Nano-Hexapod
Table of Contents
- 1. Nano-Hexapod
- 2. Function - Initialize Nano Hexapod
1 Nano-Hexapod
1.1 Nano Hexapod object
The nano-hexapod can be initialized and configured using the initializeNanoHexapodFinal function.
n_hexapod = initializeNanoHexapodFinal('flex_bot_type', '4dof', ... 'flex_top_type', '3dof', ... 'motion_sensor_type', 'struts', ... 'actuator_type', '2dof');
1.2 Jacobian from Solidworks Model
Center of joints a_i with respect to {F}:
Fa = [[-86.05, -74.78, 22.49], [86.05, -74.78, 22.49], [107.79, -37.13, 22.49], [21.74, 111.91, 22.49], [-21.74, 111.91, 22.49], [-107.79, -37.13, 22.49]]'*1e-3;
Center of joints a_i with respect to {M}:
Mb = [[-28.47, -106.25, -22.50], [28.47, -106.25, -22.50], [106.25, 28.47, -22.50], [77.78, 77.78, -22.50], [-77.78, 77.78, -22.50], [-106.25, 28.47, -22.50]]'*1e-3;
Fb = Mb + [0; 0; 95e-3]; si = Fb - Fa; si = si./vecnorm(si);
ki = ones(1,6); bi = Fb;
ki.*si*si'
| 1.8977 | 2.4659e-17 | 1.3383e-18 |
| 2.4659e-17 | 1.8977 | -2.3143e-05 |
| 1.3383e-18 | -2.3143e-05 | 2.2046 |
OkX = (ki.*cross(bi, si)*si')/(ki.*si*si'); Ok = [OkX(3,2);OkX(1,3);OkX(2,1)]
| -1.7444e-18 |
| 2.1511e-06 |
| 0.052707 |
The center of the cube is therefore 52.7mm above the bottom platform {F} frame.
Let’s compute the Jacobian at this location:
Jk = [si', cross(bi - Ok, si)'];
And the stiffness matrix:
Jk'*diag(ki)*Jk
| 1.8977 | 0 | 0 | 0 | -3.4694e-18 | 2.5509e-06 |
| 0 | 1.8977 | -2.3143e-05 | 4.1751e-06 | 1.3878e-17 | 0 |
| 0 | -2.3143e-05 | 2.2046 | -5.0916e-11 | -3.4694e-18 | 0 |
| 0 | 4.1751e-06 | -5.0916e-11 | 0.012594 | 2.1684e-19 | 8.6736e-19 |
| -3.2704e-18 | 0 | -4.206e-18 | 3.9451e-19 | 0.012594 | -9.3183e-08 |
| 2.5509e-06 | 0 | 0 | 8.6736e-19 | -9.3183e-08 | 0.043362 |
1.3 Jacobian for encoders on the plates
Goal: Compute the 6-DoF motion of the top platform (relative to the bottom platform) from the 6 encoder measurements.
The main differences with the case where the encoders are parallel with the strut are:
- the encoder and ruler may not be parallel anymore as the top platform is moving
- the derivation of the Jacobian (if possible) will not be the same
1.4 Compare encoders on the struts and encoders on the platforms
%% Options for Linearized options = linearizeOptions; options.SampleTime = 0; %% Name of the Simulink File mdl = 'nano_hexapod'; %% Input/Output definition clear io; io_i = 1; io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Actuator Inputs io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/D'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Relative Motion Outputs
n_hexapod.motion_sensor = struct();
n_hexapod.motion_sensor.type = 1; % 1: Leg / 2: Plate
Gs = linearize(mdl, io, 0.0, options);
Gs.InputName = {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6'};
Gs.OutputName = {'D1', 'D2', 'D3', 'D4', 'D5', 'D6'};
n_hexapod.motion_sensor = struct();
n_hexapod.motion_sensor.type = 2; % 1: Leg / 2: Plate
Gp = linearize(mdl, io, 0.0, options);
Gp.InputName = {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6'};
Gp.OutputName = {'D1', 'D2', 'D3', 'D4', 'D5', 'D6'};
1.5 Nano Hexapod
%% Options for Linearized options = linearizeOptions; options.SampleTime = 0; %% Name of the Simulink File mdl = 'nano_hexapod'; %% Input/Output definition clear io; io_i = 1; io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/F'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Actuator Inputs io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fe'], 1, 'openinput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % External Force io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/D'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Relative Motion Outputs io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/Fm'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Force Sensors io(io_i) = linio([mdl, '/X'], 1, 'openoutput'); io_i = io_i + 1; % Absolute Motion of top platform %% Run the linearization G = linearize(mdl, io, 0.0, options); G.InputName = {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6', ... 'Fx', 'Fy', 'Fz', 'Mx', 'My', 'Mz'}; G.OutputName = {'D1', 'D2', 'D3', 'D4', 'D5', 'D6', ... 'Fm1', 'Fm2', 'Fm3', 'Fm4', 'Fm5', 'Fm6' ... 'Dx', 'Dy', 'Dz', 'Rx', 'Ry', 'Rz'};
size(G) State-space model with 18 outputs, 12 inputs, and 60 states.
