55 KiB
Finite Element Model with Simscape
- Amplified Piezoelectric Actuator - 3D elements
- Introduction
- Import Mass Matrix, Stiffness Matrix, and Interface Nodes Coordinates
- Output parameters
- Piezoelectric parameters
- Identification of the Dynamics
- Comparison with Ansys
- Force Sensor
- Distributed Actuator
- Distributed Actuator and Force Sensor
- Dynamics from input voltage to displacement
- Dynamics from input voltage to output voltage
- APA300ML
- Flexible Joint
- Integral Force Feedback with Amplified Piezo
Amplified Piezoelectric Actuator - 3D elements
Introduction ignore
The idea here is to:
- export a FEM of an amplified piezoelectric actuator from Ansys to Matlab
- import it into a Simscape model
- compare the obtained dynamics
- add 10kg mass on top of the actuator and identify the dynamics
- compare with results from Ansys where 10kg are directly added to the FEM
Import Mass Matrix, Stiffness Matrix, and Interface Nodes Coordinates
We first extract the stiffness and mass matrices.
K = extractMatrix('piezo_amplified_3d_K.txt');
M = extractMatrix('piezo_amplified_3d_M.txt');Then, we extract the coordinates of the interface nodes.
[int_xyz, int_i, n_xyz, n_i, nodes] = extractNodes('piezo_amplified_3d.txt'); save('./mat/piezo_amplified_3d.mat', 'int_xyz', 'int_i', 'n_xyz', 'n_i', 'nodes', 'M', 'K');Output parameters
load('./mat/piezo_amplified_3d.mat', 'int_xyz', 'int_i', 'n_xyz', 'n_i', 'nodes', 'M', 'K');| Total number of Nodes | 168959 |
| Number of interface Nodes | 13 |
| Number of Modes | 30 |
| Size of M and K matrices | 108 |
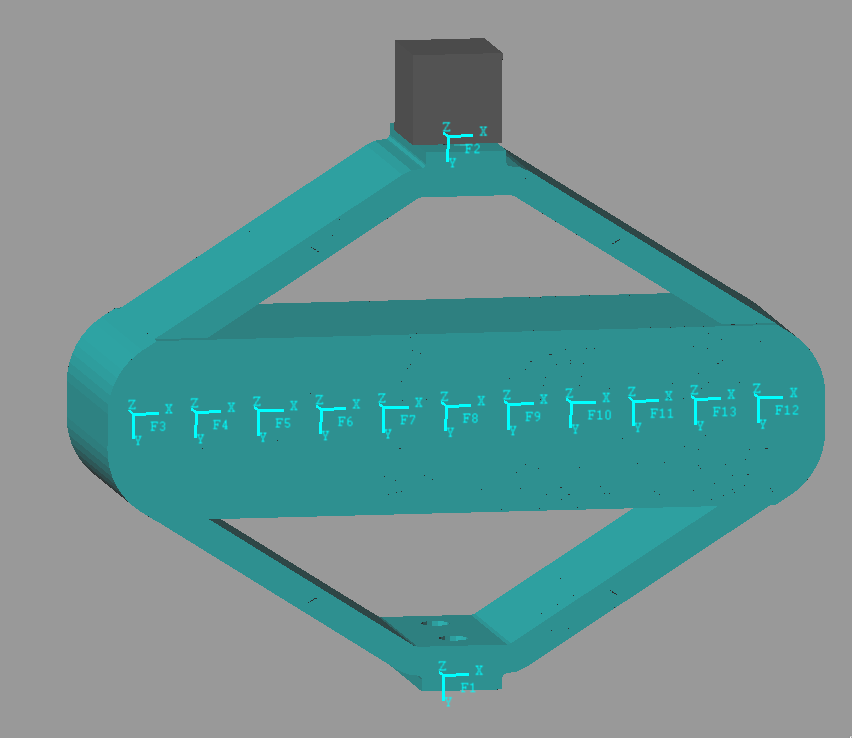
| Node i | Node Number | x [m] | y [m] | z [m] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 168947.0 | 0.0 | 0.03 | 0.0 |
| 2.0 | 168949.0 | 0.0 | -0.03 | 0.0 |
| 3.0 | 168950.0 | -0.035 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 4.0 | 168951.0 | -0.028 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 5.0 | 168952.0 | -0.021 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 6.0 | 168953.0 | -0.014 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 7.0 | 168954.0 | -0.007 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 8.0 | 168955.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 9.0 | 168956.0 | 0.007 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 10.0 | 168957.0 | 0.014 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 11.0 | 168958.0 | 0.021 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 12.0 | 168959.0 | 0.035 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 13.0 | 168960.0 | 0.028 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 300000000.0 | -30000.0 | 8000.0 | -200.0 | -30.0 | -60000.0 | 20000000.0 | -4000.0 | 500.0 | 8 |
| -30000.0 | 100000000.0 | 400.0 | 30.0 | 200.0 | -1 | 4000.0 | -8000000.0 | 800.0 | 7 |
| 8000.0 | 400.0 | 50000000.0 | -800000.0 | -300.0 | -40.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 | 5000000.0 | 40000.0 |
| -200.0 | 30.0 | -800000.0 | 20000.0 | 5 | 1 | -10.0 | -2 | -40000.0 | -300.0 |
