Nano-Hexapod - Test Bench
Table of Contents
This report is also available as a pdf.
Here are the documentation of the equipment used for this test bench:
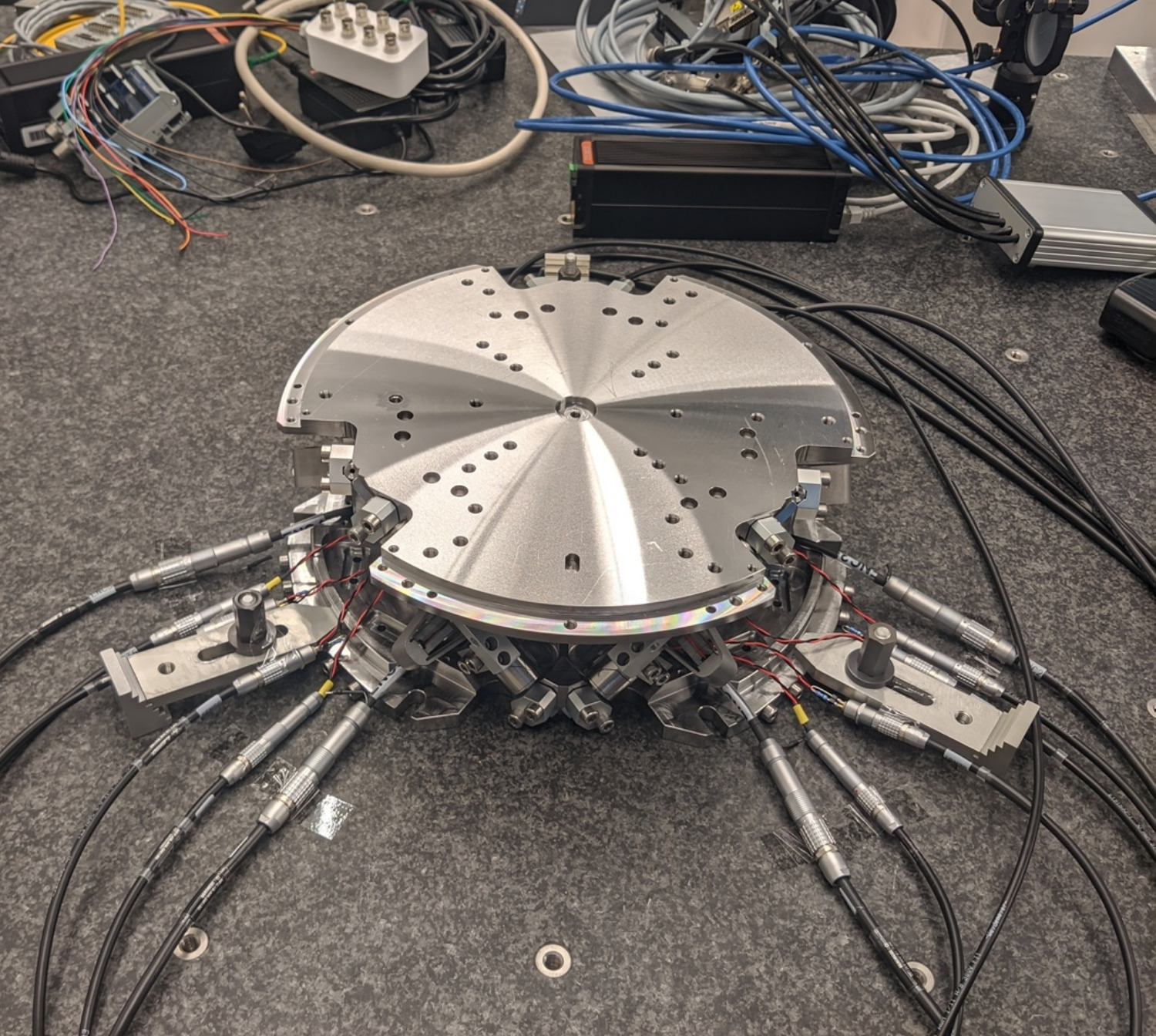
Figure 1: Nano-Hexapod
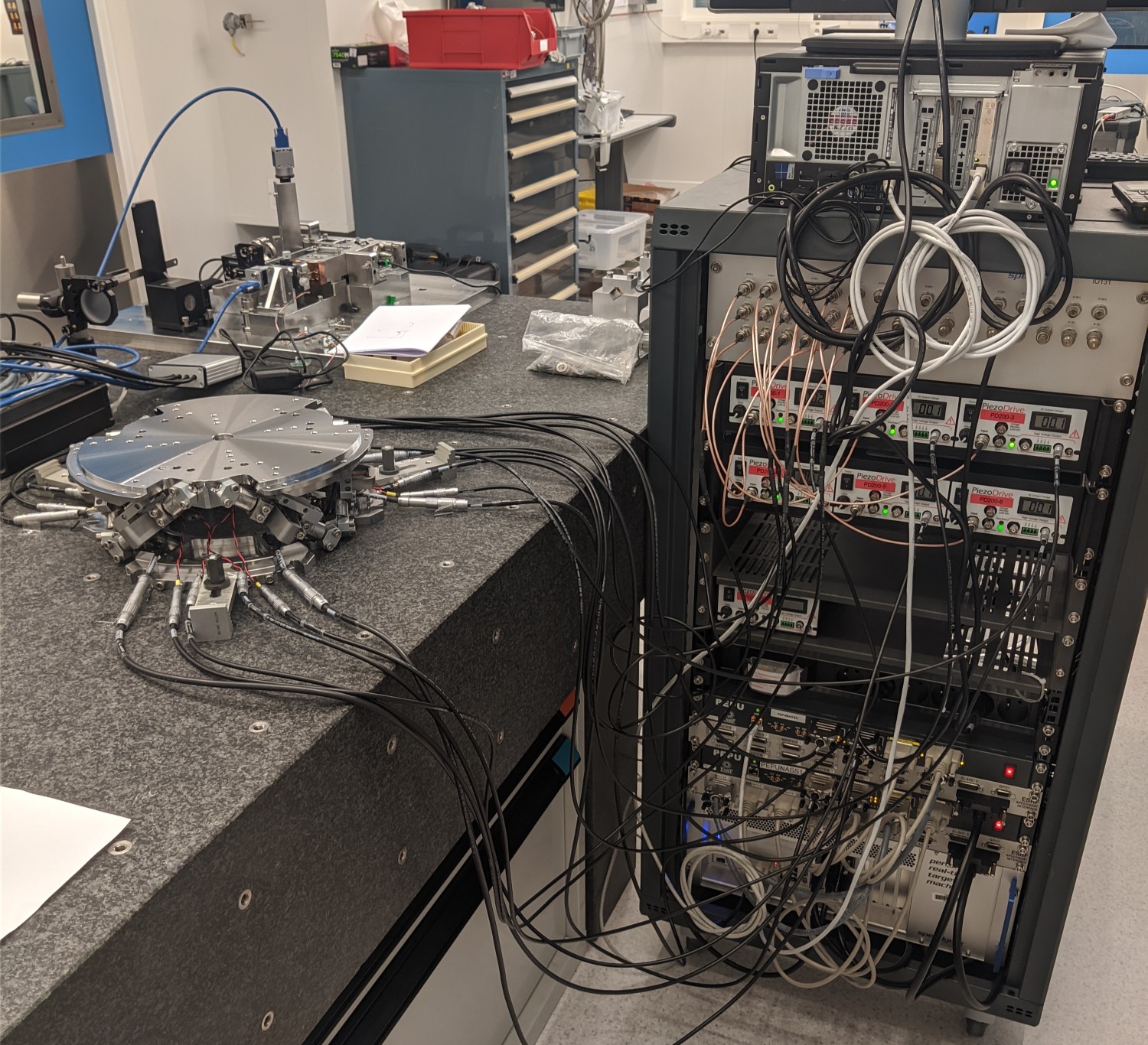
Figure 2: Nano-Hexapod and the control electronics
1 Encoders fixed to the Struts
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Load Data
meas_data_lf = {};
for i = 1:6
meas_data_lf(i) = {load(sprintf('mat/frf_data_exc_strut_%i_noise_lf.mat', i), 't', 'Va', 'Vs', 'de')};
meas_data_hf(i) = {load(sprintf('mat/frf_data_exc_strut_%i_noise_hf.mat', i), 't', 'Va', 'Vs', 'de')};
end
1.3 Spectral Analysis - Setup
% Sampling Time [s] Ts = (meas_data_lf{1}.t(end) - (meas_data_lf{1}.t(1)))/(length(meas_data_lf{1}.t)-1); % Sampling Frequency [Hz] Fs = 1/Ts; % Hannning Windows win = hanning(ceil(1*Fs));
And we get the frequency vector.