Verify the number of DOF:
| Element | DoF |
|---|---|
| Bot Plate | 0 |
| Struts | 6*4 |
| Top Plate + Sample | 12 |
| Total: | 36 |
1.5.1 DVF Plant
The DC gain from actuator to relative motion sensor should be equal to (for the 2dof APA): \[ \frac{1}{k + k_a + kk_a/k_e} \]
1.8732e-08
Which is almost the case:
| -1.8676e-08 | 5.2396e-11 | -8.8935e-11 | 2.6392e-11 | 9.7629e-11 | -1.5609e-10 |
| -1.4754e-11 | -1.8725e-08 | 1.4348e-11 | -5.7189e-11 | -3.3327e-11 | 7.0799e-11 |
| -3.4924e-11 | -7.7445e-11 | -1.8607e-08 | -4.6578e-11 | -1.9592e-11 | 4.0299e-11 |
| 6.1699e-11 | -7.1962e-11 | 1.3374e-11 | -1.8623e-08 | -1.7898e-10 | 5.4541e-11 |
| 9.735e-11 | -1.0698e-10 | -1.6424e-11 | 2.3718e-11 | -1.8826e-08 | 8.387e-11 |
| -3.94e-11 | 2.6436e-11 | -1.1338e-10 | 5.0793e-11 | 1.2358e-10 | -1.8792e-08 |
Other (off-diagonal) elements should be close to zero (probably limited to joint’s stiffness). However, when setting joint’s axial stiffness to infinity, I obtain better diagonal.
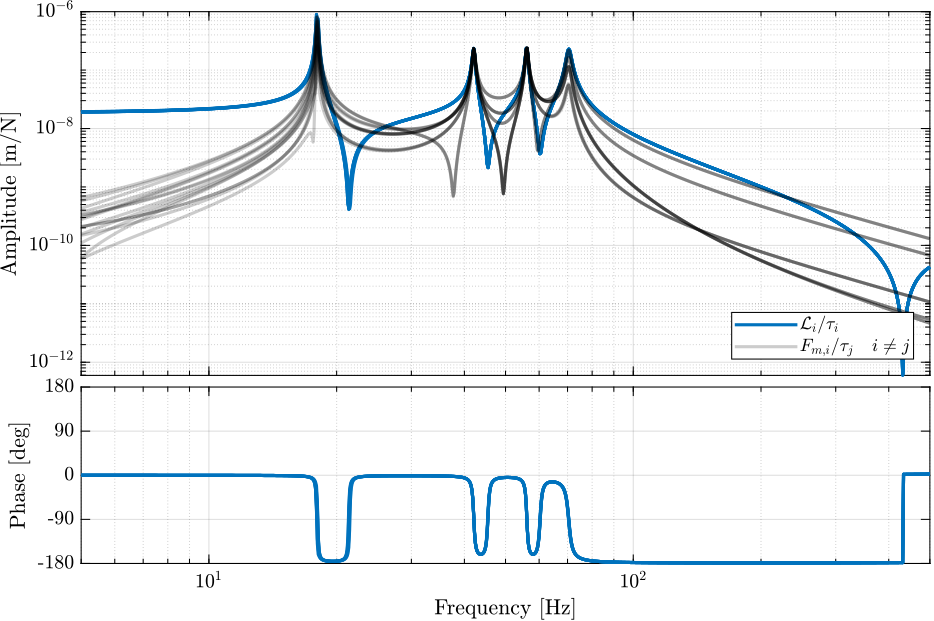
Figure 1: IFF Plant
1.5.2 IFF Plant
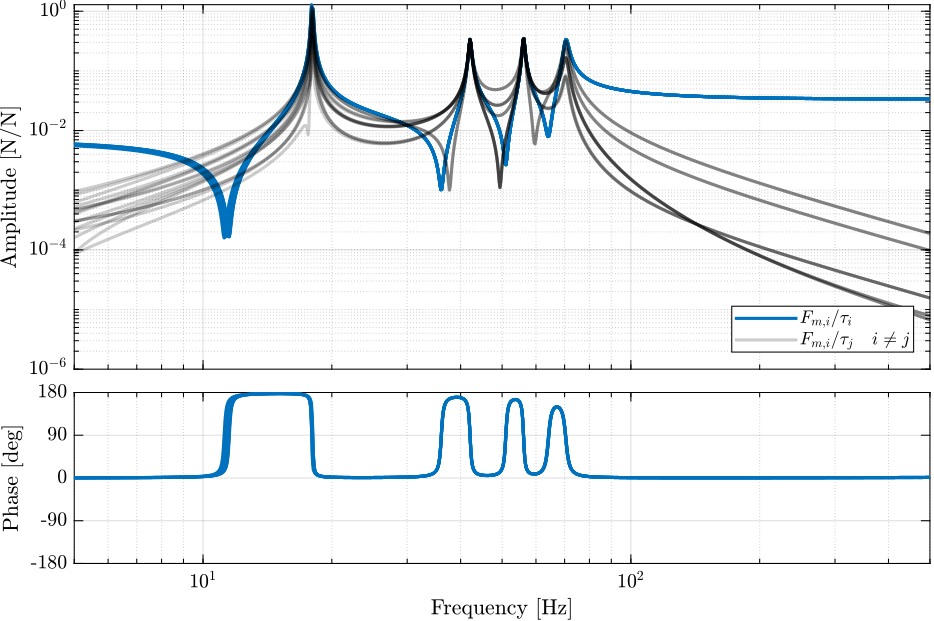
Figure 2: DVF Plant
1.6 Decoupling at the CoK
Gx = inv(Jk)*G({'D1', 'D2', 'D3', 'D4', 'D5', 'D6'}, {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6'})*inv(Jk'); Gx.inputname = {'Fx', 'Fy', 'Fz', 'Mx', 'My', 'Mz'}; Gx.outputname = {'Dx', 'Dy', 'Dz', 'Rx', 'Ry', 'Rz'};
| -9.8399e-09 | -8.0785e-11 | -1.5723e-11 | 2.6356e-10 | -4.9857e-10 | 5.2177e-11 |
| -8.7554e-11 | -9.8585e-09 | 2.6292e-11 | 2.0485e-10 | 2.0385e-10 | 8.2942e-11 |
| 4.3837e-11 | -5.5862e-14 | -8.4859e-09 | -9.0036e-12 | 2.9325e-10 | -3.104e-11 |
| 1.901e-09 | 5.3078e-10 | -7.5477e-10 | -1.4759e-06 | -7.7918e-09 | -7.491e-10 |
| -7.1795e-11 | -1.6333e-09 | -1.8359e-10 | 5.2707e-09 | -1.4794e-06 | 3.2304e-10 |
