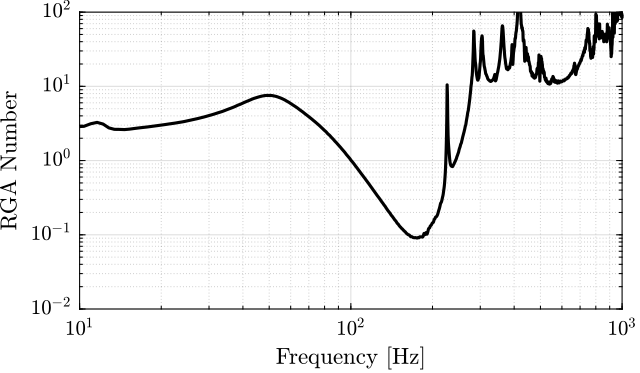
SVD Decoupling
<<sec:test_nhexa_interaction_svd>>
\begin{tikzpicture}
\node[block] (G) {$\bm{G}$};
\node[block, left=0.8 of G.west] (V) {$V^{-T}$};
\node[block, right=0.8 of G.east] (U) {$U^{-1}$};
% Connections and labels
\draw[<-] (V.west) -- ++(-1.0, 0) node[above right]{$u$};
\draw[->] (V.east) -- (G.west) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}$};
\draw[->] (G.east) -- (U.west) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}$};
\draw[->] (U.east) -- ++( 1.0, 0) node[above left]{$y$};
\begin{scope}[on background layer]
\node[fit={(V.south west) (G.north-|U.east)}, fill=black!10!white, draw, dashed, inner sep=14pt] (Gsvd) {};
\node[below right] at (Gsvd.north west) {$\bm{G}_{SVD}$};
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}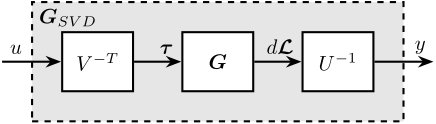
%% Compute the RGA matrix for the SVD decoupled plant
RGA_svd = zeros(size(frf_coupled));
for i = 1:length(frf_iff.f)
RGA_svd(i,:,:) = squeeze(G_dL_svd(i,:,:)).*inv(squeeze(G_dL_svd(i,:,:))).';
end
%% Compute the RGA-number
RGA_svd_sum = zeros(size(RGA_svd, 1), 1);
for i = 1:length(frf_iff.f)
RGA_svd_sum(i) = sum(sum(abs(eye(6) - squeeze(RGA_svd(i,:,:)))));
end%% RGA Number for the SVD decoupled plant
figure;
plot(frf_iff.f, RGA_svd_sum, 'k-');
set(gca, 'XScale', 'log'); set(gca, 'YScale', 'log');
xlabel('Frequency [Hz]'); ylabel('RGA Number');
xlim([10, 1e3]); ylim([1e-2, 1e2]);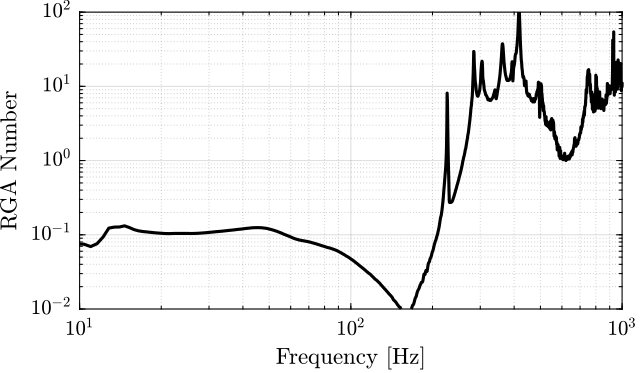
Dynamic decoupling
<<sec:test_nhexa_interaction_dynamic>>
\begin{tikzpicture}
\node[block] (G) {$\bm{G}$};
\node[block, left=0.8 of G] (Ginv) {$\bm{\hat{G}}^{-1}$};
% Connections and labels
\draw[<-] (Ginv.west) -- ++(-1.8, 0) node[above right]{$\bm{u}$};
