Measurement of Piezoelectric Amplifiers
Table of Contents
Two voltage amplifiers are tested:
The piezoelectric actuator under test is an APA95ML from Cedrat technology. It contains three stacks with a capacitance of \(5 \mu F\) each that can be connected independently to the amplifier.
1 Effect of a change of capacitance
1.1 Cedrat Technology
Load Data
piezo1 = load('mat/cedrat_la75b_med_1_stack.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
piezo2 = load('mat/cedrat_la75b_med_2_stack.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
piezo3 = load('mat/cedrat_la75b_med_3_stack.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
Compute Coherence and Transfer functions
Ts = 1e-4; win = hann(ceil(0.1/Ts)); [tf_1, f_1] = tfestimate(piezo1.V_in, piezo1.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_1, ~] = mscohere(piezo1.V_in, piezo1.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [tf_2, f_2] = tfestimate(piezo2.V_in, piezo2.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_2, ~] = mscohere(piezo2.V_in, piezo2.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [tf_3, f_3] = tfestimate(piezo3.V_in, piezo3.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_3, ~] = mscohere(piezo3.V_in, piezo3.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
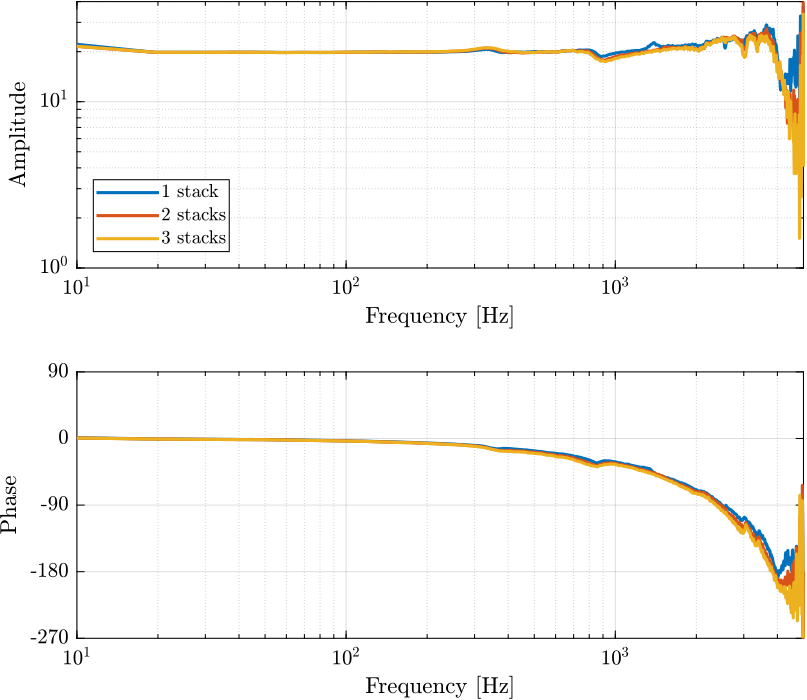
Figure 1: Effect of a change of the piezo capacitance on the Amplifier transfer function
1.2 PI
piezo1 = load('mat/pi_505_high.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
piezo2 = load('mat/pi_505_high_2_stacks.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
piezo3 = load('mat/pi_505_high_3_stacks.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
