Stewart Platform - Bibliography
Table of Contents
1. Built Stewart PLatforms
Actuators:
- Short Stroke: PZT, Voice Coil, Magnetostrictive
- Long Stroke: DC, AC, Servo + Ball Screw, Inchworm
Joints:
- Flexible: usually for short stroke
- Conventional
Sensors:
- Force Sensors
- Relative Motion Sensors: Encoders, LVDT
- Strain Gauge
- Inertial Sensors (Geophone, Accelerometer)
- External Metrology
1.1. Short Stroke
| University | Figure | Configuration | Joints | Actuators | Sensors | Application | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPL | fig:stewart_jpl | Cubic | Flexible | Voice Coil (0.5 mm) | Force (collocated) | spanos95_soft_activ_vibrat_isolat, rahman98_multiax Vibration Isolation (Space) | |
| Washinton, JPL | fig:stewart_ht_uw | Cubic | Elastomers | Voice Coil (10 mm) | Force, LVDT, Geophones | Isolation + Pointing (Space) | thayer98_stewar, thayer02_six_axis_vibrat_isolat_system, hauge04_sensor_contr_space_based_six |
| Wyoming | fig:stewart_uw_gsp | Cubic (CoM=CoK) | Flexible | Voice Coil | Force | mcinroy99_dynam, mcinroy99_precis_fault_toler_point_using_stewar_platf, mcinroy00_desig_contr_flexur_joint_hexap, li01_simul_vibrat_isolat_point_contr, jafari03_orthog_gough_stewar_platf_microm | |
| Brussels | fig:stewart_ulb_vc | Cubic | Flexible | Voice Coil | Force | Vibration Isolation | hanieh03_activ_stewar, preumont07_six_axis_singl_stage_activ |
| SRDC | fig:stewart_naval | Not Cubic | Ball joints | Voice Coil (10 mm) | taranti01_effic_algor_vibrat_suppr | ||
| SRDC | fig:stewart_pph | Non-Cubic | Flexible | Voice Coil | Accelerometers, External metrology: Eddy Current + optical | Pointing | chen03_payload_point_activ_vibrat_isolat |
