Stewart Platform - Control Study
Table of Contents
1 First Control Architecture
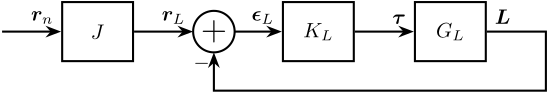
1.1 Control Schematic
1.2 Initialize the Stewart platform
stewart = initializeStewartPlatform(); stewart = initializeFramesPositions(stewart); stewart = generateGeneralConfiguration(stewart); stewart = computeJointsPose(stewart); stewart = initializeStrutDynamics(stewart); stewart = initializeCylindricalPlatforms(stewart); stewart = initializeCylindricalStruts(stewart); stewart = computeJacobian(stewart); stewart = initializeStewartPose(stewart);
1.3 Identification of the plant
Let’s identify the transfer function from \(\bm{\tau}}\) to \(\bm{L}\).
%% Options for Linearized options = linearizeOptions; options.SampleTime = 0; %% Name of the Simulink File mdl = 'stewart_platform_control'; %% Input/Output definition clear io; io_i = 1; io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/tau'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/L'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; %% Run the linearization G = linearize(mdl, io, options); G.InputName = {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6'}; G.OutputName = {'L1', 'L2', 'L3', 'L4', 'L5', 'L6'};
1.4 Plant Analysis
Diagonal terms Compare to off-diagonal terms
1.5 Controller Design
One integrator should be present in the controller.
A lead is added around the crossover frequency which is set to be around 500Hz.
% wint = 2*pi*100; % Integrate until [rad] % wlead = 2*pi*500; % Location of the lead [rad] % hlead = 2; % Lead strengh % Kl = 1e6 * ... % Gain % (s + wint)/(s) * ... % Integrator until 100Hz % (1 + s/(wlead/hlead)/(1 + s/(wlead*hlead))); % Lead wc = 2*pi*100; Kl = 1/abs(freqresp(G(1,1), wc)) * wc/s * 1/(1 + s/(3*wc)); Kl = Kl * eye(6);