Ts = 1e-4; win = hann(ceil(0.1/Ts)); [tf_1, f_1] = tfestimate(piezo1.V_in, piezo1.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_1, ~] = mscohere(piezo1.V_in, piezo1.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [tf_2, f_2] = tfestimate(piezo2.V_in, piezo2.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_2, ~] = mscohere(piezo2.V_in, piezo2.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [tf_3, f_3] = tfestimate(piezo3.V_in, piezo3.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_3, ~] = mscohere(piezo3.V_in, piezo3.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
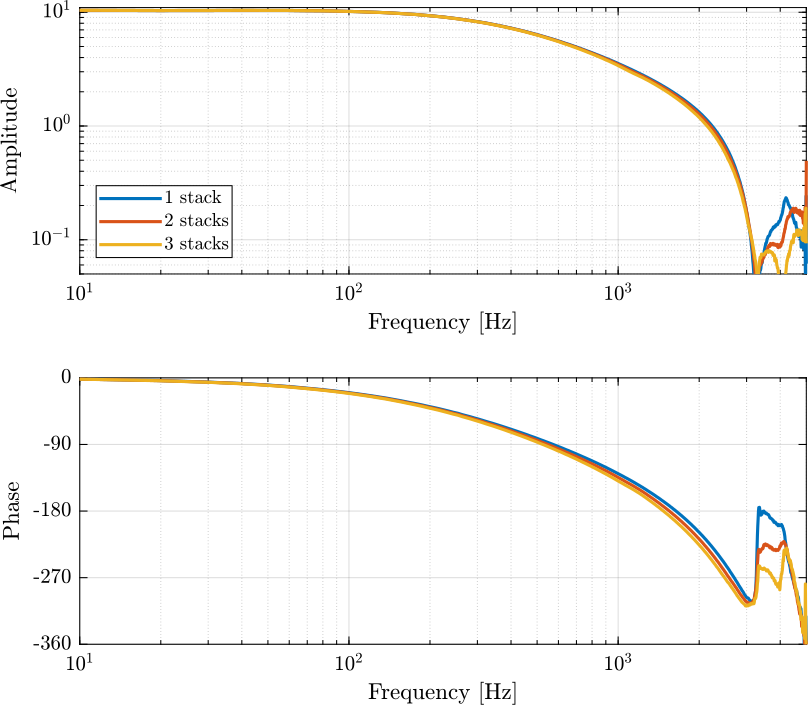
Figure 2: Effect of a change of the piezo capacitance on the Amplifier transfer function
2 Effect of a change in Voltage level
2.1 Cedrat Technology
hi = load('mat/cedrat_la75b_high_1_stack.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
me = load('mat/cedrat_la75b_med_1_stack.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
lo = load('mat/cedrat_la75b_low_1_stack.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
Ts = 1e-4; win = hann(ceil(0.1/Ts)); [tf_hi, f_hi] = tfestimate(hi.V_in, hi.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_hi, ~] = mscohere(hi.V_in, hi.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [tf_me, f_me] = tfestimate(me.V_in, me.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_me, ~] = mscohere(me.V_in, me.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [tf_lo, f_lo] = tfestimate(lo.V_in, lo.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_lo, ~] = mscohere(lo.V_in, lo.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
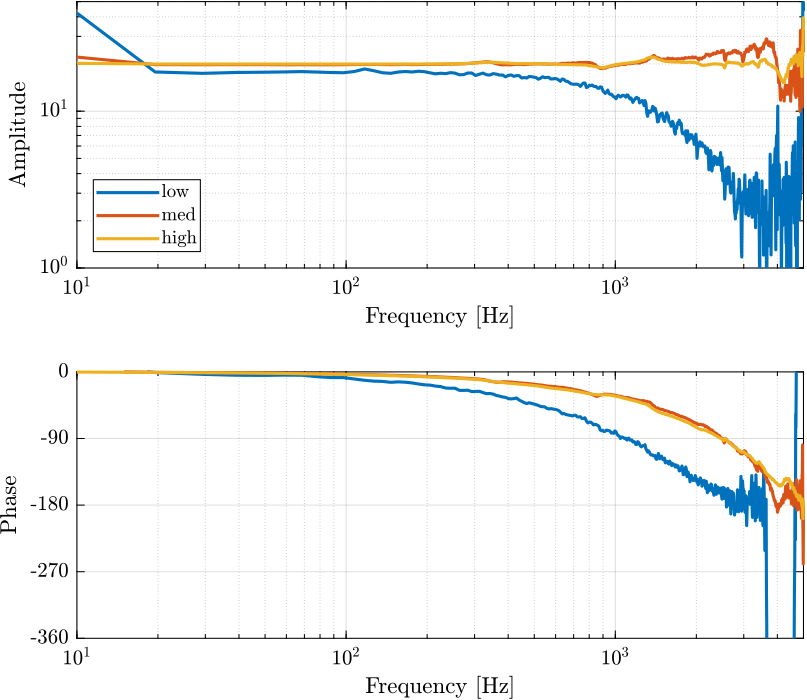
Figure 3: Effect of a change of voltage level on the Amplifier transfer function
2.2 PI
hi = load('mat/pi_505_high.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
lo = load('mat/pi_505_low.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
