SVD Control
Table of Contents
1 Simscape Model - Gravimeter
1.1 Simulink
open('gravimeter.slx')
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'gravimeter';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F1'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F2'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F3'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Acc_side'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Acc_side'], 2, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Acc_top'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Acc_top'], 2, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
G = linearize(mdl, io);
G.InputName = {'F1', 'F2', 'F3'};
G.OutputName = {'Ax1', 'Az1', 'Ax2', 'Az2'};
The plant as 6 states as expected (2 translations + 1 rotation)
size(G)
State-space model with 4 outputs, 3 inputs, and 6 states.
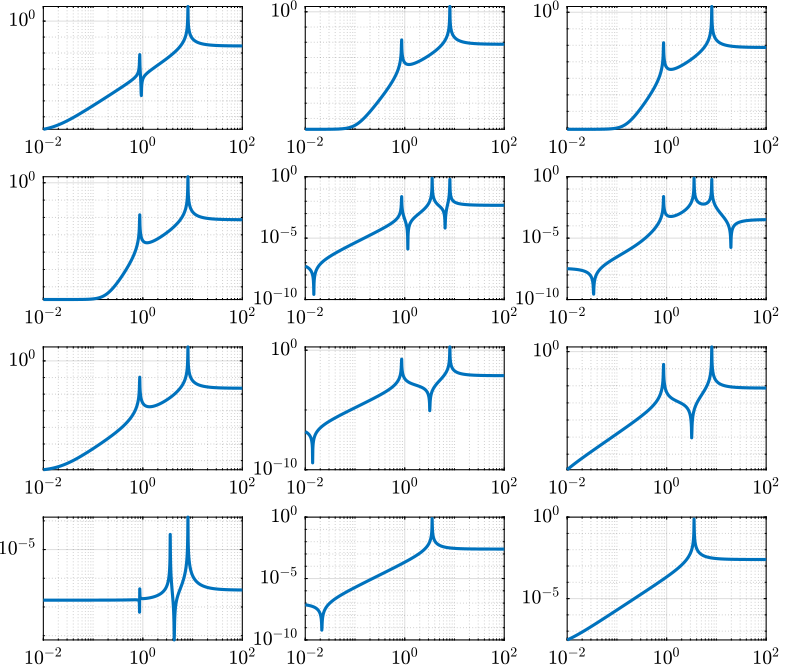
Figure 1: Open Loop Transfer Function from 3 Actuators to 4 Accelerometers
2 Simscape Model - Stewart Platform
2.1 Jacobian
First, the position of the “joints” (points of force application) are estimated and the Jacobian computed.
open('stewart_platform/drone_platform_jacobian.slx');
sim('drone_platform_jacobian');
Aa = [a1.Data(1,:);
a2.Data(1,:);
a3.Data(1,:);
a4.Data(1,:);
a5.Data(1,:);
a6.Data(1,:)]';
Ab = [b1.Data(1,:);
b2.Data(1,:);
b3.Data(1,:);
b4.Data(1,:);
b5.Data(1,:);
b6.Data(1,:)]';
As = (Ab - Aa)./vecnorm(Ab - Aa);
l = vecnorm(Ab - Aa)';
J = [As' , cross(Ab, As)'];
save('./jacobian.mat', 'Aa', 'Ab', 'As', 'l', 'J');
2.2 Simulink
open('stewart_platform/drone_platform.slx');
Definition of spring parameters
kx = 50; % [N/m] ky = 50; kz = 50; cx = 0.025; % [Nm/rad] cy = 0.025; cz = 0.025;
We load the Jacobian.
load('./jacobian.mat', 'Aa', 'Ab', 'As', 'l', 'J');
The dynamics is identified from forces applied by each legs to the measured acceleration of the top platform.
%% Name of the Simulink File
mdl = 'drone_platform';
%% Input/Output definition
clear io; io_i = 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/u'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Inertial Sensor'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1;
G = linearize(mdl, io);
G.InputName = {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6'};
G.OutputName = {'Ax', 'Ay', 'Az', 'Arx', 'Ary', 'Arz'};
size(G)
State-space model with 6 outputs, 6 inputs, and 12 states.
Thanks to the Jacobian, we compute the transfer functions in the frame of the legs and in an inertial frame.