| 7.0322e-11 | 1.7713e-12 | -5.8019e-11 | 7.4838e-11 | -8.9677e-10 | -4.2938e-07 |
1.7 Jacobian
1.7.1 Compute Jacobian
Ai = [out.b1.Data(1,:) out.b2.Data(1,:) out.b3.Data(1,:) out.b4.Data(1,:) out.b5.Data(1,:) out.b6.Data(1,:)]'; Bi = [out.a1.Data(1,:) out.a2.Data(1,:) out.a3.Data(1,:) out.a4.Data(1,:) out.a5.Data(1,:) out.a6.Data(1,:)]';
stewart = initializeStewartPlatform(); stewart = initializeFramesPositions(stewart, 'H', 95e-3, 'MO_B', 150e-3); stewart = generateGeneralConfiguration(stewart); stewart.platform_F.Fa = Ai; stewart.platform_M.Mb = Bi - [0;0;1]*stewart.geometry.H; stewart = computeJointsPose(stewart); stewart = initializeStewartPose(stewart, 'AP', [0;0;0], 'ARB', eye(3));
stewart = initializeCylindricalPlatforms(stewart); stewart = initializeCylindricalStruts(stewart);
stewart = initializeStrutDynamics(stewart, 'K', 1e6*ones(6,1), 'C', 1e2*ones(6,1)); stewart = initializeAmplifiedStrutDynamics(stewart); stewart = initializeJointDynamics(stewart);
displayArchitecture(stewart, 'views', 'all');
describeStewartPlatform(stewart)
GEOMETRY:
- The height between the fixed based and the top platform is 95 [mm].
- Frame {A} is located 150 [mm] above the top platform.
- The initial length of the struts are:
82.8, 82.8, 82.8, 82.8, 82.8, 82.8 [mm]
ACTUATORS:
- The actuators are mechanicaly amplified.
- The vertical stiffness and damping contribution of the piezoelectric stack is:
ka = 2e+07 [N/m] ca = 1e+01 [N/(m/s)]
- Vertical stiffness when the piezoelectric stack is removed is:
kr = 5e+06 [N/m] cr = 1e+01 [N/(m/s)]
JOINTS:
- The joints on the fixed based are universal joints
- The joints on the mobile based are spherical joints
- The position of the joints on the fixed based with respect to {F} are (in [mm]):
-86.2 -74.7 22.3
86.3 -74.6 22.3
108 -37.3 22.3
21.5 112 22.3
-21.5 112 22.3
-108 -37.5 22.2