Ts = 1e-4; win = hann(ceil(0.1/Ts)); [tf_hi, f_hi] = tfestimate(hi.V_in, hi.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_hi, ~] = mscohere(hi.V_in, hi.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [tf_lo, f_lo] = tfestimate(lo.V_in, lo.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [co_lo, ~] = mscohere(lo.V_in, lo.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
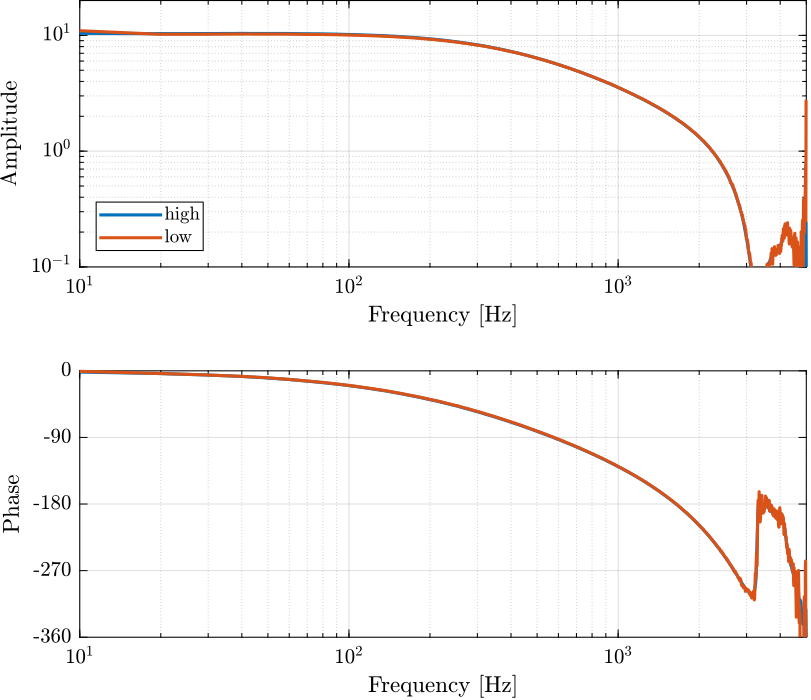
Figure 4: Effect of a change of voltage level on the Amplifier transfer function
3 Comparison PI / Cedrat
3.1 Results
ce_results = load('mat/cedrat_la75b_high_1_stack.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
pi_results = load('mat/pi_505_high.mat', 't', 'V_in', 'V_out');
Ts = 1e-4; win = hann(ceil(0.1/Ts)); [tf_ce, f_ce] = tfestimate(ce_results.V_in, ce_results.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts); [tf_pi, f_pi] = tfestimate(pi_results.V_in, pi_results.V_out, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
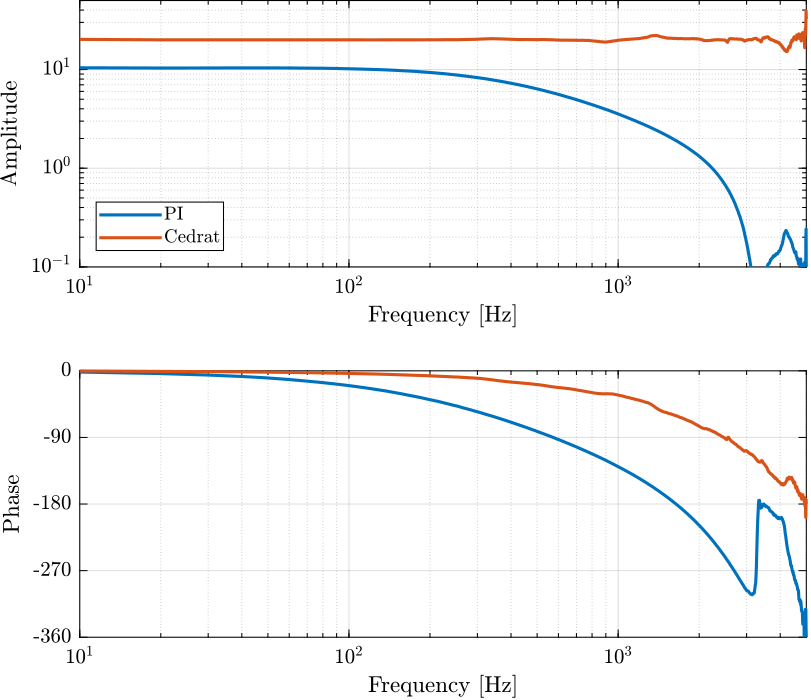
Figure 5: Comparison of the two Amplifier transfer functions
4 Impedance Measurement
The goal is to experimentally measure the output impedance of the voltage amplifiers.
To do so, the output voltage is first measure without any load (\(V\)). It is then measure when a 10Ohm load is used (\(V^\prime\)).
The load (\(R = 10\Omega\)) and the internal resistor (\(R_i\)) form a voltage divider, and thus: \[ V^\prime = \frac{R}{R + R_i} V \]
From the two values of voltage, the internal resistor value can be computed: \[ R_i = R \frac{V - V^\prime}{V^\prime} \]
4.1 Cedrat Technology
R = 10; % Resistive Load used [Ohm] V = 10.09; % Output Voltage without any load [V] Vp = 3.46; % Output Voltage with resistice load [V]
R * (V - Vp)/Vp;
19.162
C = 5e-6; % Capacitance in [F] Ri = R * (V - Vp)/Vp; % Internal resistance [Ohm] G_ce = 1/(1+Ri*C*s);
4.2 PI
R = 10; % Resistive Load used [Ohm] V = 10.35; % Output Voltage without any load [V] Vp = 4.14; % Output Voltage with resistice load [V]
R * (V - Vp)/Vp
15