\draw[->] (Ginv.east) -- (G.west) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}$};
\draw[->] (G.east) -- ++( 1.8, 0) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}$};
\begin{scope}[on background layer]
\node[fit={(Ginv.south west) (G.north east)}, fill=black!10!white, draw, dashed, inner sep=16pt] (Gx) {};
\node[below right] at (Gx.north west) {$\bm{G}_{\text{inv}}$};
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}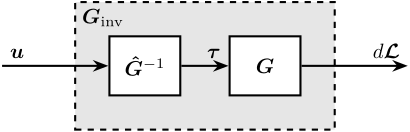
Jacobian Decoupling - Center of Stiffness
<<sec:test_nhexa_interaction_jacobian_cok>>
\begin{tikzpicture}
\node[block] (G) {$\bm{G}$};
\node[block, left=0.8 of G] (Jt) {$J_{s,\{K\}}^{-T}$};
\node[block, right=0.8 of G] (Ja) {$J_{a,\{K\}}^{-1}$};
% Connections and labels
\draw[<-] (Jt.west) -- ++(-1.8, 0) node[above right]{$\bm{\mathcal{F}}_{\{K\}}$};
\draw[->] (Jt.east) -- (G.west) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}$};
\draw[->] (G.east) -- (Ja.west) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}$};
\draw[->] (Ja.east) -- ++( 1.8, 0) node[above left]{$\bm{\mathcal{X}}_{\{K\}}$};
\begin{scope}[on background layer]
\node[fit={(Jt.south west) (Ja.north east)}, fill=black!10!white, draw, dashed, inner sep=16pt] (Gx) {};
\node[below right] at (Gx.north west) {$\bm{G}_{\{K\}}$};
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}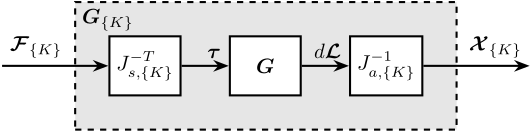
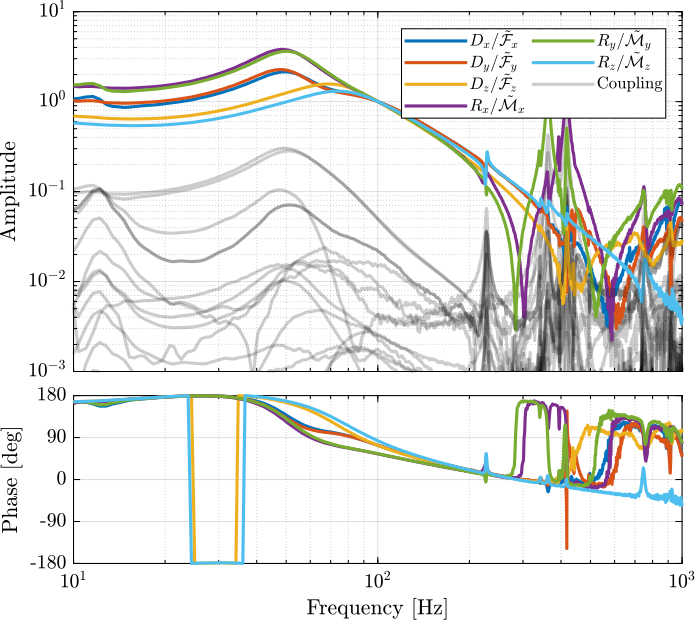
The obtained plant is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_interaction_J_cok_plant_not_normalized. We can see that the stiffness in the $x$, $y$ and $z$ directions are equal, which is due to the cubic architecture of the Stewart platform.