| -30.0 | 200.0 | -300.0 | 5 | 40000.0 | 0.3 | -4 | -10.0 | 40.0 | 0.4 |
| -60000.0 | -1 | -40.0 | 1 | 0.3 | 3000.0 | 7000.0 | 0.8 | -1 | 0.0003 |
| 20000000.0 | 4000.0 | 300.0 | -10.0 | -4 | 7000.0 | 300000000.0 | 20000.0 | 3000.0 | 80.0 |
| -4000.0 | -8000000.0 | 100.0 | -2 | -10.0 | 0.8 | 20000.0 | 100000000.0 | -4000.0 | -100.0 |
| 500.0 | 800.0 | 5000000.0 | -40000.0 | 40.0 | -1 | 3000.0 | -4000.0 | 50000000.0 | 800000.0 |
| 8 | 7 | 40000.0 | -300.0 | 0.4 | 0.0003 | 80.0 | -100.0 | 800000.0 | 20000.0 |
| 0.03 | 2e-06 | -2e-07 | 1e-08 | 2e-08 | 0.0002 | -0.001 | 2e-07 | -8e-08 | -9e-10 |
| 2e-06 | 0.02 | -5e-07 | 7e-09 | 3e-08 | 2e-08 | -3e-07 | 0.0003 | -1e-08 | 1e-10 |
| -2e-07 | -5e-07 | 0.02 | -9e-05 | 4e-09 | -1e-08 | 2e-07 | -2e-08 | -0.0006 | -5e-06 |
| 1e-08 | 7e-09 | -9e-05 | 1e-06 | 6e-11 | 4e-10 | -1e-09 | 3e-11 | 5e-06 | 3e-08 |
| 2e-08 | 3e-08 | 4e-09 | 6e-11 | 1e-06 | 2e-10 | -2e-09 | 2e-10 | -7e-09 | -4e-11 |
| 0.0002 | 2e-08 | -1e-08 | 4e-10 | 2e-10 | 2e-06 | -2e-06 | -1e-09 | -7e-10 | -9e-12 |
| -0.001 | -3e-07 | 2e-07 | -1e-09 | -2e-09 | -2e-06 | 0.03 | -2e-06 | -1e-07 | -5e-09 |
| 2e-07 | 0.0003 | -2e-08 | 3e-11 | 2e-10 | -1e-09 | -2e-06 | 0.02 | -8e-07 | -1e-08 |
| -8e-08 | -1e-08 | -0.0006 | 5e-06 | -7e-09 | -7e-10 | -1e-07 | -8e-07 | 0.02 | 9e-05 |
| -9e-10 | 1e-10 | -5e-06 | 3e-08 | -4e-11 | -9e-12 | -5e-09 | -1e-08 | 9e-05 | 1e-06 |
Using K, M and int_xyz, we can use the Reduced Order Flexible Solid simscape block.
Piezoelectric parameters
Parameters for the APA95ML:
d33 = 3e-10; % Strain constant [m/V]
n = 80; % Number of layers per stack
eT = 1.6e-7; % Permittivity under constant stress [F/m]
sD = 2e-11; % Elastic compliance under constant electric displacement [m2/N]
ka = 235e6; % Stack stiffness [N/m]
C = 5e-6; % Stack capactiance [F] na = 2; % Number of stacks used as actuator
ns = 1; % Number of stacks used as force sensorThe ratio of the developed force to applied voltage is $d_{33} n k_a$ in [N/V]. We denote this constant by $g_a$ and: \[ F_a = g_a V_a, \quad g_a = d_{33} n k_a \]
d33*(na*n)*(ka/(na + ns)) % [N/V]3.76
From cite:fleming14_desig_model_contr_nanop_system (page 123), the relation between relative displacement and generated voltage is: \[ V_s = \frac{d_{33}}{\epsilon^T s^D n} \Delta h \] where:
- $V_s$: measured voltage [V]
- $d_{33}$: strain constant [m/V]
- $\epsilon^T$: permittivity under constant stress [F/m]
- $s^D$: elastic compliance under constant electric displacement [m^2/N]
- $n$: number of layers
- $\Delta h$: relative displacement [m]
1e-6*d33/(eT*sD*ns*n) % [V/um]1.1719
Identification of the Dynamics
The flexible element is imported using the Reduced Order Flexible Solid simscape block.
To model the actuator, an Internal Force block is added between the nodes 3 and 12.
A Relative Motion Sensor block is added between the nodes 1 and 2 to measure the displacement and the amplified piezo.
One mass is fixed at one end of the piezo-electric stack actuator, the other end is fixed to the world frame.
We first set the mass to be zero.