| Harbin (China) | fig:stewart_tang18 | Cubic | Flexible | Voice Coil | Accelerometer in each leg | chi15_desig_exper_study_vcm_based, tang18_decen_vibrat_contr_voice_coil, jiao18_dynam_model_exper_analy_stewar | |
| Einhoven | fig:stewart_beijen | Almost cubic | Flexible | Voice Coil | Force Sensor + Accelerometer | Vibration Isolation | beijen18_self_tunin_mimo_distur_feedf, tjepkema12_activ_ph |
| JPL | fig:stewart_geng | Cubic (6-UPU) | Flexible | Magnetostrictive | Force (collocated), Accelerometers | Vibration Isolation | geng93_six_degree_of_freed_activ, geng94_six_degree_of_freed_activ, geng95_intel_contr_system_multip_degree |
| China | fig:stewart_zhang11 | Non-cubic | Flexible | Magnetostrictive | Inertial | zhang11_six_dof | |
| Brussels | fig:stewart_ulb_pz | Cubic | Flexible | Piezoelectric, Amplified | Piezo Force | Active Damping | abu02_stiff_soft_stewar_platf_activ |
| SRDC | fig:stewart_uqp | Cubic | Piezoelectric (50 um) | Geophone | Vibration | agrawal04_algor_activ_vibrat_isolat_spacec | |
| Taiwan | fig:stewart_nanoscale | Cubic | Flexible | Piezoelectric (120 um) | External capacitive | ting06_desig_stewar_nanos_platf, ting13_compos_contr_desig_stewar_nanos_platf | |
| Taiwan | fig:stewart_ting07 | Non-Cubic | Flexible | Piezoelectric (160 um) | External capacitive (LION) | ting07_measur_calib_stewar_microm_system | |
| Harbin (China) | fig:stewart_du14 | 6-SPS (Optimized) | Flexible | Piezoelectric | Strain Gauge | du14_piezo_actuat_high_precis_flexib | |
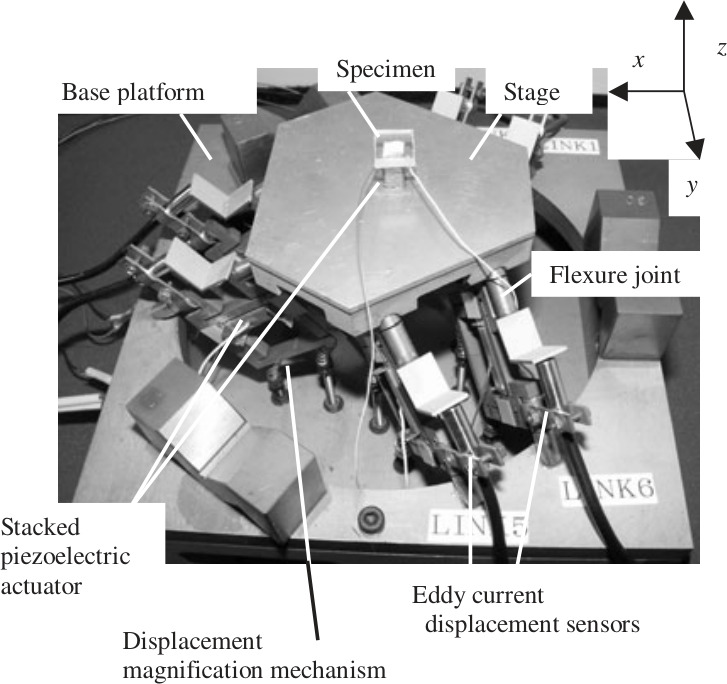
| Japan | fig:stewart_furutani | Non-Cubic | Flexible | Piezoelectric (16 um) | Eddy Current Displacement Sensors | Cutting machine | furutani04_nanom_cuttin_machin_using_stewar |