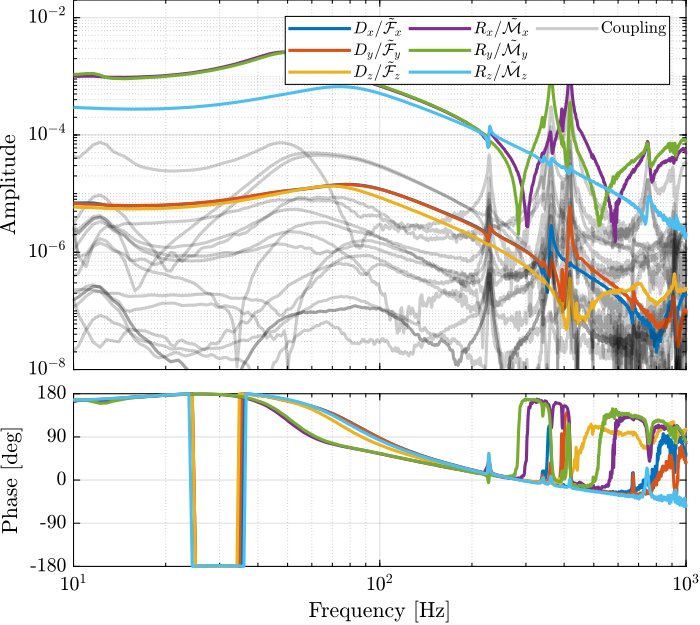
Because the plant in translation and rotation has very different gains, we choose to normalize the plant inputs such that the gain of the diagonal term is equal to $1$ at 100Hz.
The results is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_interaction_J_cok_plant.
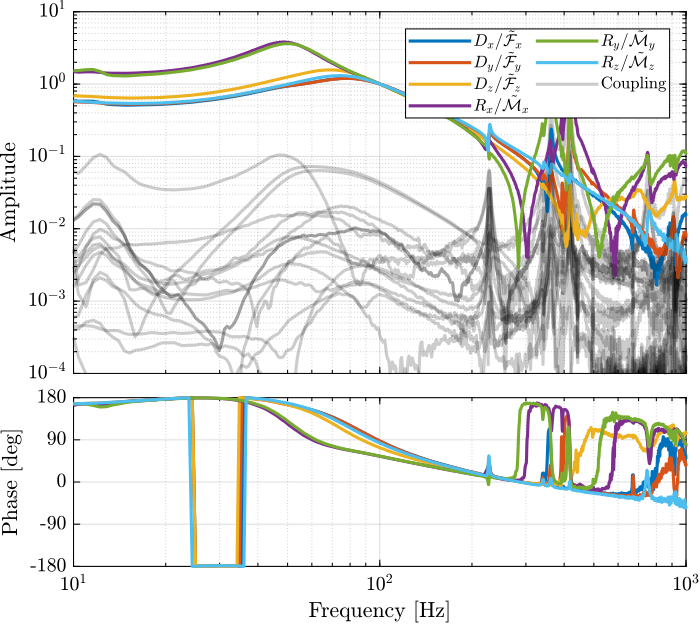
Jacobian Decoupling - Center of Mass
<<sec:test_nhexa_interaction_jacobian_com>>
\begin{tikzpicture}
\node[block] (G) {$\bm{G}$};
\node[block, left=0.8 of G] (Jt) {$J_{s,\{M\}}^{-T}$};
\node[block, right=0.8 of G] (Ja) {$J_{a,\{M\}}^{-1}$};
% Connections and labels
\draw[<-] (Jt.west) -- ++(-1.8, 0) node[above right]{$\bm{\mathcal{F}}_{\{M\}}$};
\draw[->] (Jt.east) -- (G.west) node[above left]{$\bm{\tau}$};
\draw[->] (G.east) -- (Ja.west) node[above left]{$d\bm{\mathcal{L}}$};
\draw[->] (Ja.east) -- ++( 1.8, 0) node[above left]{$\bm{\mathcal{X}}_{\{M\}}$};
\begin{scope}[on background layer]
\node[fit={(Jt.south west) (Ja.north east)}, fill=black!10!white, draw, dashed, inner sep=16pt] (Gx) {};
\node[below right] at (Gx.north west) {$\bm{G}_{\{M\}}$};
\end{scope}
\end{tikzpicture}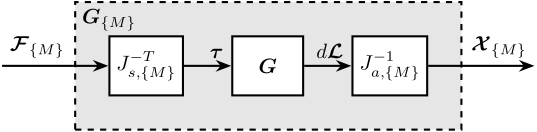
Decoupling Comparison
<<sec:test_nhexa_interaction_comparison>>
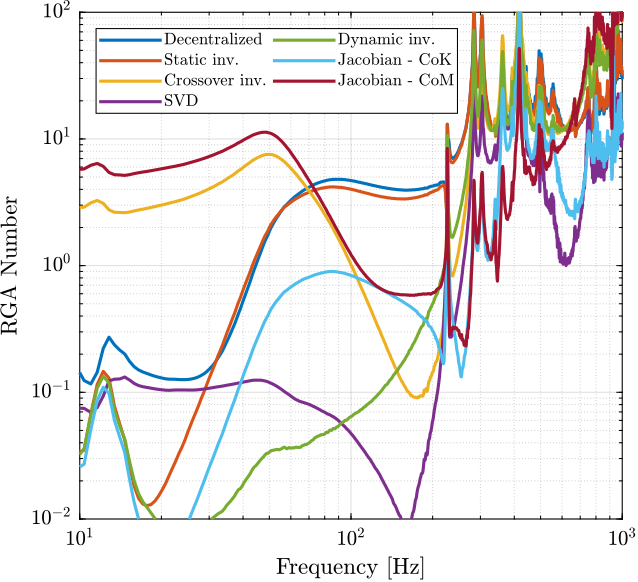
Let's now compare all of the decoupling methods (Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_interaction_compare_rga_numbers).
From Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_interaction_compare_rga_numbers, the following remarks are made:
- Decentralized plant: well decoupled below suspension modes
- Static inversion: similar to the decentralized plant as the decentralized plant has already a good decoupling at low frequency
- Crossover inversion: the decoupling is improved around the crossover frequency as compared to the decentralized plant. However, the decoupling is increased at lower frequency.
- SVD decoupling: Very good decoupling up to 235Hz. Especially between 100Hz and 200Hz.
- Dynamic Inversion: the plant is very well decoupled at frequencies where the model is accurate (below 235Hz where flexible modes are not modelled).
- Jacobian - Stiffness: good decoupling at low frequency. The decoupling increases at the frequency of the suspension modes, but is acceptable up to the strut flexible modes (235Hz).
- Jacobian - Mass: bad decoupling at low frequency. Better decoupling above the frequency of the suspension modes, and acceptable decoupling up to the strut flexible modes (235Hz).
Decoupling Robustness
<<sec:test_nhexa_interaction_robustness>>
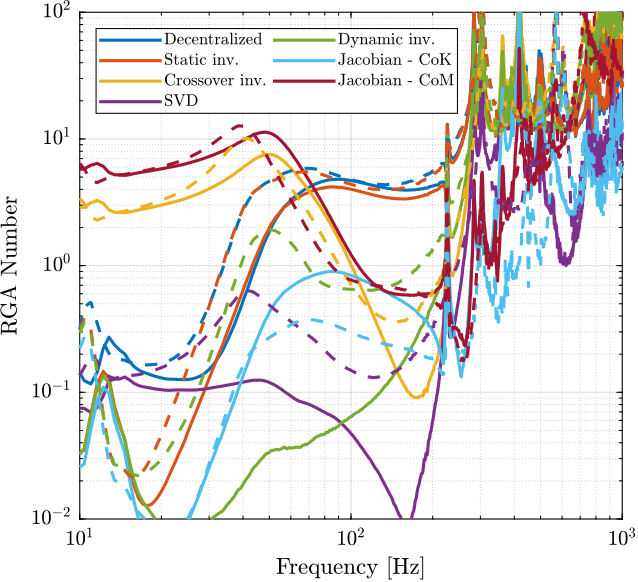
Let's now see how the decoupling is changing when changing the payload's mass.
frf_new = frf_iff.G_dL{3};The obtained RGA-numbers are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_interaction_compare_rga_numbers_rob.
From Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_interaction_compare_rga_numbers_rob:
- The decoupling using the Jacobian evaluated at the "center of stiffness" seems to give the most robust results.
Conclusion
Several decoupling methods can be used:
- SVD
- Inverse
- Jacobian (CoK)
| Method | RGA | Diag Plant | Robustness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decentralized | – | Equal | ++ |
| Static dec. | – | Equal | ++ |
| Crossover dec. | - | Equal | 0 |
| SVD | ++ | Diff | + |
| Dynamic dec. | ++ | Unity, equal | - |
| Jacobian - CoK | + | Diff | ++ |
| Jacobian - CoM | 0 | Diff | + |
Robust High Authority Controller
<<sec:test_nhexa_robust_hac_design>>
Introduction ignore
In this section we wish to develop a robust High Authority Controller (HAC) that is working for all payloads.
cite:indri20_mechat_robot
Using Jacobian evaluated at the center of stiffness
Decoupled Plant
G_nom = frf_iff.G_dL{2}; % Nominal Plant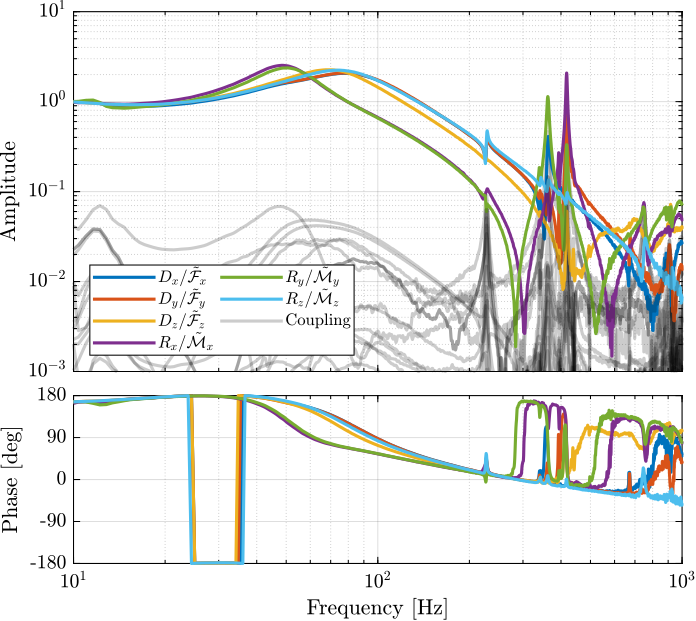
SISO Controller Design
As the diagonal elements of the plant are not equal, several SISO controllers are designed and then combined to form a diagonal controller. All the diagonal terms of the controller consists of:
- A double integrator to have high gain at low frequency
- A lead around the crossover frequency to increase stability margins
- Two second order low pass filters above the crossover frequency to increase the robustness to high frequency modes
Obtained Loop Gain
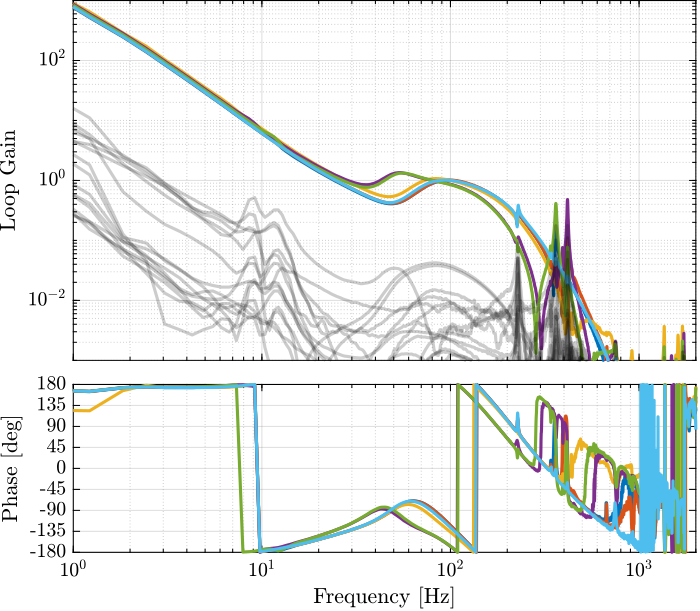
%% Controller to be implemented
Kd = inv(J_cok')*input_normalize*ss(Kd_diag)*inv(Js_cok);Verification of the Stability
Now the stability of the feedback loop is verified using the generalized Nyquist criteria.