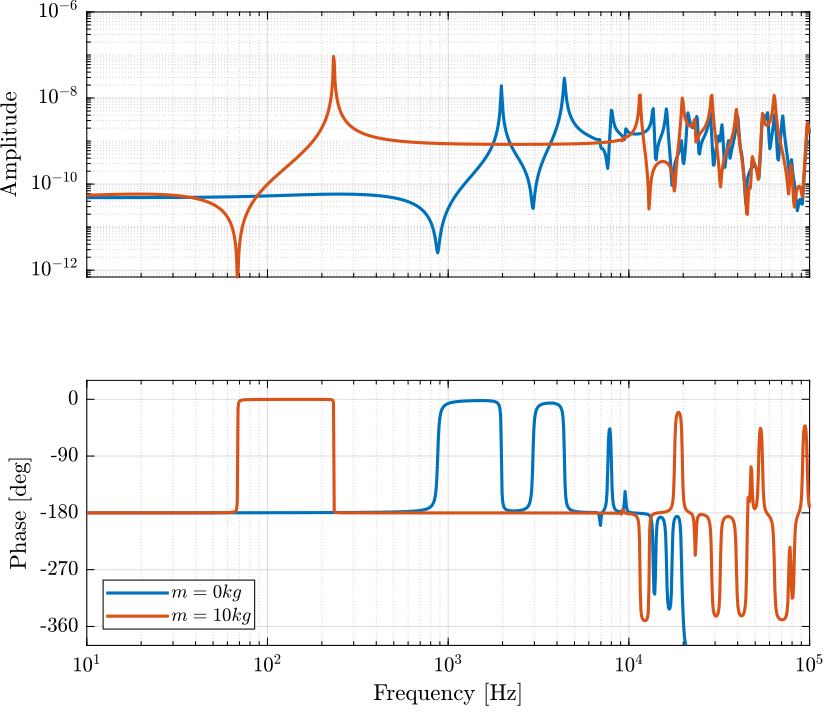
m = 0.01;The dynamics is identified from the applied force to the measured relative displacement.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_3d';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/y'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
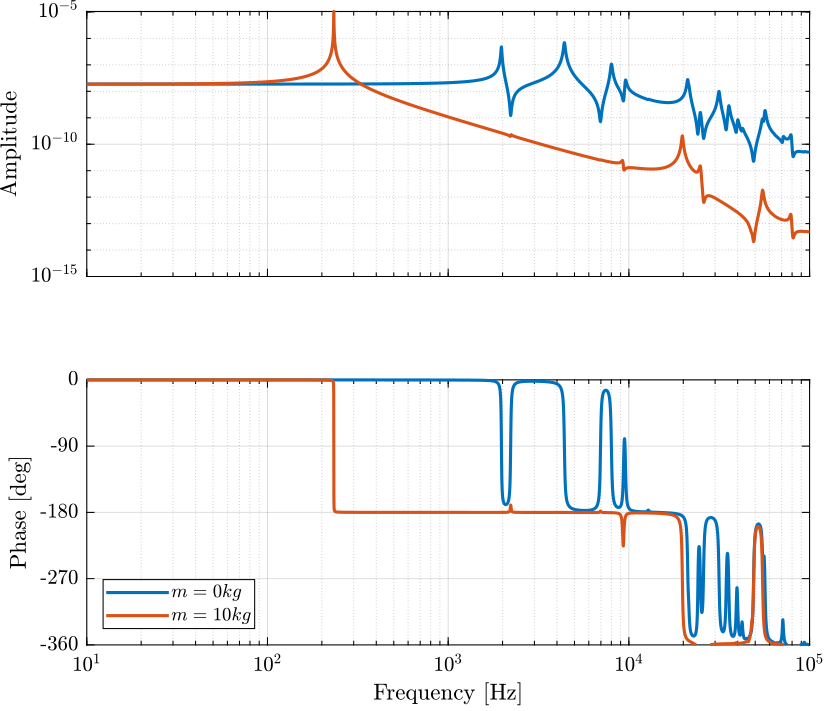
Gh = -linearize(mdl, io);Then, we add 10Kg of mass:
m = 5;And the dynamics is identified.
The two identified dynamics are compared in Figure fig:dynamics_act_disp_comp_mass.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_3d';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/y'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
Ghm = -linearize(mdl, io);Comparison with Ansys
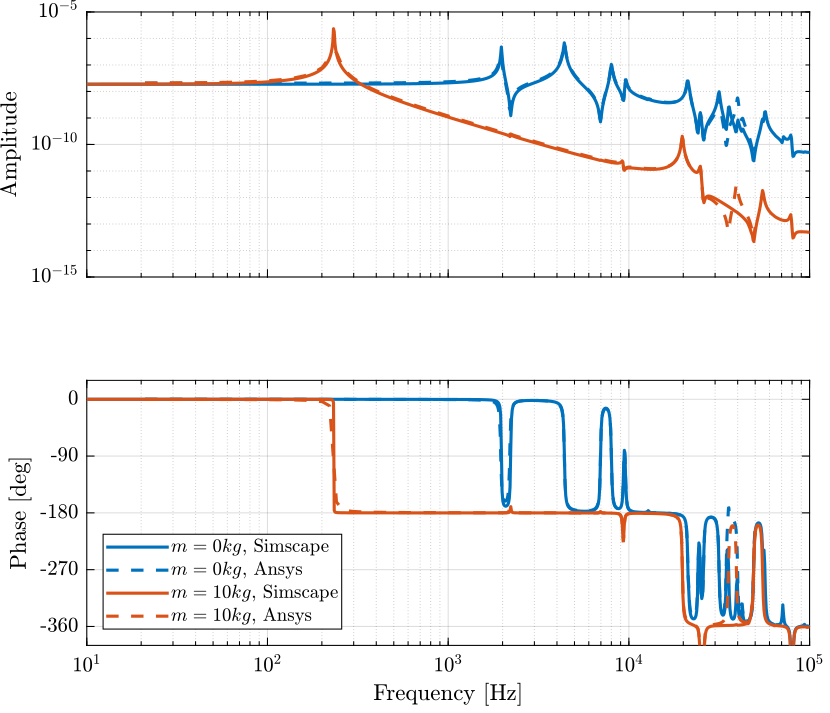
Let's import the results from an Harmonic response analysis in Ansys.
Gresp0 = readtable('FEA_HarmResponse_00kg.txt');
Gresp10 = readtable('FEA_HarmResponse_10kg.txt');The obtained dynamics from the Simscape model and from the Ansys analysis are compare in Figure fig:dynamics_force_disp_comp_anasys.