[~, f] = tfestimate(meas_data_lf{1}.Va, meas_data_lf{1}.de, win, [], [], 1/Ts);
i_lf = f < 250; % Points for low frequency excitation i_hf = f > 250; % Points for high frequency excitation
1.4 DVF Plant
First, let’s compute the coherence from the excitation voltage and the displacement as measured by the encoders (Figure 3).
%% Coherence coh_dvf_lf = zeros(length(f), 6, 6); coh_dvf_hf = zeros(length(f), 6, 6); for i = 1:6 coh_dvf_lf(:, :, i) = mscohere(meas_data_lf{i}.Va, meas_data_lf{i}.de, win, [], [], 1/Ts); coh_dvf_hf(:, :, i) = mscohere(meas_data_hf{i}.Va, meas_data_hf{i}.de, win, [], [], 1/Ts); end
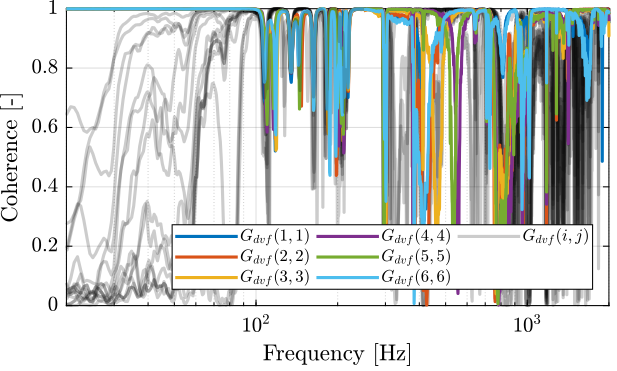
Figure 3: Obtained coherence for the DVF plant
Then the 6x6 transfer function matrix is estimated (Figure 4).
%% DVF Plant G_dvf_lf = zeros(length(f), 6, 6); G_dvf_hf = zeros(length(f), 6, 6); for i = 1:6 G_dvf_lf(:, :, i) = tfestimate(meas_data_lf{i}.Va, meas_data_lf{i}.de, win, [], [], 1/Ts); G_dvf_hf(:, :, i) = tfestimate(meas_data_hf{i}.Va, meas_data_hf{i}.de, win, [], [], 1/Ts); end
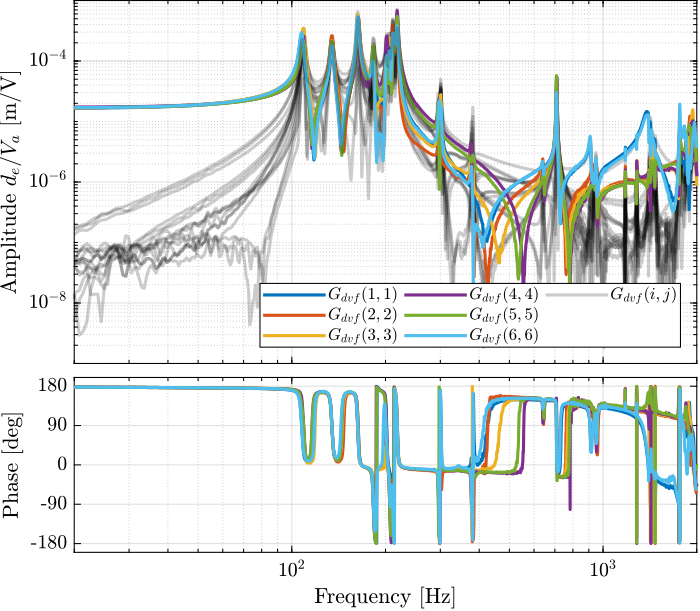
Figure 4: Measured FRF for the DVF plant
1.5 IFF Plant
First, let’s compute the coherence from the excitation voltage and the displacement as measured by the encoders (Figure 5).