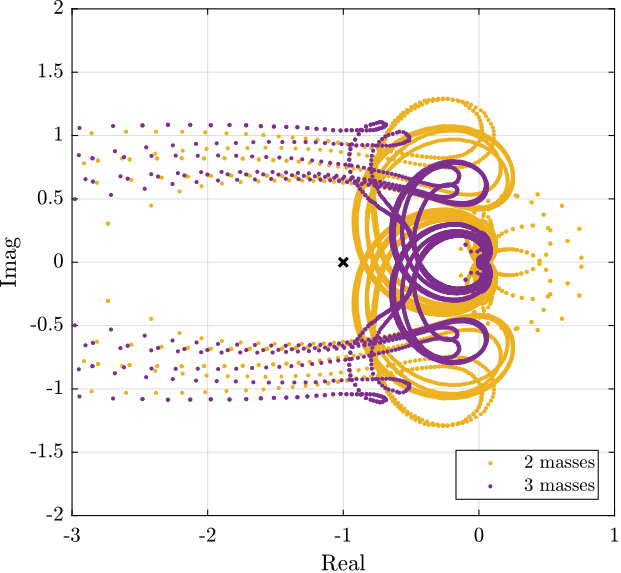
Save for further analysis
save('data_sim/Khac_iff_struts_jacobian_cok.mat', 'Kd')Sensitivity transfer function from the model
The results are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_sensitivity_hac_jacobian_cok_3m_comp_model.
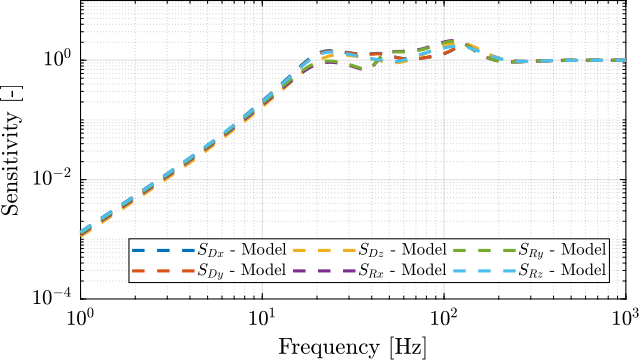
Using Singular Value Decomposition
Decoupled Plant
G_nom = frf_iff.G_dL{2}; % Nominal Plant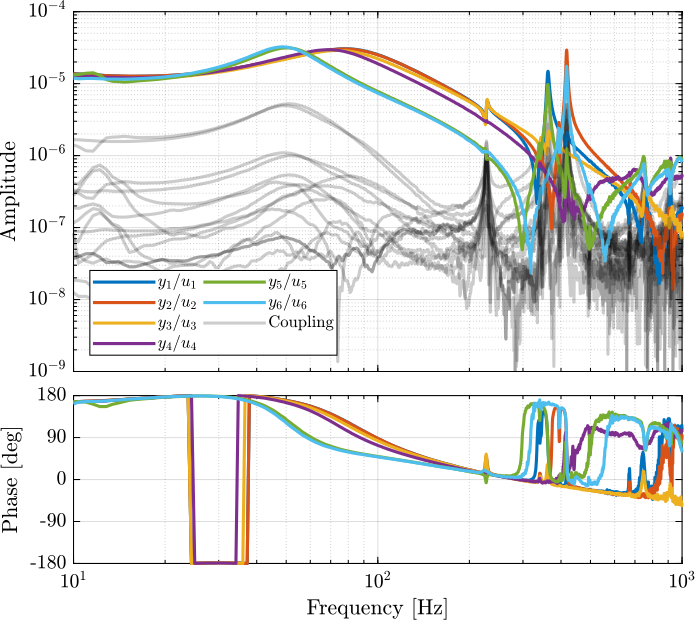
Controller Design
Loop Gain
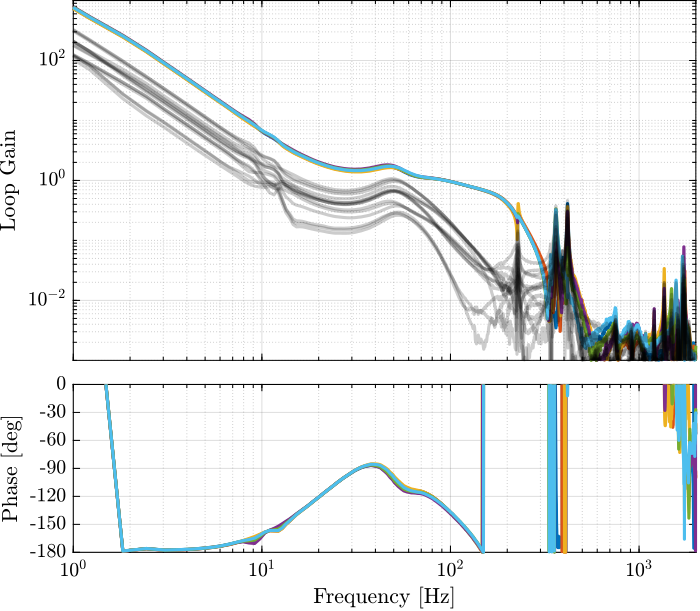
Stability Verification
%% Compute the Eigenvalues of the loop gain