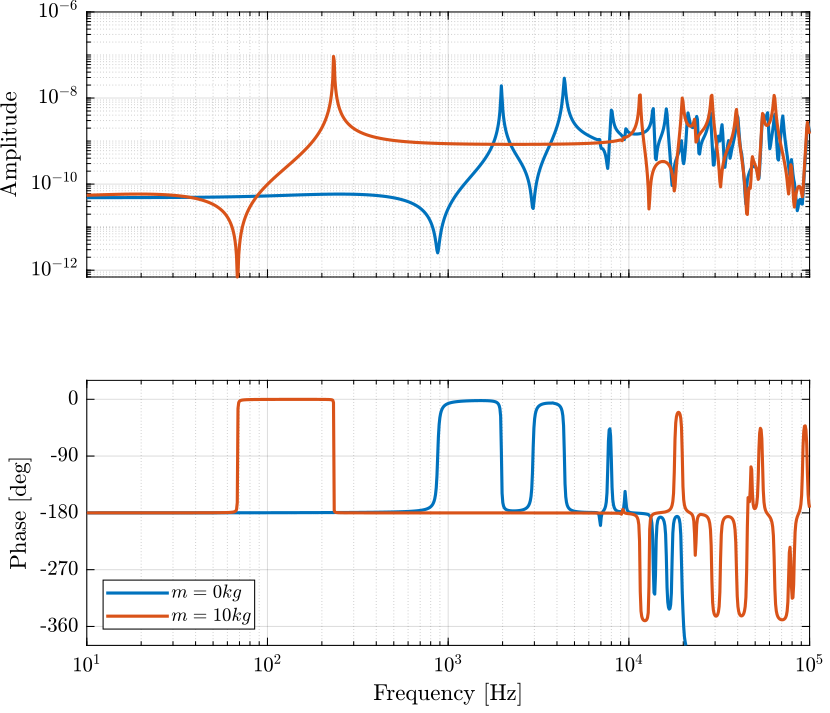
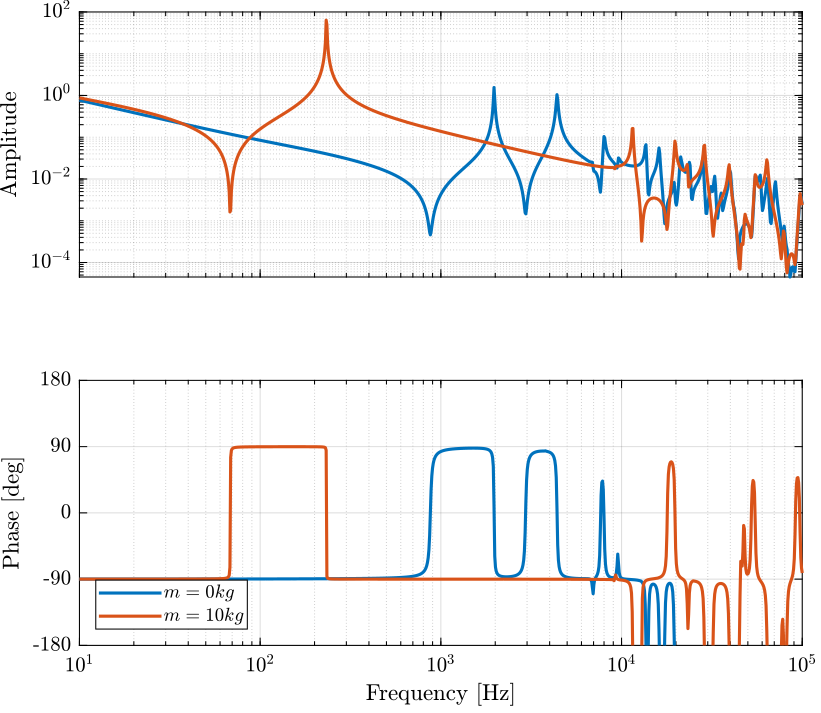
Force Sensor
The dynamics is identified from internal forces applied between nodes 3 and 11 to the relative displacement of nodes 11 and 13.
The obtained dynamics is shown in Figure fig:dynamics_force_force_sensor_comp_mass.
m = 0; %% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_3d';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fa'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fs'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
Gf = linearize(mdl, io); m = 10; %% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_3d';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fa'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fs'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
Gfm = linearize(mdl, io);Distributed Actuator
m = 0;The dynamics is identified from the applied force to the measured relative displacement.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_3d_distri';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/y'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
Gd = linearize(mdl, io);Then, we add 10Kg of mass:
m = 10;And the dynamics is identified.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_3d_distri';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/y'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
Gdm = linearize(mdl, io);Distributed Actuator and Force Sensor
m = 0; %% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_3d_distri_act_sens';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fm'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
Gfd = linearize(mdl, io); m = 10; %% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_3d_distri_act_sens';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fm'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
Gfdm = linearize(mdl, io);Dynamics from input voltage to displacement
m = 5;And the dynamics is identified.
The two identified dynamics are compared in Figure fig:dynamics_act_disp_comp_mass.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_3d';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/V'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/y'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
G = -linearize(mdl, io); save('../test-bench-apa/mat/fem_model_5kg.mat', 'G')Dynamics from input voltage to output voltage
m = 5; %% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_3d';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Va'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Vs'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
G = -linearize(mdl, io);APA300ML
Import Mass Matrix, Stiffness Matrix, and Interface Nodes Coordinates
We first extract the stiffness and mass matrices.