| China | fig:stewart_yang19 | 6-UPS (Cubic?) | Flexible | Piezoelectric | Force, Position | yang19_dynam_model_decoup_contr_flexib | |
| Shangai | fig:stewart_wang16 | Cubic | Flexible | Piezoelectric | Force Sensor + Accelerometer | wang16_inves_activ_vibrat_isolat_stewar | |
| Matra (France) | fig:stewart_mais | Cubic | Flexible | Piezoelectric (25 um) | Piezo force sensors | Vibration control | defendini00_techn |
| Japan | fig:stewart_torii | Non-Cubic | Flexible | Inchworm | torii12_small_size_self_propel_stewar_platf | ||
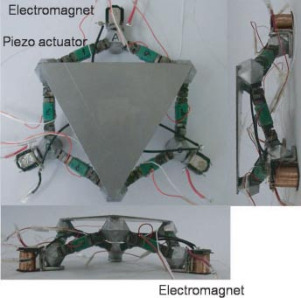
| Netherlands | fig:stewart_naves | Non-Cubic | Flexible | 3-phase rotary motor | Rotary Encoders | &naves20_desig;&naves20_t_flex |
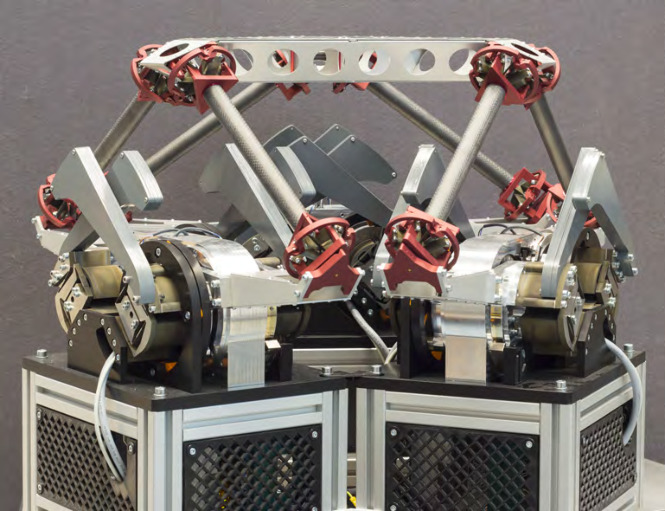
Figure 1: T-flex &naves20_desig
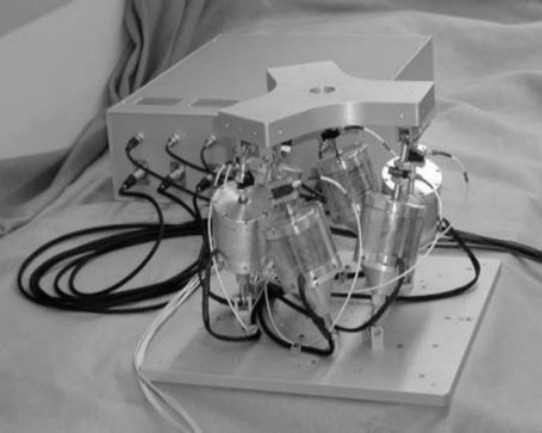
Figure 2: &taranti01_effic_algor_vibrat_suppr
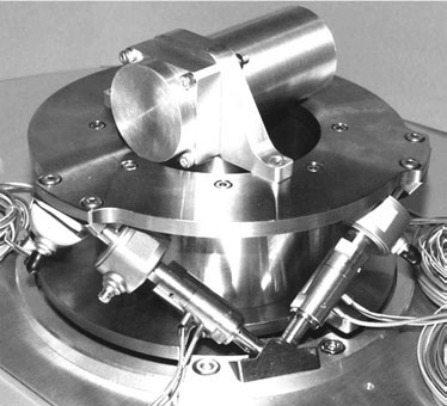

Figure 3: &defendini00_techn
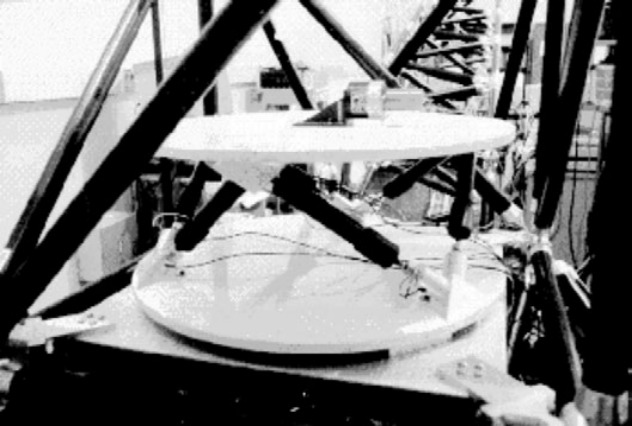

Figure 4: &geng94_six_degree_of_freed_activ
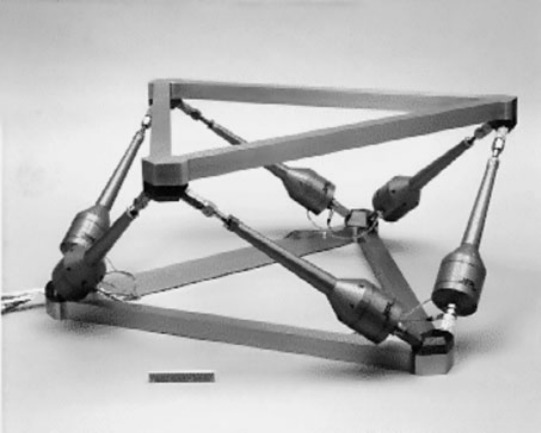

Figure 5: &spanos95_soft_activ_vibrat_isolat
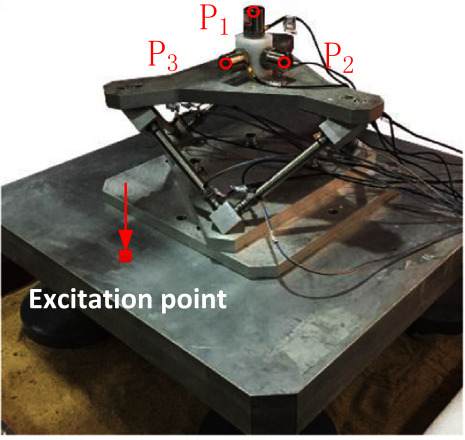
Figure 8: &wang16_inves_activ_vibrat_isolat_stewar
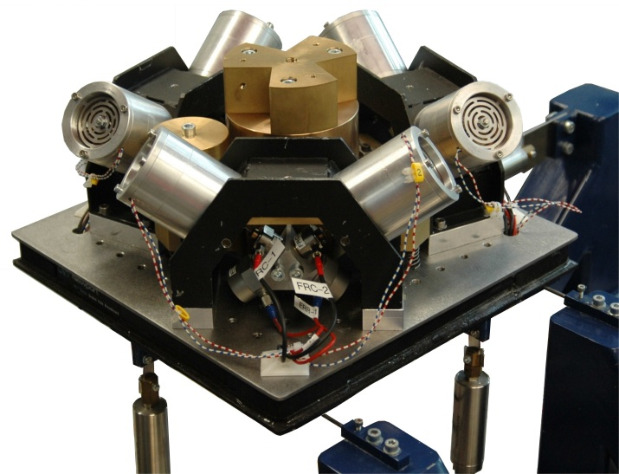
Figure 9: &beijen18_self_tunin_mimo_distur_feedf

Figure 10: &zhang11_six_dof
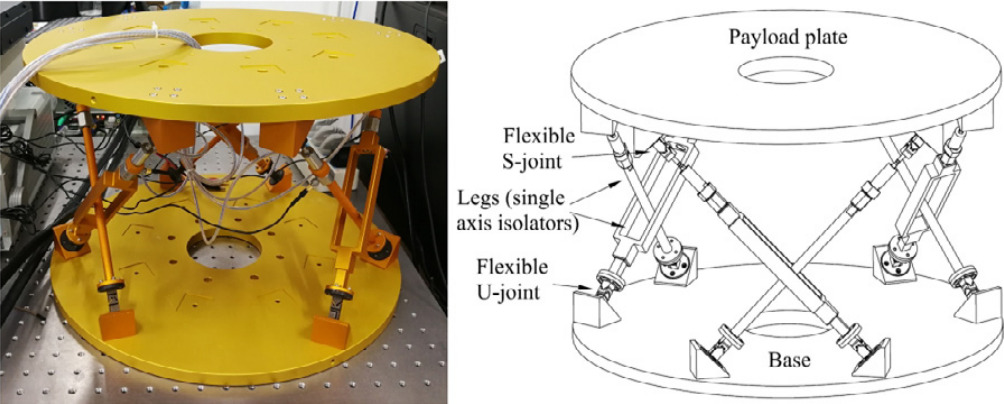
Figure 11: &yang19_dynam_model_decoup_contr_flexib
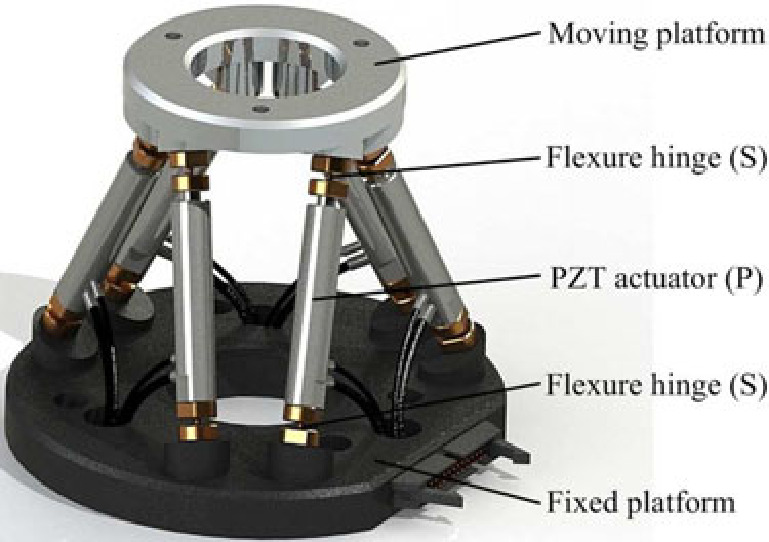
Figure 12: &du14_piezo_actuat_high_precis_flexib

Figure 13: &tang18_decen_vibrat_contr_voice_coil

Figure 14: &ting06_desig_stewar_nanos_platf

Figure 15: &ting07_measur_calib_stewar_microm_system
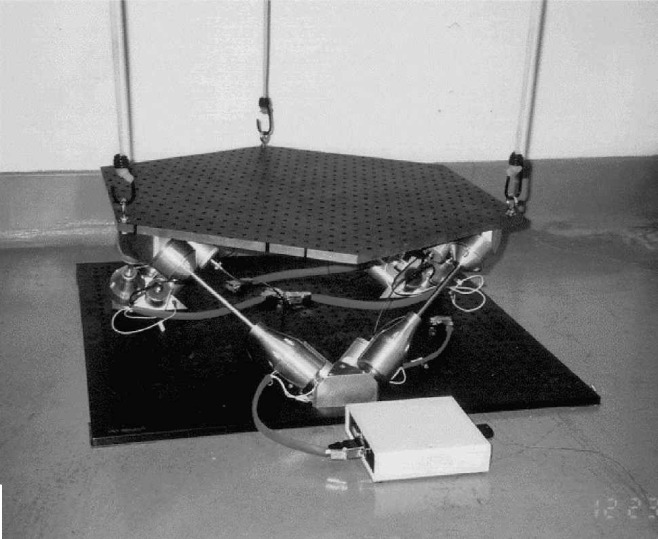