- The position of the joints on the mobile based with respect to {M} are (in [mm]):
-28.4 -106 -22.4
28.5 -106 -22.5
106 28.5 -22.5
77.8 77.8 -22.5
-77.8 77.8 -22.5
-106 28.4 -22.5
stewart = computeJacobian(stewart);
1.7.2 Verify Jacobian
load('./mat/nano_hexapod_object.mat', 'stewart'); J = stewart.kinematics.J;
Transformation of motion:
G1 = -inv(J)*G({'D1', 'D2', 'D3', 'D4', 'D5', 'D6'}, {'Fx', 'Fy', 'Fz', 'Mx', 'My', 'Mz'}); G2 = G({'Dx', 'Dy', 'Dz', 'Rx', 'Ry', 'Rz'}, {'Fx', 'Fy', 'Fz', 'Mx', 'My', 'Mz'});
Transformation of Forces and Torques
G1 = G({'Dx', 'Dy', 'Dz', 'Rx', 'Ry', 'Rz'}, {'Fx', 'Fy', 'Fz', 'Mx', 'My', 'Mz'});
G2 = G({'Dx', 'Dy', 'Dz', 'Rx', 'Ry', 'Rz'}, {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6'})*inv(J');
Not working because the forces applied on the APA are not really forces applied on the top platform (reduced by a factor ~ka/ke)
1.7.3 Plant from APA forces to sample’s displacement
Gx = G({'Dx', 'Dy', 'Dz', 'Rx', 'Ry', 'Rz'}, {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6'})*inv(J');
Gx.inputname = {'Fx', 'Fy', 'Fz', 'Mx', 'My', 'Mz'};
1.7.4 Plant in the Cartesian frame
Transfer function from forces/torque to displacement/rotation:
GJ = inv(J)*G({'D1', 'D2', 'D3', 'D4', 'D5', 'D6'}, {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6'})*inv(J'); GJ.inputname = {'Fx', 'Fy', 'Fz', 'Mx', 'My', 'Mz'}; GJ.outputname = {'Dx', 'Dy', 'Dz', 'Rx', 'Ry', 'Rz'};
1.7.5 Plant in the frame of the legs => Verification of Jacobian for displacements
Transfer Function in the frame of the legs
G1 = -J*G({'Dx', 'Dy', 'Dz', 'Rx', 'Ry', 'Rz'}, {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6'}); G1.outputname = {'D1', 'D2', 'D3', 'D4', 'D5', 'D6'}; G2 = G({'D1', 'D2', 'D3', 'D4', 'D5', 'D6'}, {'F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6'});
It is working fine (until internal resonance of strut).