K = extractMatrix('mat_K-48modes-7MDoF.matrix');
M = extractMatrix('mat_M-48modes-7MDoF.matrix'); K = extractMatrix('mat_K-80modes-7MDoF.matrix');
M = extractMatrix('mat_M-80modes-7MDoF.matrix');Then, we extract the coordinates of the interface nodes.
[int_xyz, int_i, n_xyz, n_i, nodes] = extractNodes('Nodes_MDoF_NLIST_MLIST.txt'); save('./mat/APA300ML.mat', 'int_xyz', 'int_i', 'n_xyz', 'n_i', 'nodes', 'M', 'K');Output parameters
load('./mat/APA300ML.mat', 'int_xyz', 'int_i', 'n_xyz', 'n_i', 'nodes', 'M', 'K');| Total number of Nodes | 7 |
| Number of interface Nodes | 7 |
| Number of Modes | 38 |
| Size of M and K matrices | 80 |
| Node i | Node Number | x [m] | y [m] | z [m] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 53917.0 | 0.0 | -0.015 | 0.0 |
| 2.0 | 53918.0 | 0.0 | 0.015 | 0.0 |
| 3.0 | 53919.0 | -0.0325 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 4.0 | 53920.0 | -0.0125 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 5.0 | 53921.0 | -0.0075 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 6.0 | 53922.0 | 0.0125 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 7.0 | 53923.0 | 0.0325 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 200000000.0 | 30000.0 | 50000.0 | 200.0 | -100.0 | -300000.0 | 10000000.0 | -6000.0 | 20000.0 | -60.0 |
| 30000.0 | 7000000.0 | 10000.0 | 30.0 | -30.0 | -70.0 | 7000.0 | -500000.0 | 3000.0 | -10.0 |
| 50000.0 | 10000.0 | 30000000.0 | 200000.0 | -200.0 | -100.0 | 20000.0 | -2000.0 | 2000000.0 | -9000.0 |
| 200.0 | 30.0 | 200000.0 | 1000.0 | -0.8 | -0.4 | 50.0 | -6 | 9000.0 | -30.0 |
| -100.0 | -30.0 | -200.0 | -0.8 | 10000.0 | 0.2 | -40.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | -0.05 |
| -300000.0 | -70.0 | -100.0 | -0.4 | 0.2 | 900.0 | -30000.0 | 10.0 | -40.0 | 0.1 |
| 10000000.0 | 7000.0 | 20000.0 | 50.0 | -40.0 | -30000.0 | 200000000.0 | -50000.0 | 30000.0 | -50.0 |
| -6000.0 | -500000.0 | -2000.0 | -6 | 10.0 | 10.0 | -50000.0 | 7000000.0 | -4000.0 | 8 |
| 20000.0 | 3000.0 | 2000000.0 | 9000.0 | 20.0 | -40.0 | 30000.0 | -4000.0 | 30000000.0 | -200000.0 |
| -60.0 | -10.0 | -9000.0 | -30.0 | -0.05 | 0.1 | -50.0 | 8 | -200000.0 | 1000.0 |
| 0.01 | 7e-06 | -5e-06 | -6e-08 | 3e-09 | -5e-05 | -0.0005 | -2e-07 | -3e-06 | 1e-08 |
| 7e-06 | 0.009 | 4e-07 | 6e-09 | -4e-09 | -3e-08 | -2e-07 | 6e-05 | 5e-07 | -1e-09 |
| -5e-06 | 4e-07 | 0.01 | 2e-05 | 2e-08 | 3e-08 | -2e-06 | -1e-07 | -0.0002 | 9e-07 |
| -6e-08 | 6e-09 | 2e-05 | 3e-07 | 1e-10 | 3e-10 | -7e-09 | 2e-10 | -9e-07 | 3e-09 |
| 3e-09 | -4e-09 | 2e-08 | 1e-10 | 1e-07 | -3e-12 | 6e-09 | -2e-10 | -3e-09 | 9e-12 |
| -5e-05 | -3e-08 | 3e-08 | 3e-10 | -3e-12 | 6e-07 | 1e-06 | -3e-09 | 2e-08 | -7e-11 |
| -0.0005 | -2e-07 | -2e-06 | -7e-09 | 6e-09 | 1e-06 | 0.01 | -8e-06 | -2e-06 | 9e-09 |
| -2e-07 | 6e-05 | -1e-07 | 2e-10 | -2e-10 | -3e-09 | -8e-06 | 0.009 | 1e-07 | 2e-09 |
| -3e-06 | 5e-07 | -0.0002 | -9e-07 | -3e-09 | 2e-08 | -2e-06 | 1e-07 | 0.01 | -2e-05 |
| 1e-08 | -1e-09 | 9e-07 | 3e-09 | 9e-12 | -7e-11 | 9e-09 | 2e-09 | -2e-05 | 3e-07 |
Using K, M and int_xyz, we can use the Reduced Order Flexible Solid simscape block.