Ldet = zeros(3, 6, length(frf_iff.f));
for i = 1:3
Lmimo = pagemtimes(permute(frf_iff.G_dL{i}, [2,3,1]),squeeze(freqresp(Kd, frf_iff.f, 'Hz')));
for i_f = 2:length(frf_iff.f)
Ldet(i,:, i_f) = eig(squeeze(Lmimo(:,:,i_f)));
end
end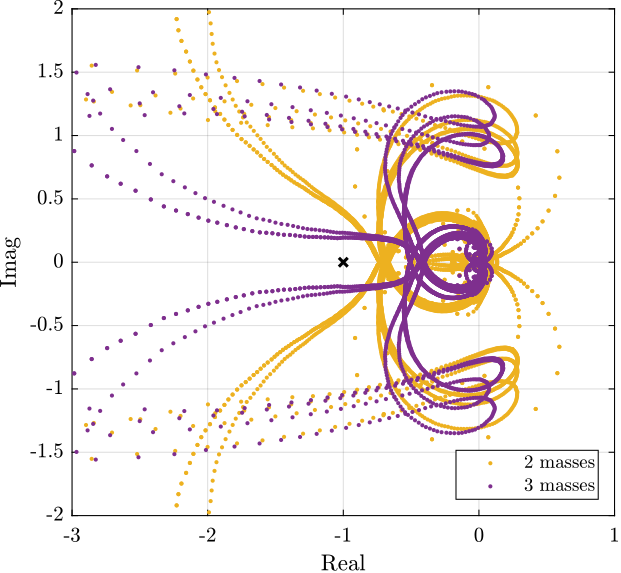
Save for further analysis
save('data_sim/Khac_iff_struts_svd.mat', 'Kd')Measured Sensitivity Transfer Function
The sensitivity transfer function is estimated by adding a reference signal $R_x$ consisting of a low pass filtered white noise, and measuring the position error $E_x$ at the same time.