1.8 Stiffness matrix
Neglecting stiffness of the joints, we have: \[ K = J^t \mathcal{K} J \] where \(\mathcal{K}\) is a diagonal 6x6 matrix with axial stiffness of the struts on the diagonal.
Let’s note the axial stiffness of the APA: \[ k_{\text{APA}} = k + \frac{k_e k_a}{k_e + k_a} \]
Them axial stiffness of the struts \(k_s\): \[ k_s = \frac{k_z k_{\text{APA}}}{k_z + 2 k_{\text{APA}}} \]
kAPA = k + ke*ka/(ke + ka); ks = kz*kAPA/(kz + 2*kAPA);
Ks = J'*(ks*eye(6))*J
| 1.9937e-06 | 7.7027e-12 | -1.5885e-11 | -1.6811e-10 | 8.7902e-06 | 3.0476e-11 |
| 7.7027e-12 | 1.9937e-06 | 2.7221e-11 | -8.7901e-06 | 6.5081e-12 | 2.8619e-11 |
| -1.5885e-11 | 2.7221e-11 | 2.6114e-07 | -1.3209e-10 | -6.1725e-11 | 4.0402e-11 |
| -1.6811e-10 | -8.7901e-06 | -1.3209e-10 | 4.5712e-05 | -5.7781e-10 | -4.5817e-10 |
| 8.7902e-06 | 6.5081e-12 | -6.1725e-11 | -5.7781e-10 | 4.5712e-05 | 5.1628e-10 |
| 3.0476e-11 | 2.8619e-11 | 4.0402e-11 | -4.5817e-10 | 5.1628e-10 | 1.3277e-05 |
| 1.9869e-06 | 2.043e-08 | 1.6444e-09 | -4.094e-08 | 8.7579e-06 | -3.5002e-09 |
| 3.746e-09 | 1.9841e-06 | -5.5274e-09 | -8.7257e-06 | -5.5082e-08 | -7.6978e-09 |
| -3.2056e-09 | -6.4295e-11 | 2.6079e-07 | 3.4103e-10 | -9.3873e-09 | 9.6146e-10 |
| -1.1677e-08 | -8.736e-06 | 2.4322e-08 | 4.5343e-05 | 2.52e-07 | 2.5932e-08 |
| 8.7439e-06 | 8.441e-08 | 5.9144e-09 | -1.6879e-07 | 4.546e-05 | -9.8986e-09 |
| 3.3453e-09 | 4.508e-10 | 1.8718e-09 | -2.7294e-09 | 2.8776e-08 | 1.3193e-05 |
We can see that we have almost the same stiffness:
| 1.0034 | 0.00037703 | -0.0096597 | 0.0041063 | 1.0037 | -0.0087071 |
| 0.0020562 | 1.0048 | -0.0049247 | 1.0074 | -0.00011815 | -0.0037178 |
| 0.0049552 | -0.42338 | 1.0013 | -0.38734 | 0.0065754 | 0.042021 |
| 0.014397 | 1.0062 | -0.005431 | 1.0081 | -0.0022929 | -0.017668 |
| 1.0053 | 7.7101e-05 | -0.010436 | 0.0034233 | 1.0055 | -0.052157 |
| 0.0091102 | 0.063485 | 0.021584 | 0.16786 | 0.017941 | 1.0063 |
2 Function - Initialize Nano Hexapod
Function description
function [nano_hexapod] = initializeNanoHexapodFinal(args)
Optional Parameters
arguments %% Bottom Flexible Joints args.flex_bot_type char {mustBeMember(args.flex_bot_type,{'2dof', '3dof', '4dof', 'flexible'})} = '4dof' args.flex_bot_kRx (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*5 % X bending stiffness [Nm/rad] args.flex_bot_kRy (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*5 % Y bending stiffness [Nm/rad] args.flex_bot_kRz (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*260 % Torsionnal stiffness [Nm/rad] args.flex_bot_kz (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*1e8 % Axial Stiffness [N/m] args.flex_bot_cRx (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*0.1 % X bending Damping [Nm/(rad/s)] args.flex_bot_cRy (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*0.1 % Y bending Damping [Nm/(rad/s)] args.flex_bot_cRz (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*0.1 % Torsionnal Damping [Nm/(rad/s)] args.flex_bot_cz (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*1e2 % Axial Damping [N/(m/s)] %% Top Flexible Joints args.flex_top_type char {mustBeMember(args.flex_top_type,{'2dof', '3dof', '4dof', 'flexible'})} = '4dof' args.flex_top_kRx (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*5 % X bending stiffness [Nm/rad] args.flex_top_kRy (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*5 % Y bending stiffness [Nm/rad] args.flex_top_kRz (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*260 % Torsionnal stiffness [Nm/rad] args.flex_top_kz (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*1e8 % Axial Stiffness [N/m] args.flex_top_cRx (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*0.1 % X bending Damping [Nm/(rad/s)] args.flex_top_cRy (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*0.1 % Y bending Damping [Nm/(rad/s)] args.flex_top_cRz (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*0.1 % Torsionnal Damping [Nm/(rad/s)] args.flex_top_cz (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*1e2 % Axial Damping [N/(m/s)] %% Relative Motion Sensor args.motion_sensor_type char {mustBeMember(args.motion_sensor_type,{'struts', 'plates'})} = 'struts' %% Actuators args.actuator_type char {mustBeMember(args.actuator_type,{'2dof', 'flexible frame', 'flexible'})} = 'flexible' args.actuator_Ga (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*1 % Actuator gain [N/V] args.actuator_Gs (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*1 % Sensor gain [V/m] % For 2DoF args.actuator_k (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*0.35e6 % [N/m] args.actuator_ke (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*1.5e6 % [N/m] args.actuator_ka (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*43e6 % [N/m] args.actuator_c (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*3e1 % [N/(m/s)] args.actuator_ce (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*1e1 % [N/(m/s)] args.actuator_ca (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*1e1 % [N/(m/s)] args.actuator_Leq (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*0.056 % [m] % For Flexible Frame args.actuator_ks (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*235e6 % Stiffness of one stack [N/m] args.actuator_cs (6,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = ones(6,1)*1e1 % Stiffness of one stack [N/m] % For Flexible args.actuator_xi (1,1) double {mustBeNumeric} = 0.01 % Sensor gain [V/m] end
Nano Hexapod Object
nano_hexapod = struct();
Flexible Joints - Bot
nano_hexapod.flex_bot = struct(); switch args.flex_bot_type case '2dof' nano_hexapod.flex_bot.type = 1; case '3dof' nano_hexapod.flex_bot.type = 2; case '4dof' nano_hexapod.flex_bot.type = 3; case 'flexible' nano_hexapod.flex_bot.type = 4; end nano_hexapod.flex_bot.kRx = args.flex_bot_kRx; % X bending stiffness [Nm/rad] nano_hexapod.flex_bot.kRy = args.flex_bot_kRy; % Y bending stiffness [Nm/rad] nano_hexapod.flex_bot.kRz = args.flex_bot_kRz; % Torsionnal stiffness [Nm/rad] nano_hexapod.flex_bot.kz = args.flex_bot_kz; % Axial stiffness [N/m] nano_hexapod.flex_bot.cRx = args.flex_bot_cRx; % [Nm/(rad/s)] nano_hexapod.flex_bot.cRy = args.flex_bot_cRy; % [Nm/(rad/s)] nano_hexapod.flex_bot.cRz = args.flex_bot_cRz; % [Nm/(rad/s)] nano_hexapod.flex_bot.cz = args.flex_bot_cz; %[N/(m/s)]