%% Coherence coh_iff_lf = zeros(length(f), 6, 6); coh_iff_hf = zeros(length(f), 6, 6); for i = 1:6 coh_iff_lf(:, :, i) = mscohere(meas_data_lf{i}.Va, meas_data_lf{i}.Vs, win, [], [], 1/Ts); coh_iff_hf(:, :, i) = mscohere(meas_data_hf{i}.Va, meas_data_hf{i}.Vs, win, [], [], 1/Ts); end
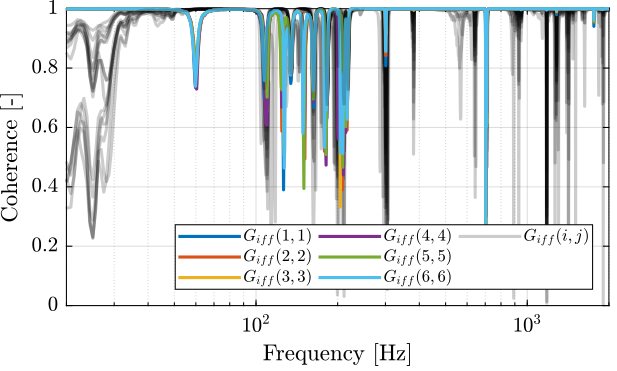
Figure 5: Obtained coherence for the IFF plant
Then the 6x6 transfer function matrix is estimated (Figure 6).
%% IFF Plant G_iff_lf = zeros(length(f), 6, 6); G_iff_hf = zeros(length(f), 6, 6); for i = 1:6 G_iff_lf(:, :, i) = tfestimate(meas_data_lf{i}.Va, meas_data_lf{i}.Vs, win, [], [], 1/Ts); G_iff_hf(:, :, i) = tfestimate(meas_data_hf{i}.Va, meas_data_hf{i}.Vs, win, [], [], 1/Ts); end
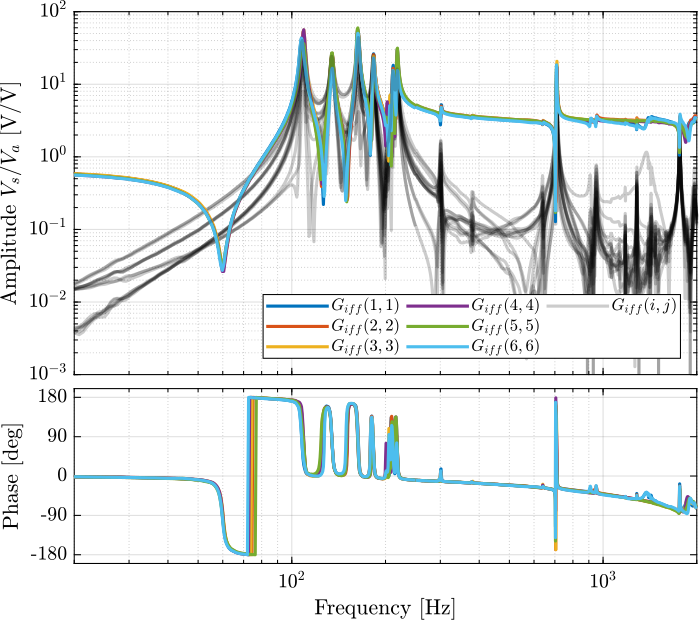
Figure 6: Measured FRF for the IFF plant
1.6 Jacobian
load('jacobian.mat', 'J');
1.6.1 DVF Plant
G_dvf_J_lf = permute(pagemtimes(inv(J), pagemtimes(permute(G_dvf_lf, [2 3 1]), inv(J'))), [3 1 2]); G_dvf_J_hf = permute(pagemtimes(inv(J), pagemtimes(permute(G_dvf_hf, [2 3 1]), inv(J'))), [3 1 2]);
1.6.2 IFF Plant
G_iff_J_lf = permute(pagemtimes(inv(J), pagemtimes(permute(G_iff_lf, [2 3 1]), inv(J'))), [3 1 2]); G_iff_J_hf = permute(pagemtimes(inv(J), pagemtimes(permute(G_iff_hf, [2 3 1]), inv(J'))), [3 1 2]);