Figure 16: Hood Technology Corporation (HT) and the University of Washington (UW) have designed and tested a unique hexapod design for spaceborne interferometry missions &thayer02_six_axis_vibrat_isolat_system
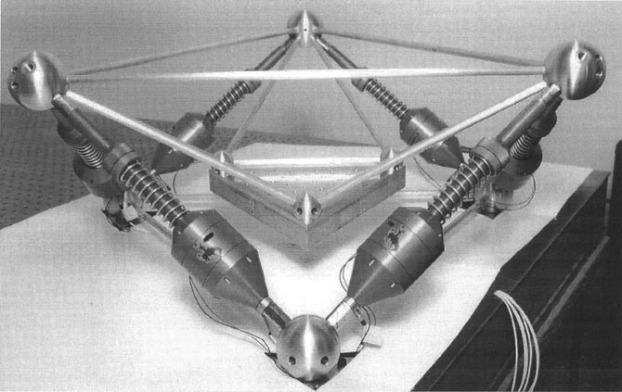
Figure 17: UW GSP: Mutually Orthogonal Stewart Geometry &li01_simul_fault_vibrat_isolat_point
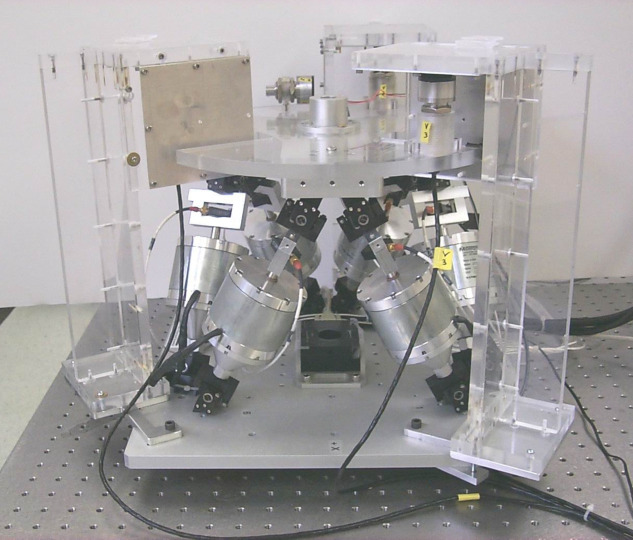
Figure 18: Precision Pointing Hexapod (PPH) &chen03_payload_point_activ_vibrat_isolat
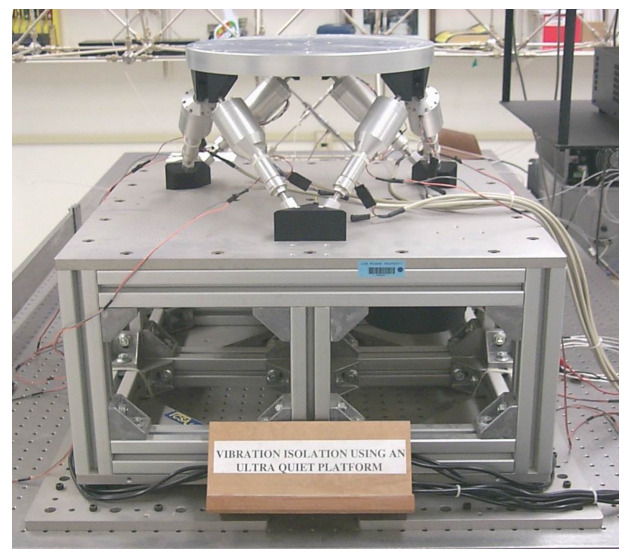
Figure 19: Ultra Quiet Platform (UQP) &agrawal04_algor_activ_vibrat_isolat_spacec

Figure 20: ULB - Piezoelectric &abu02_stiff_soft_stewar_platf_activ
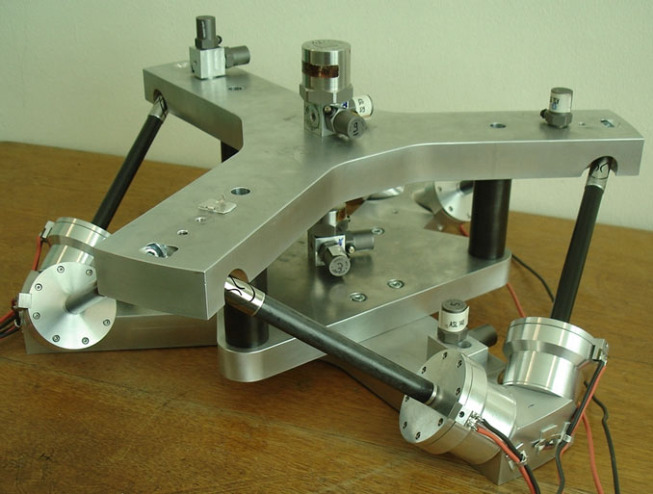

Figure 21: ULB - Voice Coil &hanieh03_activ_stewar
1.2. Long Stroke
| University | Figure | Configuration | Joints | Actuators | Sensors | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | fig:stewart_cleary | 6-UPS | Conventional | DC, gear + rack pinion | Encoder, 7um res | cleary91_protot_paral_manip |
| Seoul | fig:stewart_kim00 | Non-Cubic | Conventional | Hydraulic | LVDT | kim00_robus_track_contr_desig_dof_paral_manip |
| Xidian (China) | fig:stewart_su04 | Non-Cubic | Conventional | Servo Motor + Screwball | Encoder | su04_distur_rejec_high_precis_motion |
| Czech | fig:stewart_czech | 6-UPS | Conventional | DC, Ball Screw | Absolute Linear position | brezina08_ni_labview_matlab_simmec_stewar_platf_desig, houska10_desig_implem_absol_linear_posit, brezina10_contr_desig_stewar_platf_linear_actuat |
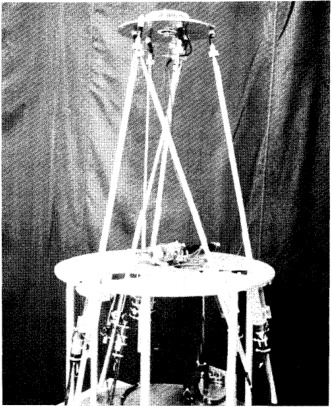
Figure 22: &cleary91_protot_paral_manip
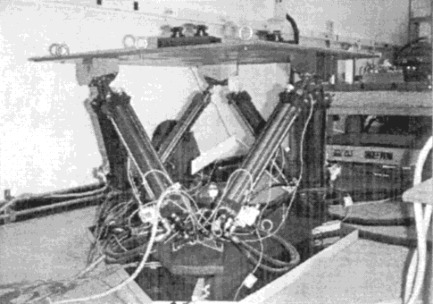
Figure 23: &kim01_six

Figure 24: &su04_distur_rejec_high_precis_motion
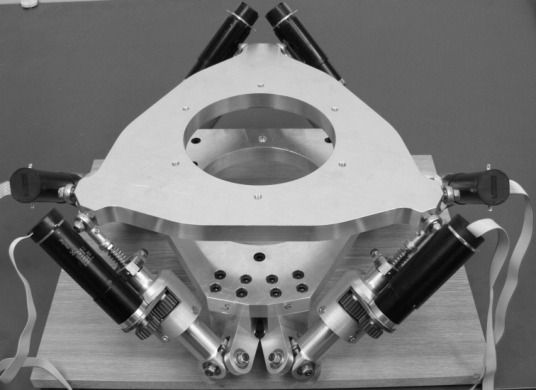
Figure 25: Stewart platform from Brno University (Czech) &brezina08_ni_labview_matlab_simmec_stewar_platf_desig