The transfer function from $R_x$ to $E_x$ is the sensitivity transfer function.
In order to identify the sensitivity transfer function for all directions, six reference signals are used, one for each direction.
An example is shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_ref_track_hac_svd_3m where both the reference signal and the measured position are shown for translations in the $x$ direction.
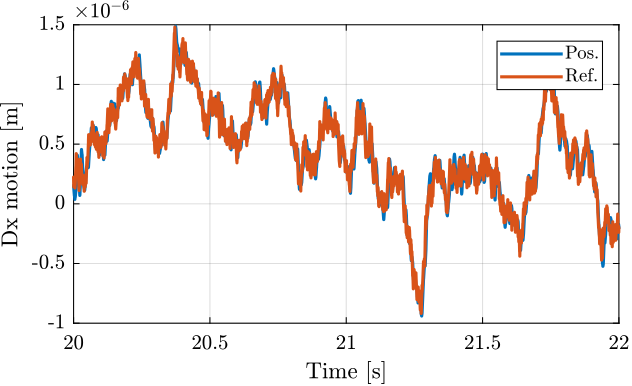
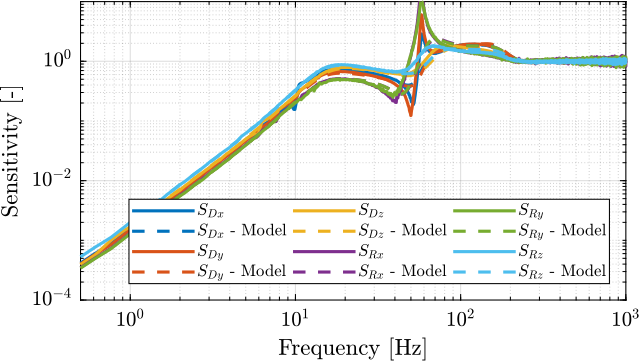
The sensitivity transfer functions estimated for all directions are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_sensitivity_hac_svd_3m.
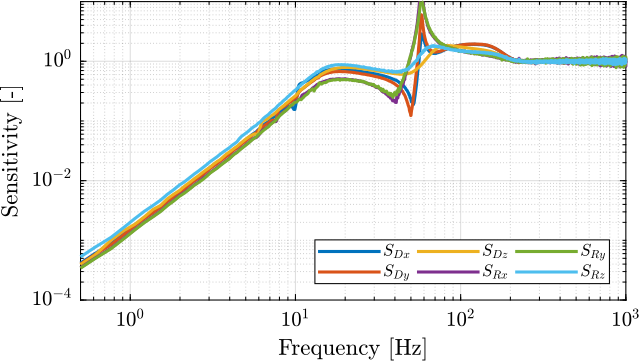
From Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_sensitivity_hac_svd_3m:
- The sensitivity transfer functions are similar for all directions
- The disturbance attenuation at 1Hz is almost a factor 1000 as wanted
- The sensitivity transfer functions for $R_x$ and $R_y$ have high peak values which indicate poor stability margins.
Sensitivity transfer function from the model
The sensitivity transfer function is now estimated using the model and compared with the one measured.
The results are shown in Figure ref:fig:test_nhexa_sensitivity_hac_svd_3m_comp_model. The model is quite effective in estimating the sensitivity transfer functions except around 60Hz were there is a peak for the measurement.