Flexible Joints - Top
nano_hexapod.flex_top = struct(); switch args.flex_top_type case '2dof' nano_hexapod.flex_top.type = 1; case '3dof' nano_hexapod.flex_top.type = 2; case '4dof' nano_hexapod.flex_top.type = 3; case 'flexible' nano_hexapod.flex_top.type = 4; end nano_hexapod.flex_top.kRx = args.flex_top_kRx; % X bending stiffness [Nm/rad] nano_hexapod.flex_top.kRy = args.flex_top_kRy; % Y bending stiffness [Nm/rad] nano_hexapod.flex_top.kRz = args.flex_top_kRz; % Torsionnal stiffness [Nm/rad] nano_hexapod.flex_top.kz = args.flex_top_kz; % Axial stiffness [N/m] nano_hexapod.flex_top.cRx = args.flex_top_cRx; % [Nm/(rad/s)] nano_hexapod.flex_top.cRy = args.flex_top_cRy; % [Nm/(rad/s)] nano_hexapod.flex_top.cRz = args.flex_top_cRz; % [Nm/(rad/s)] nano_hexapod.flex_top.cz = args.flex_top_cz; %[N/(m/s)]
Relative Motion Sensor
nano_hexapod.motion_sensor = struct(); switch args.motion_sensor_type case 'struts' nano_hexapod.motion_sensor.type = 1; case 'plates' nano_hexapod.motion_sensor.type = 2; end
Amplified Piezoelectric Actuator
nano_hexapod.actuator = struct(); switch args.actuator_type case '2dof' nano_hexapod.actuator.type = 1; case 'flexible frame' nano_hexapod.actuator.type = 2; case 'flexible' nano_hexapod.actuator.type = 3; end
nano_hexapod.actuator.Ga = args.actuator_Ga; % Actuator gain [N/V] nano_hexapod.actuator.Gs = args.actuator_Gs; % Sensor gain [V/m]
2dof
nano_hexapod.actuator.k = args.actuator_k; % [N/m] nano_hexapod.actuator.ke = args.actuator_ke; % [N/m] nano_hexapod.actuator.ka = args.actuator_ka; % [N/m] nano_hexapod.actuator.c = args.actuator_c; % [N/(m/s)] nano_hexapod.actuator.ce = args.actuator_ce; % [N/(m/s)] nano_hexapod.actuator.ca = args.actuator_ca; % [N/(m/s)] nano_hexapod.actuator.Leq = args.actuator_Leq; % [m]
Flexible frame and fully flexible
switch args.actuator_type case 'flexible frame' nano_hexapod.actuator.K = readmatrix('APA300ML_b_mat_K.CSV'); % Stiffness Matrix nano_hexapod.actuator.M = readmatrix('APA300ML_b_mat_M.CSV'); % Mass Matrix nano_hexapod.actuator.P = extractNodes('APA300ML_b_out_nodes_3D.txt'); % Node coordinates [m] case 'flexible' nano_hexapod.actuator.K = readmatrix('APA300ML_full_mat_K.CSV'); % Stiffness Matrix nano_hexapod.actuator.M = readmatrix('APA300ML_full_mat_M.CSV'); % Mass Matrix nano_hexapod.actuator.P = extractNodes('APA300ML_full_out_nodes_3D.txt'); % Node coordiantes [m] end nano_hexapod.actuator.xi = args.actuator_xi; % Damping ratio nano_hexapod.actuator.ks = args.actuator_ks; % Stiffness of one stack [N/m] nano_hexapod.actuator.cs = args.actuator_cs; % Damping of one stack [N/m]
Save the Structure
if nargout == 0 save('./mat/stages.mat', 'nano_hexapod', '-append'); end