2. Articles - Design Related
- Flexible joints (Section sec:design_flexure)
- Specific geometry to have good decoupling properties (Section sec:design_decoupling)
- Alternative architectures for 6DoF parallel mechanisms (Section sec:design_architecture)
- Workspace (Section sec:design_workspace)
- Modelling (Section sec:design_modelling)
2.1. Flexures
From &hauge04_sensor_contr_space_based_six:
Elastomer flexures, rather than steel, reduce lateral stiffness and improve passive performance at payload resonance (damping) and at frequencies greater than 100 Hz.
| Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|
| Effect of flexures | mcinroy02_model_desig_flexur_joint_stewar |
2.2. Decoupling
| Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|
| Geometry for decoupling (CoM, CoK) | mcinroy00_desig_contr_flexur_joint_hexap |
| afzali-far16_vibrat_dynam_isotr_hexap_analy_studies |
2.3. Alternative Architectures
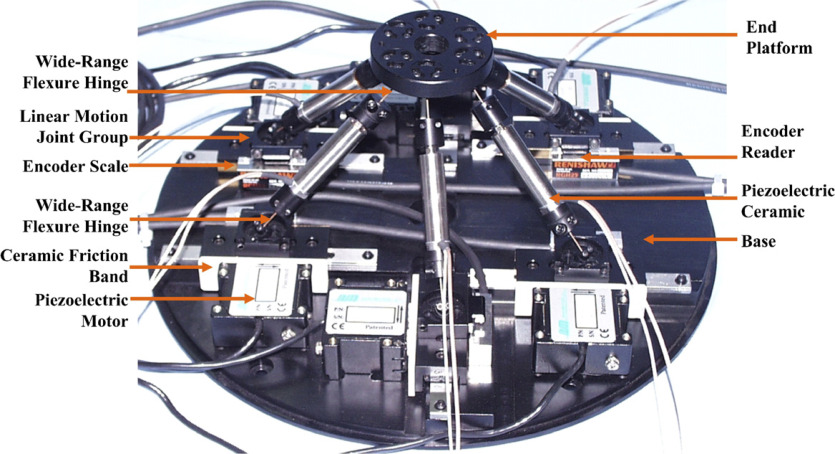
Figure 26: &dong07_desig_precis_compl_paral_posit
2.4. Workspace
| Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|
| Compute orientation | bonev01_new_approac_to_orien_works |
| Reachable Workspace | pernkopf06_works_analy_stewar_gough_type_paral_manip |
| Determination of the max. singularity free workspace | jiang09_deter_maxim_singul_free_orien |
| Orientation Workspace | jiang09_evaluat_repres_theor_orien_works |
3. Control
Different control objectives:
- Vibration Control (Section sec:control_isolation)
- Position Control (Section sec:control_position)
Sometimes, the two objectives are simultaneous, in that case multiple sensors needs to be combined in the control architecture (Section sec:control_multi_sensor).