Piezoelectric parameters
Parameters for the APA95ML:
d33 = 3e-10; % Strain constant [m/V]
n = 80; % Number of layers per stack
eT = 1.6e-8; % Permittivity under constant stress [F/m]
sD = 2e-11; % Elastic compliance under constant electric displacement [m2/N]
ka = 235e6; % Stack stiffness [N/m]
C = 5e-6; % Stack capactiance [F] na = 3; % Number of stacks used as actuator
ns = 0; % Number of stacks used as force sensorThe ratio of the developed force to applied voltage is $d_{33} n k_a$ in [N/V]. We denote this constant by $g_a$ and: \[ F_a = g_a V_a, \quad g_a = d_{33} n k_a \]
d33*(na*n)*(ka/(na + ns)) % [N/V]1.88
From cite:fleming14_desig_model_contr_nanop_system (page 123), the relation between relative displacement and generated voltage is: \[ V_s = \frac{d_{33}}{\epsilon^T s^D n} \Delta h \] where:
- $V_s$: measured voltage [V]
- $d_{33}$: strain constant [m/V]
- $\epsilon^T$: permittivity under constant stress [F/m]
- $s^D$: elastic compliance under constant electric displacement [m^2/N]
- $n$: number of layers
- $\Delta h$: relative displacement [m]
1e-6*d33/(eT*sD*ns*n) % [V/um]5.8594
Identification of the Dynamics
The flexible element is imported using the Reduced Order Flexible Solid simscape block.
To model the actuator, an Internal Force block is added between the nodes 3 and 12.
A Relative Motion Sensor block is added between the nodes 1 and 2 to measure the displacement and the amplified piezo.
One mass is fixed at one end of the piezo-electric stack actuator, the other end is fixed to the world frame.
We first set the mass to be zero.
m = 0.01;The dynamics is identified from the applied force to the measured relative displacement.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'APA300ML_test_bench';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/y'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
Gh = -linearize(mdl, io);Then, we add 10Kg of mass:
m = 10;And the dynamics is identified.
The two identified dynamics are compared in Figure fig:dynamics_act_disp_comp_mass.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'APA300ML_test_bench';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/y'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
Ghm = -linearize(mdl, io);IFF
Then, we add 10Kg of mass:
m = 10;And the dynamics is identified.
The two identified dynamics are compared in Figure fig:dynamics_act_disp_comp_mass.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'APA300ML_test_bench';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Va'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Vs'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
G = -linearize(mdl, io); figure;
gains = logspace(0, 5, 500);
hold on;
plot(real(pole(G)), imag(pole(G)), 'kx');
plot(real(tzero(G)), imag(tzero(G)), 'ko');
for k = 1:length(gains)
cl_poles = pole(feedback(G, gains(k)/s));
plot(real(cl_poles), imag(cl_poles), 'k.');
end
hold off;
axis square;
xlim([-500, 10]); ylim([0, 510]);
xlabel('Real Part'); ylabel('Imaginary Part');DVF
m = 10;And the dynamics is identified.
The two identified dynamics are compared in Figure fig:dynamics_act_disp_comp_mass.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'APA300ML_test_bench';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/y'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
G = -linearize(mdl, io); figure;
gains = logspace(0, 5, 500);
hold on;
plot(real(pole(G)), imag(pole(G)), 'kx');
plot(real(tzero(G)), imag(tzero(G)), 'ko');
for k = 1:length(gains)
cl_poles = pole(feedback(G, gains(k)*s));
plot(real(cl_poles), imag(cl_poles), 'k.');
end
hold off;
axis square;
xlim([-500, 10]); ylim([0, 510]);
xlabel('Real Part'); ylabel('Imaginary Part');Sensor Fusion
- What is the goal of that? Special control properties, lower the sensor noise?
Use the relative motion sensor at low frequency and the force sensor at high frequency.
m = 10; %% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'APA300ML_test_bench';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Va'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Vs'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/y'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
G = linearize(mdl, io);Merge around 1kHz
LPF and HPF
n = 3; w0 = 2*pi*1e3; G0 = 1/10; G1 = 1e5; Gc = 1/2;
W1 = (((1/w0)*sqrt((1-(G0/Gc)^(2/n))/(1-(Gc/G1)^(2/n)))*s + (G0/Gc)^(1/n))/((1/G1)^(1/n)*(1/w0)*sqrt((1-(G0/Gc)^(2/n))/(1-(Gc/G1)^(2/n)))*s + (1/Gc)^(1/n)))^n;
n = 3; w0 = 2*pi*1e3; G0 = 1e5; G1 = 0.1; Gc = 1/2;
W2 = (((1/w0)*sqrt((1-(G0/Gc)^(2/n))/(1-(Gc/G1)^(2/n)))*s + (G0/Gc)^(1/n))/((1/G1)^(1/n)*(1/w0)*sqrt((1-(G0/Gc)^(2/n))/(1-(Gc/G1)^(2/n)))*s + (1/Gc)^(1/n)))^n; P = [W1 -W1;
0 W2;
1 0];
[H2, ~, gamma, ~] = hinfsyn(P, 1, 1,'TOLGAM', 0.001, 'METHOD', 'ric', 'DISPLAY', 'on');
H1 = 1 - H2;Root locus
figure;
gains = logspace(4, 7, 100);
hold on;
plot(real(pole(Gss)), imag(pole(Gss)), 'kx');
plot(real(tzero(Gss)), imag(tzero(Gss)), 'ko');
for k = 1:length(gains)
cl_poles = pole(feedback(Gss, gains(k)*s));
plot(real(cl_poles), imag(cl_poles), 'k.');
end
hold off;
axis square;
xlim([-500, 10]); ylim([0, 510]);
xlabel('Real Part'); ylabel('Imaginary Part');Flexible Joint
Import Mass Matrix, Stiffness Matrix, and Interface Nodes Coordinates
We first extract the stiffness and mass matrices.
K = extractMatrix('mat_K_6modes_2MDoF.matrix');
M = extractMatrix('mat_M_6modes_2MDoF.matrix');Then, we extract the coordinates of the interface nodes.