Gx = -G*inv(J');
Gx.InputName = {'Fx', 'Fy', 'Fz', 'Mx', 'My', 'Mz'};
Gl = -J*G;
Gl.OutputName = {'A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'A4', 'A5', 'A6'};
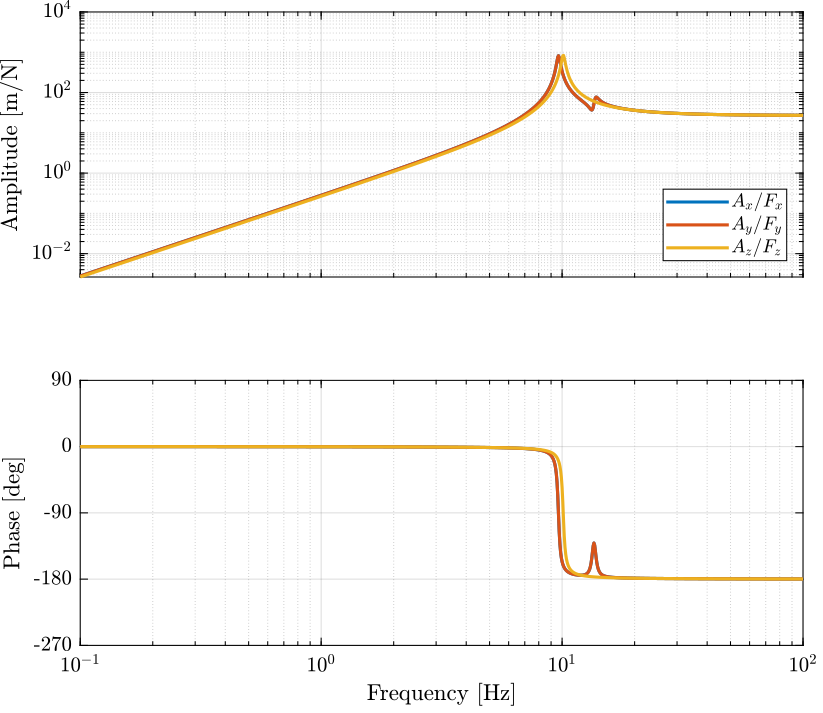
Figure 2: Stewart Platform Plant from forces applied by the legs to the acceleration of the platform
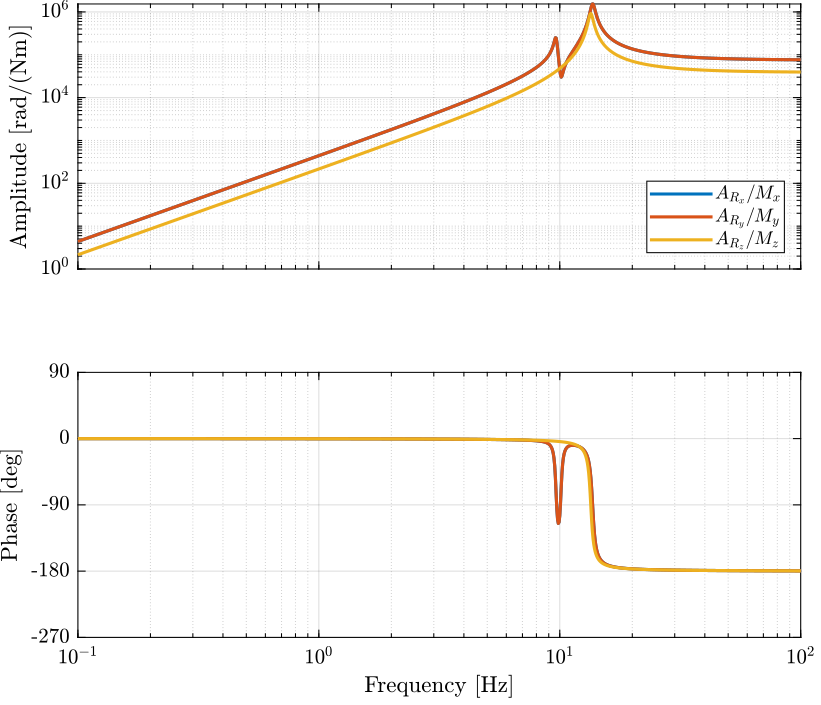
Figure 3: Stewart Platform Plant from torques applied by the legs to the angular acceleration of the platform
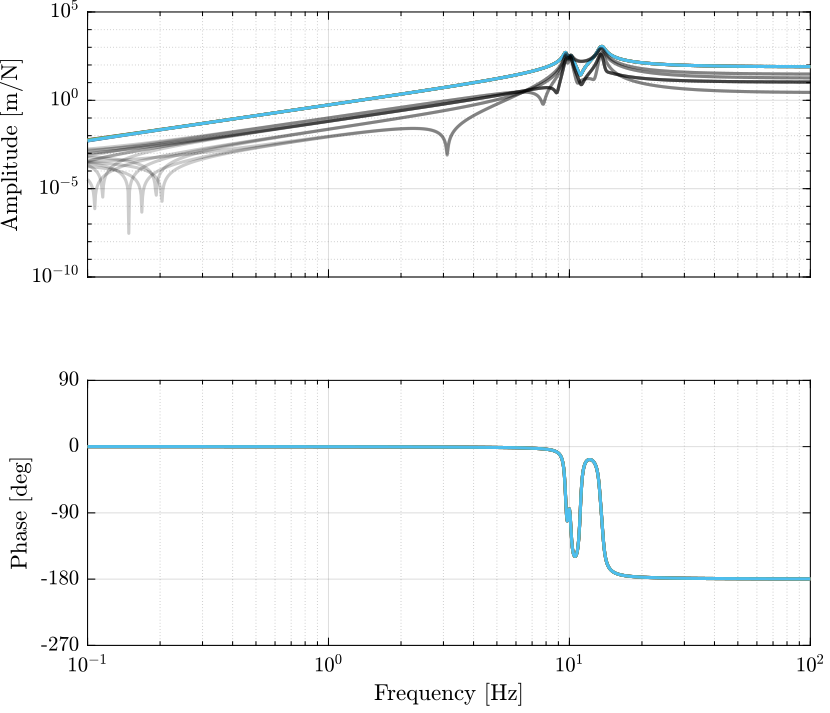
Figure 4: Stewart Platform Plant from forces applied by the legs to displacement of the legs