Stewart platform, being 6DoF parallel mechanisms, have a coupled dynamics. In order to ease the control design, decoupling is generally required. Several approaches can be used (Section sec:control_decoupling).
3.1. Vibration Control and Active Damping
From &hauge04_sensor_contr_space_based_six:
In general, force sensors such as load cells, work well to measure vibration, but have difficulty with cross-axis dynamics. Inertial sensors, on the other hand, do not have this cross-axis limitation, but are usually more sensitive to payload and base dynamics and are more difficult to control due to the non-collocated nature of the sensor and actuator. Force sensors typically work well because they are not as sensitive to payload and base dynamics, but are limited in performance by a low-frequency zero pair resulting from the cross-axial stiffness. This zero pair has confused many researchers because it is very sensitive, occasionally becoming non-minimum phase. The zero pair is the current limitation in performance using load cell sensors.
3.1.1. Integral Force Feedback
| University | Actuators | Sensors | Control | Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPL | Magnetostrictive | Force (collocated), Accelerometers | Two layers: Decentralized IFF, Robust Adaptive Control | Two layer control for active damping and vibration isolation | geng95_intel_contr_system_multip_degree |
| JPL | Voice Coil | Force (collocated) | Decentralized IFF | Decentralized force feedback to reduce the transmissibility | spanos95_soft_activ_vibrat_isolat, rahman98_multiax |
| Washinton | Voice Coil | Force, LVDT, Geophones | LQG, Force + geophones for vibration, LVDT for pointing | Centralized control is no better than decentralized. Geophone + Force MISO control is good | thayer98_stewar, thayer02_six_axis_vibrat_isolat_system |
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Force | Centralized (cartesian) IFF | Difficult to decouple in practice | obrien98_lesson |
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Force | IFF, centralized (decouple) + decentralized (coupled) | Specific geometry: decoupled force plant. Better perf with centralized IFF | mcinroy99_dynam, mcinroy99_precis_fault_toler_point_using_stewar_platf, mcinroy00_desig_contr_flexur_joint_hexap |
| Brussels | APA | Piezo force sensor | Decentralized IFF | abu02_stiff_soft_stewar_platf_activ | |
| Brussels | Voice Coil | Force Sensor | Decentralized IFF | Effect of flexible joints | preumont07_six_axis_singl_stage_activ |
| Shangai | Piezoelectric | Force Sensor + Accelerometer | Vibration isolation, HAC-LAC (IFF + FxLMS) | Dynamic Model + Vibration Control | wang16_inves_activ_vibrat_isolat_stewar |
| China | Decentralized IFF | Design cubic configuration to have same modal frequencies: optimal damping of all modes | yang17_dynam_isotr_desig_decen_activ | ||
| Washinton | Voice Coil | Force | Decentralized IFF | Comparison of force sensor and inertial sensors. Issue on non-minimum phase zero | hauge04_sensor_contr_space_based_six |
| China | Piezoelectric | Force, Position | Vibration isolation, Model-Based, Modal control: 6x PI controllers | Stiffness of flexible joints is compensated using feedback, then the system is decoupled in the modal space | yang19_dynam_model_decoup_contr_flexib |
3.1.2. Sky-Hood Damping
| University | Actuators | Sensors | Control | Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Accelerometer (collocated), ext. Rx/Ry sensors | Cartesian acceleration feedback (isolation) + 2DoF pointing control (external sensor) | Decoupling, both vibration + pointing control | li01_simul_vibrat_isolat_point_contr |
| China | Voice Coil | Geophone + Eddy Current (Struts, collocated) | Decentralized (Sky Hook) + Centralized (modal) Control | pu11_six_degree_of_freed_activ | |
| China | Voice Coil | Accelerometer in each leg | Centralized Vibration Control, PI, Skyhook | abbas14_vibrat_stewar_platf | |
| Einhoven | Voice Coil | 6dof Accelerometers on mobile and fixed platforms | Self learning feedforward (FIR), Centralized MIMO feedback (sky hood damping) | beijen18_self_tunin_mimo_distur_feedf | |
| Harbin (China) | Voice Coil | Accelerometer in each leg | Decentralized vibration control | Vibration Control with VCM and Decentralized control | tang18_decen_vibrat_contr_voice_coil |
| Washinton | Voice Coil | Geophones | Decentralized Inertial Feedback | Centralized control is no better than decentralized. Geophone + Force MISO control is good | thayer02_six_axis_vibrat_isolat_system |
| Washinton | Voice Coil | Geophones | Decentralized Sky Hood Damping | Comparison of force sensor and inertial sensors | hauge04_sensor_contr_space_based_six |
| Harbin (China) | Voice Coil | Accelerometers | MIMO H-Infinity, active damping | Model + active damping with flexible hinges | jiao18_dynam_model_exper_analy_stewar |
3.1.3. Vibration Control of Narrowband Disturbances
| University | Actuators | Sensors | Control | Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPL | Magnetostrictive | Force, Accelerometers | Robust Adaptive Filter | Hardware implementation | geng93_six_degree_of_freed_activ, geng94_six_degree_of_freed_activ |
| SRDC | LMS with FIR (feedforward), disturbance rejection, Decentralized (struts) PID | Rejection of narrowband periodic disturbances | chen03_payload_point_activ_vibrat_isolat | ||
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Adaptive sinusoidal disturbance (Phase Lock Loop) | lin03_adapt_sinus_distur_cancel_precis | ||
| SRDC | Piezo | Geophone (collocated) | “multiple error LMS” (require measured disturbance) vs “clear box” | agrawal04_algor_activ_vibrat_isolat_spacec | |
| China | Magnetostrictive | Inertial | Sinusoidal vibration, adaptive filters (LMS) | Design and Control of flexure joint Hexapods | zhang11_six_dof |
| Shangai | Piezoelectric | Force Sensor + Accelerometer | Vibration isolation, HAC-LAC (IFF + FxLMS) | Dynamic Model + Vibration Control | wang16_inves_activ_vibrat_isolat_stewar |
3.2. Position Control
Here, the objective is to position the mobile platform with respect to an external metrology or internal metrology.