[int_xyz, int_i, n_xyz, n_i, nodes] = extractNodes('out_nodes_3D.txt'); save('./mat/flexor_ID16.mat', 'int_xyz', 'int_i', 'n_xyz', 'n_i', 'nodes', 'M', 'K');Output parameters
load('./mat/flexor_ID16.mat', 'int_xyz', 'int_i', 'n_xyz', 'n_i', 'nodes', 'M', 'K');| Total number of Nodes | 2 |
| Number of interface Nodes | 2 |
| Number of Modes | 6 |
| Size of M and K matrices | 18 |
| Node i | Node Number | x [m] | y [m] | z [m] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 181278.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2.0 | 181279.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | -0.0 |
| 11200000.0 | 195.0 | 2220.0 | -0.719 | -265.0 | 1.59 | -11200000.0 | -213.0 | -2220.0 | 0.147 |
| 195.0 | 11400000.0 | 1290.0 | -148.0 | -0.188 | 2.41 | -212.0 | -11400000.0 | -1290.0 | 148.0 |
| 2220.0 | 1290.0 | 119000000.0 | 1.31 | 1.49 | 1.79 | -2220.0 | -1290.0 | -119000000.0 | -1.31 |
| -0.719 | -148.0 | 1.31 | 33.0 | 0.000488 | -0.000977 | 0.141 | 148.0 | -1.31 | -33.0 |
| -265.0 | -0.188 | 1.49 | 0.000488 | 33.0 | 0.00293 | 266.0 | 0.154 | -1.49 | 0.00026 |
| 1.59 | 2.41 | 1.79 | -0.000977 | 0.00293 | 236.0 | -1.32 | -2.55 | -1.79 | 0.000379 |
| -11200000.0 | -212.0 | -2220.0 | 0.141 | 266.0 | -1.32 | 11400000.0 | 24600.0 | 1640.0 | 120.0 |
| -213.0 | -11400000.0 | -1290.0 | 148.0 | 0.154 | -2.55 | 24600.0 | 11400000.0 | 1290.0 | -72.0 |
| -2220.0 | -1290.0 | -119000000.0 | -1.31 | -1.49 | -1.79 | 1640.0 | 1290.0 | 119000000.0 | 1.32 |
| 0.147 | 148.0 | -1.31 | -33.0 | 0.00026 | 0.000379 | 120.0 | -72.0 | 1.32 | 34.7 |
| 0.02 | 1e-09 | -4e-08 | -1e-10 | 0.0002 | -3e-11 | 0.004 | 5e-08 | 7e-08 | 1e-10 |
| 1e-09 | 0.02 | -3e-07 | -0.0002 | -1e-10 | -2e-09 | 2e-08 | 0.004 | 3e-07 | 1e-05 |
| -4e-08 | -3e-07 | 0.02 | 7e-10 | -2e-09 | 1e-09 | 3e-07 | 7e-08 | 0.003 | 1e-09 |
| -1e-10 | -0.0002 | 7e-10 | 4e-06 | -1e-12 | -6e-13 | 2e-10 | -7e-06 | -8e-10 | -1e-09 |
| 0.0002 | -1e-10 | -2e-09 | -1e-12 | 3e-06 | 2e-13 | 9e-06 | 4e-11 | 2e-09 | -3e-13 |
| -3e-11 | -2e-09 | 1e-09 | -6e-13 | 2e-13 | 4e-07 | 8e-11 | 9e-10 | -1e-09 | 2e-12 |
| 0.004 | 2e-08 | 3e-07 | 2e-10 | 9e-06 | 8e-11 | 0.02 | -7e-08 | -3e-07 | -2e-10 |
| 5e-08 | 0.004 | 7e-08 | -7e-06 | 4e-11 | 9e-10 | -7e-08 | 0.01 | -4e-08 | 0.0002 |
| 7e-08 | 3e-07 | 0.003 | -8e-10 | 2e-09 | -1e-09 | -3e-07 | -4e-08 | 0.02 | -1e-09 |
| 1e-10 | 1e-05 | 1e-09 | -1e-09 | -3e-13 | 2e-12 | -2e-10 | 0.0002 | -1e-09 | 2e-06 |
Using K, M and int_xyz, we can use the Reduced Order Flexible Solid simscape block.
Flexible Joint Characteristics
| Caracteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Axial Stiffness [N/um] | 119 |
| Bending Stiffness [Nm/rad] | 33 |
| Bending Stiffness [Nm/rad] | 33 |
| Torsion Stiffness [Nm/rad] | 236 |
Identification
m = 10;The dynamics is identified from the applied force to the measured relative displacement.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'flexor_ID16';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/T'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/D'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
G = linearize(mdl, io);| Caracteristic | Value | Identification |
|---|---|---|
| Axial Stiffness Dz [N/um] | 119 | 119 |
| Bending Stiffness Rx [Nm/rad] | 33 | 34 |
| Bending Stiffness Ry [Nm/rad] | 33 | 126 |
| Torsion Stiffness Rz [Nm/rad] | 236 | 238 |
Integral Force Feedback with Amplified Piezo
Import Mass Matrix, Stiffness Matrix, and Interface Nodes Coordinates
We first extract the stiffness and mass matrices.
K = extractMatrix('piezo_amplified_IFF_K.txt');
M = extractMatrix('piezo_amplified_IFF_M.txt');Then, we extract the coordinates of the interface nodes.
[int_xyz, int_i, n_xyz, n_i, nodes] = extractNodes('piezo_amplified_IFF.txt');IFF Plant
The transfer function from the force actuator to the force sensor is identified and shown in Figure fig:piezo_amplified_iff_plant.
Kiff = tf(0); m = 0; %% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_IFF';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Kiff'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/G'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
Gf = linearize(mdl, io); m = 10; Gfm = linearize(mdl, io);IFF controller
The controller is defined and the loop gain is shown in Figure fig:piezo_amplified_iff_loop_gain.
Kiff = -1e12/s;Closed Loop System
m = 10; Kiff = -1e12/s; %% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'piezo_amplified_IFF';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Dw'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fd'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/d'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/G'], 1, 'output'); io_i = io_i + 1;
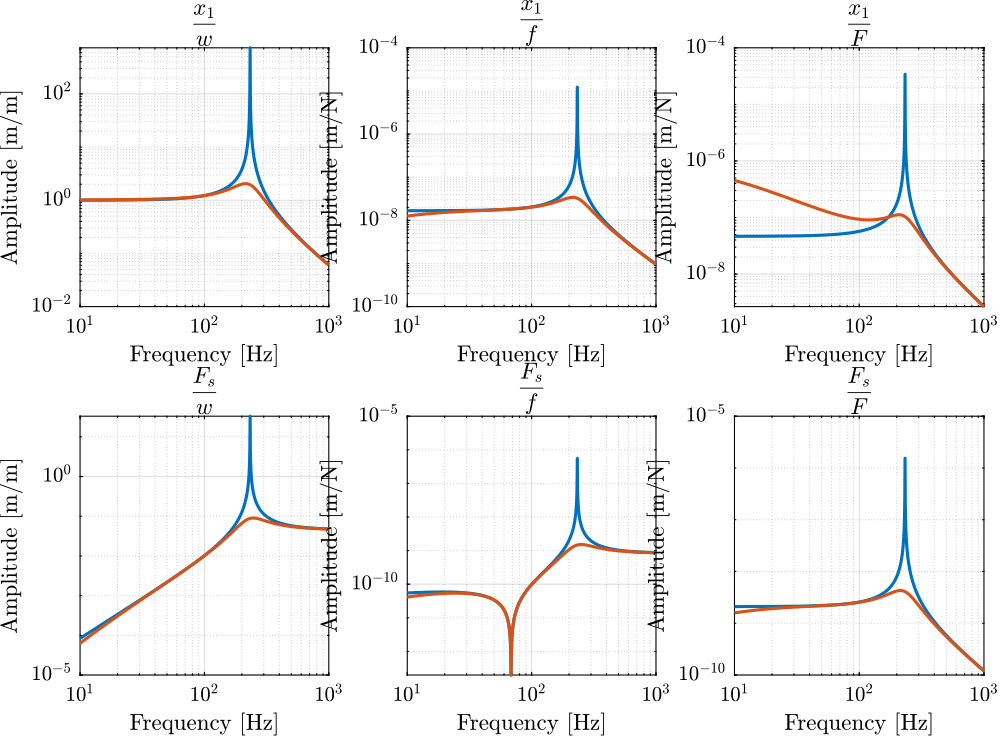
Giff = linearize(mdl, io);
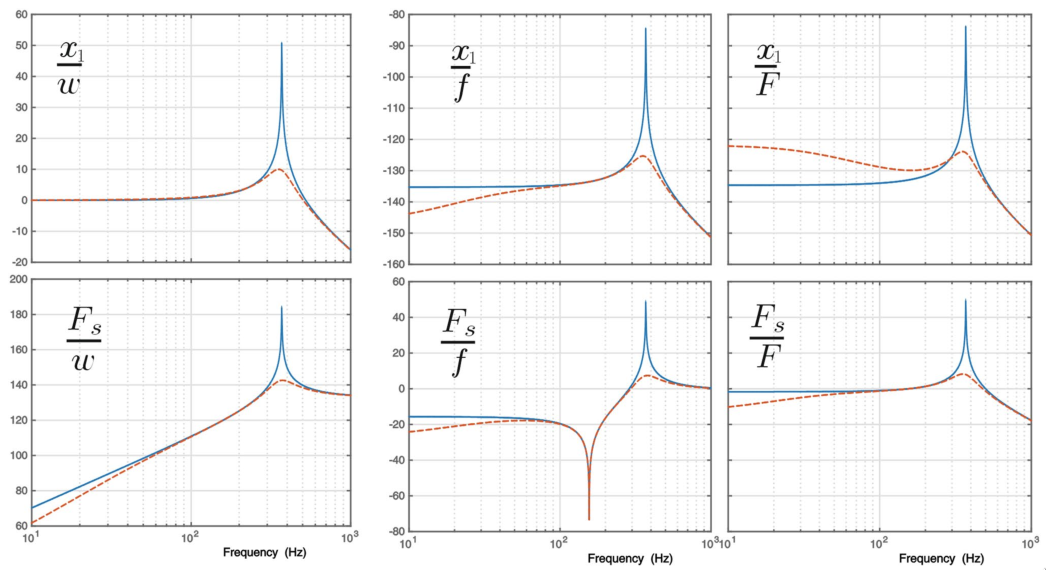
Giff.InputName = {'w', 'f', 'F'};
Giff.OutputName = {'x1', 'Fs'}; Kiff = tf(0); G = linearize(mdl, io);
G.InputName = {'w', 'f', 'F'};
G.OutputName = {'x1', 'Fs'};