Control Strategy:
- Decentralized P, PI or PID
- LQR, LQG
- H-Infinity
- Two Layer
| University | Actuators | Sensors | Control | Modelling | Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Washinton | Voice Coil | Force, LVDT, Geophones | LQG, Force + geophones for vibration, LVDT for pointing | FEM => State Space | Centralized control is no better than decentralized. Geophone + Force MISO control is good | thayer98_stewar, thayer02_six_axis_vibrat_isolat_system |
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Force, LVDT | IFF, centralized (decouple) + decentralized (coupled) | Lumped | Specific geometry: decoupled force plant. Better perf with centralized IFF | mcinroy99_dynam, mcinroy99_precis_fault_toler_point_using_stewar_platf, mcinroy00_desig_contr_flexur_joint_hexap |
| Seoul | Hydraulic | LVDT | Decentralized (strut) vs Centralized (cartesian) | kim00_robus_track_contr_desig_dof_paral_manip | ||
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Accelerometer (collocated), ext. Rx/Ry sensors | Cartesian acceleration feedback (isolation) + 2DoF pointing control (external sensor) | Analytical equations | Decoupling, both vibration + pointing control | li01_simul_vibrat_isolat_point_contr |
| Japan | APA | Eddy current displacement | Decentralized (struts) PI + LPF control | furutani04_nanom_cuttin_machin_using_stewar | ||
| China | Voice Coil | Geophone + Eddy Current (Struts, collocated) | Decentralized (Sky Hook) + Centralized (modal) Control | pu11_six_degree_of_freed_activ | ||
| Harbin (China) | PZT Piezo | Strain Gauge | Decentralized position feedback | Workspace, Stiffness analyzed | du14_piezo_actuat_high_precis_flexib | |
| China | Piezoelectric | Leg length | Tracking control, ADRC, State observer | Analytical | Use of ADRC for tracking control of cubic hexapod | min19_high_precis_track_cubic_stewar |
| China | Piezoelectric | Force, Position | Vibration isolation, Model-Based, Modal control: 6x PI controllers | Solid/Flexible | Stiffness of flexible joints is compensated using feedback, then the system is decoupled in the modal space | yang19_dynam_model_decoup_contr_flexib |
From: yang19_dynam_model_decoup_contr_flexib:
On the other hand, the traditional modal decoupled control strategy cannot deal with the flexible Stewart platform governed by Eq. (34) because it is impossible to achieve simultaneous diagonalization of the mass, damping and stiffness matrices. To make the six-DOF system decoupled into six single-DOF isolators, we design a new controller based on the leg’s force and position feedback. The idea is to synthesize the control force that can compensate the parasitic bending and torsional torques of the flexible joints and simultaneously achieve diagonalization of the matrices M, C and K.
3.3. Multi Sensor Control
Improvement by the use of several sensors:
- HAC-LAC
- Two sensor control
- Sensor Fusion
Comparison between “two sensor control” and “sensor fusion” is given in &beijen14_two_sensor_contr_activ_vibrat.
3.3.1. Two sensor control
| University | Actuators | Sensors | Control | Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Washinton | Voice Coil | Force and Inertial | LQG, Decentralized, Sensor Fusion | Combine force/inertial sensors. Comparison of force sensor and inertial sensors. Issue on non-minimum phase zero | hauge04_sensor_contr_space_based_six |
| Netherlands | Voice Coil | Sensor Fusion, Two Sensor Control | tjepkema12_activ_ph |
3.3.2. HAC-LAC
| University | Actuators | Sensors | Control | Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPL | Magnetostrictive | Force (collocated), Accelerometers | Two layers: Decentralized IFF, Robust Adaptive Control | Two layer control for active damping and vibration isolation | geng95_intel_contr_system_multip_degree |
| Shangai | Piezoelectric | Force Sensor + Accelerometer | Vibration isolation, HAC-LAC (IFF + FxLMS) | Dynamic Model + Vibration Control | wang16_inves_activ_vibrat_isolat_stewar |
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Accelerometer (collocated), ext. Rx/Ry sensors | Cartesian acceleration feedback (isolation) + 2DoF pointing control (external sensor) | Decoupling, both vibration + pointing control | li01_simul_vibrat_isolat_point_contr |
| China | Voice Coil | Geophone + Eddy Current (Struts, collocated) | Decentralized (Sky Hook) + Centralized (modal) Control | pu11_six_degree_of_freed_activ | |
| China | Voice Coil | Force sensors (strus) + accelerometer (cartesian) | Decentralized Force Feedback + Centralized H2 control based on accelerometers | xie17_model_contr_hybrid_passiv_activ |
3.3.3. Sensor Fusion
| University | Actuators | Sensors | Control | Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Netherlands | Voice Coil | Force (HF) and Inertial (LF) | Sensor Fusion, Two Sensor Control | tjepkema12_activ_ph, tjepkema12_sensor_fusion_activ_vibrat_isolat_precis_equip | |
| Washinton | Voice Coil | Force (HF) and Inertial (LF) | LQG, Decentralized, Sensor Fusion | Combine force/inertial sensors. Comparison of force sensor and inertial sensors. Issue on non-minimum phase zero | hauge04_sensor_contr_space_based_six |
3.3.4. Other Strategies
| University | Actuators | Sensors | Control | Main Object | Link to bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Piezoelectric | Force, Position | Vibration isolation, Model-Based, Modal control: 6x PI controllers | Stiffness of flexible joints is compensated using feedback, then the system is decoupled in the modal space | yang19_dynam_model_decoup_contr_flexib |
| Washinton | Voice Coil | Force, LVDT, Geophones | LQG, Force + geophones for vibration, LVDT for pointing | Centralized control is no better than decentralized. Geophone + Force MISO control is good | thayer98_stewar, thayer02_six_axis_vibrat_isolat_system |
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Force | IFF, centralized (decouple) + decentralized (coupled) | Specific geometry: decoupled force plant. Better perf with centralized IFF | mcinroy99_dynam, mcinroy99_precis_fault_toler_point_using_stewar_platf, mcinroy00_desig_contr_flexur_joint_hexap |
3.4. Decoupling Strategies
Different strategies:
- Jacobian decoupling: in the cartesian frame or in the frame of the struts
- Modal decoupling
- SVD decoupling
Identify Jacobian for better decoupling: cheng04_multi_body_system_model_gough, gexue04_vibrat_contr_with_stewar_paral_mechan.
3.4.1. Jacobian - Struts
| Japan | APA | Eddy current displacement | Decentralized (struts) PI + LPF control | furutani04_nanom_cuttin_machin_using_stewar |
| Harbin (China) | PZT Piezo | Strain Gauge | Decentralized position feedback | du14_piezo_actuat_high_precis_flexib |
3.4.2. Jacobian - Cartesian
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Force | Cartesian frame decoupling | obrien98_lesson |
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Force | IFF, Cartesian Frame, Jacobians | mcinroy99_dynam, mcinroy99_precis_fault_toler_point_using_stewar_platf, mcinroy00_desig_contr_flexur_joint_hexap |
| Seoul | Hydraulic | LVDT | Decentralized (strut) vs Centralized (cartesian) | kim00_robus_track_contr_desig_dof_paral_manip |
| Wyoming | Voice Coil | Accelerometer (collocated), ext. Rx/Ry sensors | Cartesian acceleration feedback (isolation) + 2DoF pointing control (external sensor) | li01_simul_vibrat_isolat_point_contr |
| China | Voice Coil | Accelerometer in each leg | Centralized Vibration Control, PI, Skyhook | abbas14_vibrat_stewar_platf |
3.4.3. Modal Decoupling
| China | Voice Coil | Geophone + Eddy Current (Struts, collocated) | Decentralized (Sky Hook) + Centralized (modal) Control | pu11_six_degree_of_freed_activ |
| China | Piezoelectric | Force, Position | Vibration isolation, Model-Based, Modal control: 6x PI controllers | yang19_dynam_model_decoup_contr_flexib |
3.4.4. Multivariable Control
From &thayer02_six_axis_vibrat_isolat_system:
Experimental closed-loopcontrol results using the hexapod have shown that controllers designed using a decentralized single-strut design work well when compared to full multivariable methodologies.
| China | PZT | Geophone (struts) | H-Infinity and mu-synthesis | lei08_multi_objec_robus_activ_vibrat |
| China | Voice Coil | Force sensors (strus) + accelerometer (cartesian) | Decentralized Force Feedback + Centralized H2 control based on accelerometers | xie17_model_contr_hybrid_passiv_activ |
| Harbin (China) | Voice Coil | Accelerometers | MIMO H-Infinity, active damping | jiao18_dynam_model_exper_analy_stewar |
3.5. Long Stroke Stewart Platforms
| Link to bibliography | University | Actuators | Sensors | Control | Main Object |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cleary91_protot_paral_manip | Japan | DC, gear + rack pinion | Encoder, 7um res | Decentralized (struts), PID control | Singular configuration analysis, workspace |
| su04_distur_rejec_high_precis_motion | Xidian (China) | ||||
| huang05_smoot_stewar | Taiwan | ||||
| brezina08_ni_labview_matlab_simmec_stewar_platf_desig, houska10_desig_implem_absol_linear_posit | Czech | DC | Modeling with sim-mechanics | ||
| molina08_simul_stewar | Brazil | Simulation with Matlab/Simulink | |||
| yang10_model_dof_simul_simmec | China | Decentralized PID | Simulation with Simulink/SimMechanics | ||
| kim00_robus_track_contr_desig_dof_paral_manip | Seoul | Hydraulic | LVDT | Decentralized (strut) vs Centralized (cartesian) |